DNA and RNA libraries are concurrently generated from a single input FFPE sample using the KAPA Total Prep FFPE procedure.
Advantages over separate DNA and RNA library prep:
- Saves labware, resources, and time
- Preserves frequently finite FFPE sample
- Increases the accuracy of tumor profiling by mitigating the bias caused by FFPE sample variability
Compared to parallel or sequential library preparation, it saves resources and time.
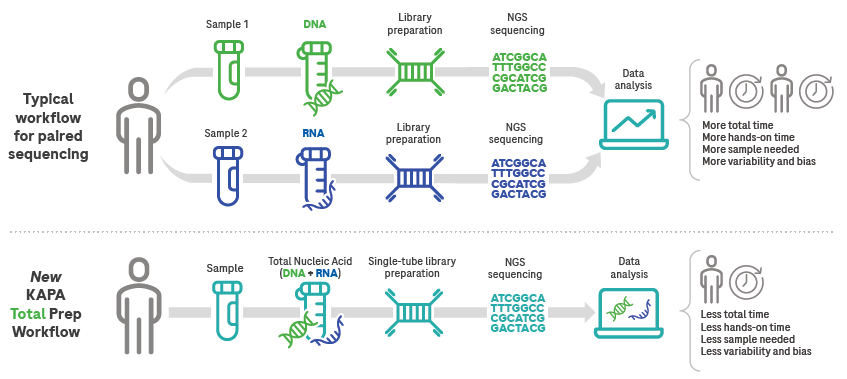
Image Credit: Roche Sequencing and Life Science
It collects regions of interest from the genome and related transcripts, with optional target enrichment.
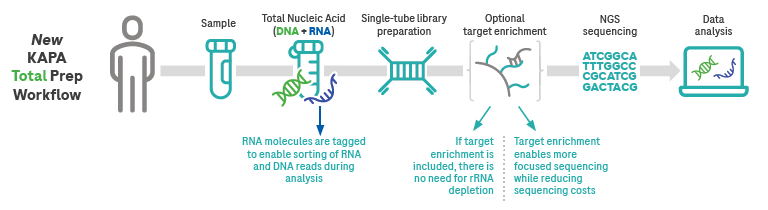
Image Credit: Roche Sequencing and Life Science
It preserves samples while recognizing both genomic variations and expressed transcripts.
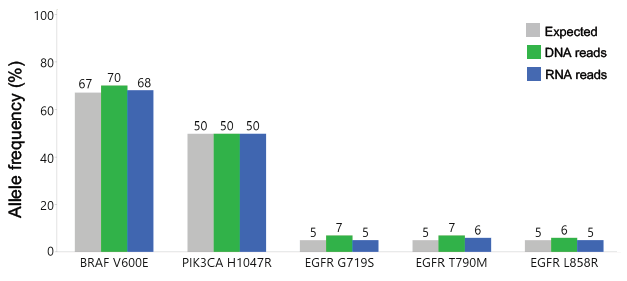
Image Credit: Roche Sequencing and Life Science
The frequency of SNV alleles is consistent across DNA and RNA readings. Using the KAPA Total Prep FFPE methodology and the KAPA HyperCap Oncology Panel, SNVs were discovered in an FFPE sample with known expected allele frequencies. Both DNA and RNA read results were compared to expected allele frequencies.
It identifies DNA and RNA biomarkers from the same total nucleic acid input.
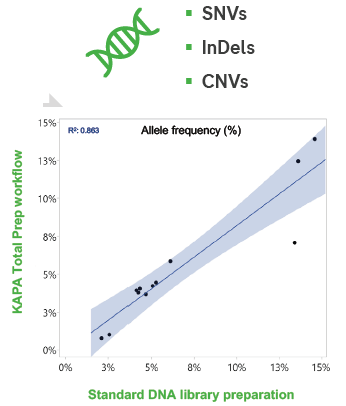
Image Credit: Roche Sequencing and Life Science
The prevalence of SNV and InDel alleles in DNA readings is consistent between manual and KAPA Total Prep library preparation processes. Target enrichment with the KAPA HyperCap Oncology Panel was incorporated in both workflows.
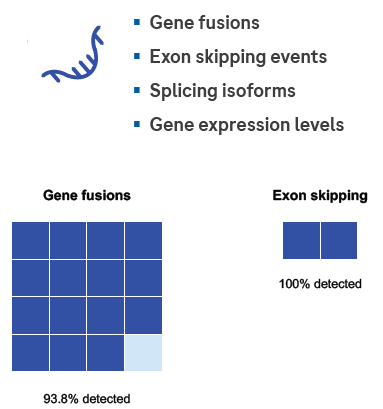
Image Credit: Roche Sequencing and Life Science
The KAPA Total Prep method can detect RNA fusions and exon-skipping events. The KAPA Total Prep FFPE technique was used to detect 16 RNA known fusions and 2 exon-skipping events.