Gas sensor technology covers a wide range of areas. The breath alcohol test, which measures the amount of alcohol in the breath, is one such example. However, the airport’s search for bombs and narcotics also makes use of gas sensor technologies. Here, microfluidics aids in enhancing the speed and accuracy of the examinations.
Obtaining a sufficient supply of the gas to be tested by the sensor is a significant issue in gas sensing. A sensor does not fill properly on its own, and it takes a while for changes in the gas to manifest.
Additionally, the concentration of the different elements in the air is usually not consistent. The mp6 micropump allows for active air supply and air removal. As a result, the sensor receives fresh samples on a frequent basis and can produce results that are more accurate.
The case study from Bartels Mikrotechnik uses a CO2 sensor as an example to demonstrate how the mp6 micropump is used in gas sensor technology.
Case study: CO2 gas sensors
Micropumps and active gas sensor technologies can be utilized to measure the CO2 concentration. The usage of sensors is continually growing as industrial processes are urged to become safer and more efficient.
The environmental conditions of the sensor must be maintained at a consistent level in these procedures to yield stable and specified measured data.
This case study makes use of the example of CO2 sensors to demonstrate how the mp6 micropump can be used in the field of sensor technology.
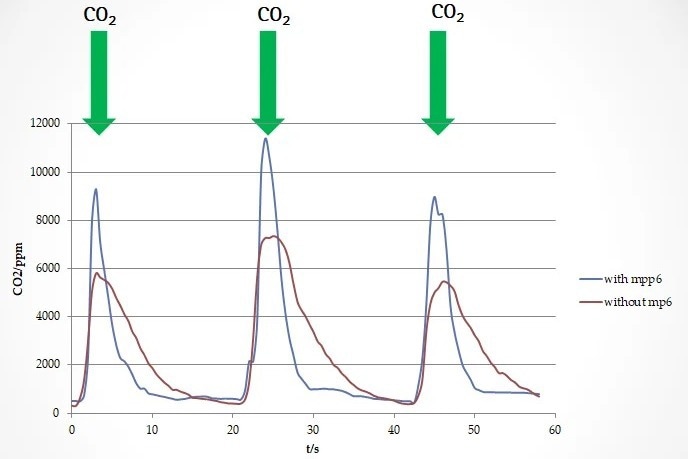
Image Credit: Bartels Mikrotechnik GmbH

 Read the Case Study
Read the Case Study
Adolf Kühner - A real-life example of gas analysis
The mp6 micropump is employed in the “Kühner TOM” analysis unit at Kühner AG, a client of Bartels. This device concurrently measures the respiratory quotient (RQ), carbon dioxide transfer rate (CTR), and oxygen transfer rate (OTR) in up to 16 separate shake flasks.
This gas sensor analysis allows for a better understanding of cultivation processes and efficient and rational process development.

Image Credit: Bartels Mikrotechnik GmbH
Through gas sensing, the system facilitates cell growth analysis. The mp6 micropump here supplies the flow of fresh air required for cell development. The mp6 also removes used air from the bioreactor and directs it to the required sensors. All of this takes place in the smallest possible space.