Cytometry is a widely used biological technique that is used to characterize different cell parameters. In this article, performance testing of the CytoFLEX flow cytometer was carried out to ascertain its ability to perform highly complex applications.
To that end, the new CytoFLEX flow cytometer from Beckman Coulter was evaluated against the performance measurements for small particle resolution, population resolution, dynamic range, sensitivity, stability, linearity, and reproducibility. Performance expectations across various parameters were assessed using commercially available bead standards.
Evaluation of the CytoFLEX system was performed at the Beckman Coulter, Miami site; Purdue University Cytometry Laboratory (PUCL); and the La Jolla Bioengineering Institute. Further information was also obtained through collaboration with School of Medicine at Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China; and Al Donnenberg from University of Pittsburgh Cancer Center.
The CytoFLEX systems were configured with 3 laser (405, 488 and 638nm), 12 parameter and 9 fluorescence detectors. In addition, the instrument featured the violet laser side scatter channel (VSSC) option for the detection of small particles.
Methods and Materials
CytoFLEX Daily QC Fluorospheres and CytExpert Software were used to determine the quality control robust CV (rCV). The rCV is roughly the 75th percentile minus the 25th percentile divided by the median, and is not as skewed by outlying values as the CV. CytoFLEX Daily QC Fluorospheres were gathered on three different CytoFLEX systems and Spherotech 8 Peak Rainbow beads were used for linearity, resolution, stability and separation testing.
The following products were used for microparticle testing
- Laboratory 1 (Beckman Coulter Miami): Spherotech beads. 0.5 and 0.2 μm
- Laboratory 2 (La Jolla Bioengineering Institute): Polybead Polystyrene Sampler Kit II PolySciences # 21756-1, and Polybead Polystyrene Sampler Kit III PolySciences # 16905-1
- Laboratory 3 (PUCL): PolySciences beads 0.2, 0.3, 0.35, 0.4, and 0.5μm beads
- Laboratory 4 (School of Medicine, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China): Beckman Coulter Particle Sizing Standards 0.2, 0.3 and 0.5 μm latex beads (non-fluorescent) mixture was used for evaluation, and UPW (UltraPure Water) was used to dilute the beads.
Following this, comparison was made against a competitive instrument with similar laser and filter configurations.
Separation index refers to the separation of adjacent peaks of Rainbow beads calculated by differences between the peak MFIs divided by the geometric average of their standard deviations. The formula given below is used to calculate the separation Index:
Separation index = (MFIpeak2-MFIpeak1)/(SQRT(SDpeak1^2+SDpeak2^2)/2)
Results and Discussion
QC beads were run on the system for a period of 18 days. Twelve startup and shutdown cycles were recorded and rCVs were monitored using Levey-Jennings. The following data shows the comparative parameters for each laser. Figure 1 shows the rCV testing of QC beads performed over 18 days and Figure 2 shows the rCVs on 8 peak beads run continuously for a period of one hour.
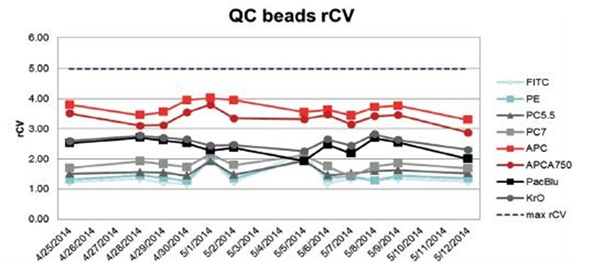
Figure 1. rCV analysis of QC beads over 18 days. Image credit: Beckman Coulter
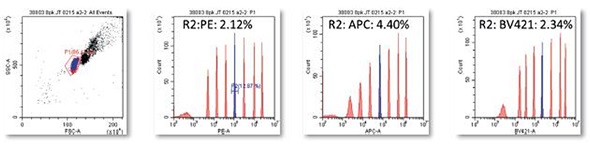
Figure 2. rCVs on 8 peak beads run continuously for one hour period. Image credit: Beckman Coulter
On the CytoFLEX system, the Spherotech 8 Peak Rainbow beads were run continuously for a period of one hour and rCV data was obtained on Peak#5 PE: 2.12%, APC: 4.40%, and BV421: 2.34%, indicating system stability.
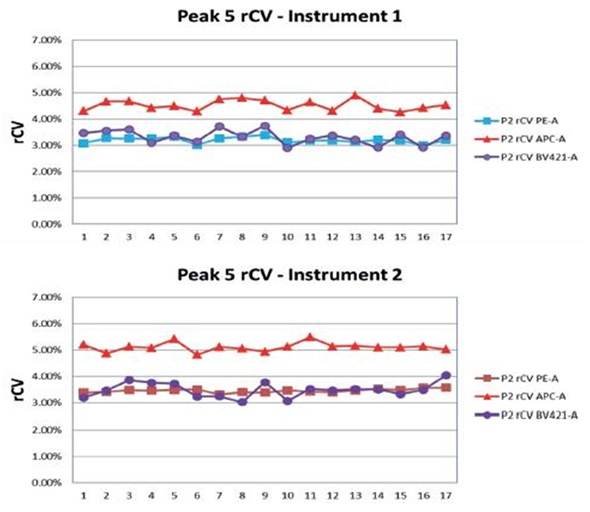
Figure 3. Spherotech 8 Peak Rainbow beads were run every day for seventeen days on two instruments and the rCV data was collected and plotted on Peak#5. Image credit: Beckman Coulter
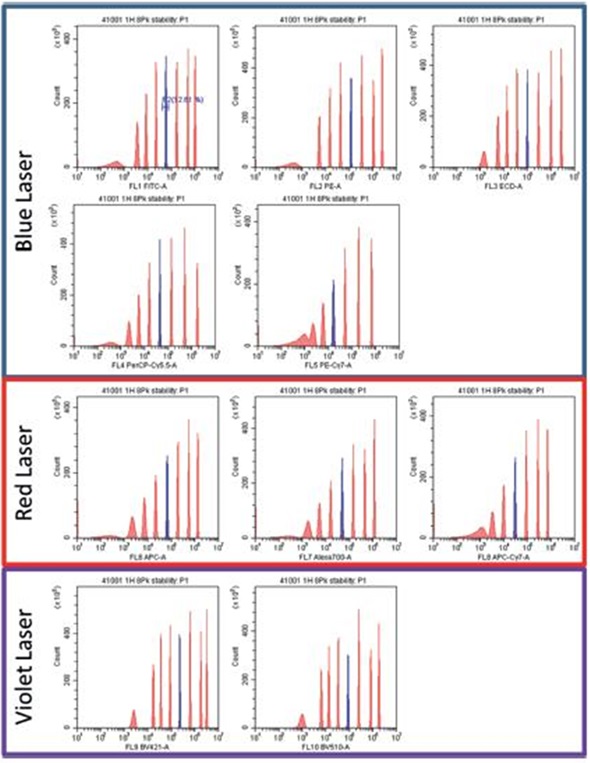
Figure 4. Spherotech 8 peak rainbow bead data for 3 laser 10 color detectors. Data provided by University of Pittsburgh Cancer Center. Image credit: Beckman Coulter
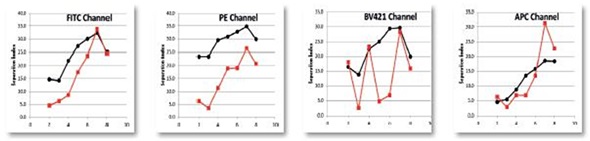
Figure 5. Spherotech 8 peak rainbow bead data calculated for a Separation Index between bead peaks as compared to a standard high complexity research cytometer. Data provided by University of Pittsburgh Cancer Center. Image credit: Beckman Coulter
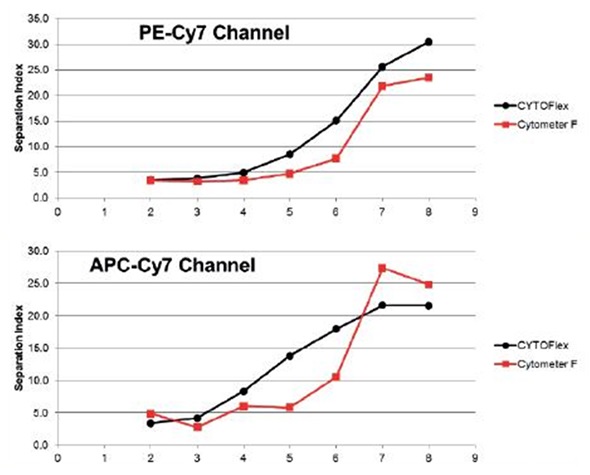
Figure 6. Spherotech 8 peak rainbow bead data calculated for a Separation Index between bead peaks as compared to a standard high complexity research cytometer. Data is specific for red channel sensitivity. Data provided by University of Pittsburgh Cancer Center. Image credit: Beckman Coulter
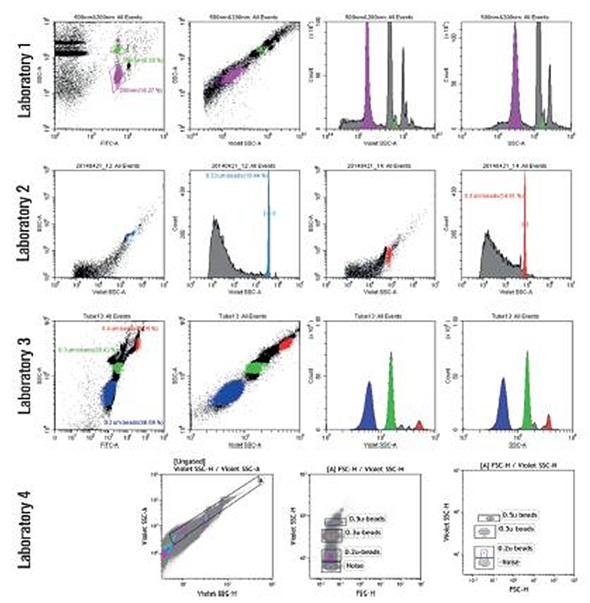
Figure 7. Microparticle detection. Four separate labs ran bead based small particles detected using side scatter and VSSC. Data provided by University of Pittsburgh Cancer Center, PUCL, La Jolla Bioengineering Institute, Sun Yat- Sen University Medical College. Image credit: Beckman Coulter
Conclusion
Results of performance testing confirm that the advanced CytoFLEX flow cytometer developed by Beckman Coulter is not only stable and reproducible, but is also sensitive, particularly in far red and violet channels. The capability of the instrument to isolate populations as quantified by the separation index is generally superior to that of other comparable systems. Moreover, evaluation of small particles demonstrated clear resolution of 0.2μm particles from noise using the Violet Side Scatter (VSSC) option. In addition, the CytoFLEX system is capable of clearly differentiating submicron beads of varying sizes.
 About Beckman Coulter
About Beckman Coulter
Beckman Coulter develops, manufactures and markets products that simplify, automate and innovate complex biomedical tests. More than a quarter of a million Beckman Coulter instruments operate in laboratories around the world, supplying critical information for improving patient health and reducing the cost of care.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.