Hyperplasia is an abnormal but non-cancerous pattern of cell growth within the ducts or lobes of the breast. A hyperplastic breast shows a higher number of cells and layers in the ducts and lobules than the normal 2 layers of cells on microscopic examination.
If the arrangement of the cells in the proliferative region appears more or less similar to the normal cell pattern, it is called usual hyperplasia. If the growth pattern is abnormally disorganized, it is called atypical hyperplasia.
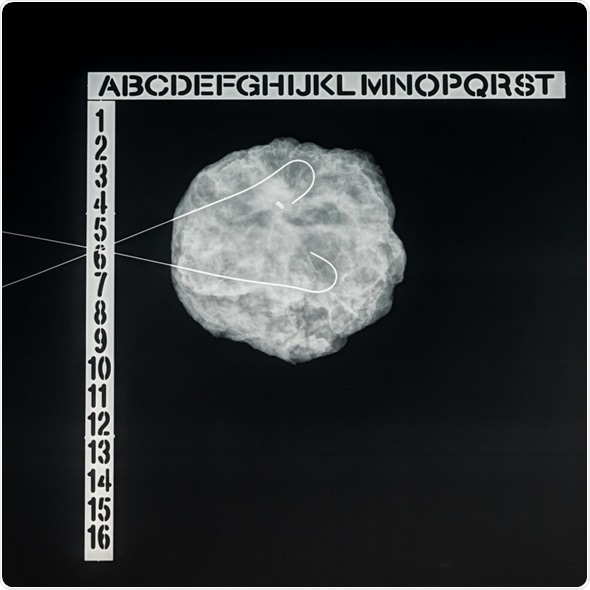
Wire-guided (needle) localization: specimen radiograph of breast biopsy (lumpectomy) for atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH). A metallic clip marks prior biopsy site, needles bracket abnormality. Image Copyright: David Litman / Shutterstock
Atypical hyperplasia is thus described as an accumulation of abnormally proliferating cells in the breast. It is not cancer, but can be a pre-cancerous condition, where the abnormal cells causing atypical hyperplasia keep dividing. This may result in non-invasive or invasive breast cancer in the long term.
Women with a diagnosis of atypical hyperplasia have a higher risk of developing breast cancer in future, than those who do not have the condition. For this reason, intensive breast cancer screening and preventive medications to lower the risk of breast cancer is recommended in these cases. However, it is worth noting that the majority of women with atypical hyperplasia never develop breast cancer in their lifetime.
Signs and Symptoms
Atypical hyperplasia does not cause any signs or symptoms in most cases, though breast changes may be detected on a mammogram.
Types of Atypical Hyperplasia
There are 2 types of atypical hyperplasia – ductal and lobular. This indicates the site of origin of the abnormal cells. ‘Ductal’ means the abnormal cells are present in the duct through which the breast milk travels to reach the nipple. ‘Lobular’ means that the abnormal cell growth is in the lobules, which are the areas in the breast that make milk. While atypical ductal hyperplasia increases the breast cancer risk in the area where it was found, atypical lobular hyperplasia increases the risk that cancer may develop in either breast.
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia
If the abnormal pattern of cell growth is found to occur within the ducts, it is called atypical ductal hyperplasia. It is not a pre-cancerous condition yet, but is linked to breast cancer risk in the future. The tissue removed for biopsy needs to be thoroughly investigated under a microscope. More tissue may be removed from the surrounding area to confirm the diagnosis. If cancerous changes are not detected, no treatment is necessary. Follow-up breast imaging and examinations must be scheduled as part of screening.
Atypical Lobular Hyperplasia
Atypical lobular hyperplasia occurs within the breast lobules and is linked to an increased risk of breast cancer in the future. Similar to ductal hyperplasia, microscopic examination of tissue reveals the cell growth pattern and based on the results, doctors will decide if more tests are required. Follow up with imaging and physical exams are recommended.
Diagnosis of Atypical Hyperplasia
Atypical hyperplasia is normally detected during a biopsy to study suspicious areas revealed during routine breast examination or by a mammogram. It is usually diagnosed during a breast biopsy performed in order to investigate the abnormal pattern detected on a mammogram. Rarely, it may be discovered during a biopsy performed for an unrelated condition.
Samples of tissue are removed during biopsy and sent to a lab for analysis by a pathologist. These samples are studied under a microscope which reveals the presence or absence of atypical hyperplasia.
In case atypical hyperplasia is diagnosed, a surgical biopsy may be performed to remove the affected breast tissue. Further evaluation via surgery may be recommended by the doctor and this involves removal of a larger tissue sample from the breast and testing it for the presence of cancerous cells. The larger sample is analyzed by the pathologist for any evidence of invasive or non-invasive cancer.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Feb 26, 2019