What FIRAZYR is used for
FIRAZYR is used for treating the symptoms of an acute attack of hereditary angioedema
(HAE) in adults, adolescents and children aged 2 years and older.
During attacks of HAE, levels of a substance in your bloodstream called bradykinin
are increased and this leads to symptoms like swelling, pain, nausea, and diarrhoea.
How it works
FIRAZYR contains the active ingredient icatibant. It blocks the activity of bradykinin
and therefore, helps reduce the symptoms of an HAE attack.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why this medicine has been prescribed
for you.
This medicine is not addictive.
This medicine is available only with a doctor's prescription.
Before you use FIRAZYR
When you must not use it
Do not use FIRAZYR if you have an allergy (hypersensitivity) to icatibant, or any
of the other ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty breathing
swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body, skin rash, itching
or hives.
It is important to be able to tell when you might be having an allergic reaction as
the symptoms are very similar to those of an attack of HAE, so you should discuss
this with your doctor.
Do not give FIRAZYR to a child under 2 years of age or weighing less than 12 kg.
FIRAZYR is not registered for use in children under 2 years of age or weighing less
than 12 kg.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date printed on the pack or if the packaging
is torn or shows signs of tampering.
If it has expired or is damaged, return it to your pharmacist for disposal.
Do not use FIRAZYR if there are any visible signs of deterioration, for example if
the solution is cloudy, if it has floating particles, or if the solution is not colourless.
If you are not sure whether you should use FIRAZYR, talk to your doctor.
Before you start to use it
Consult your doctor before using FIRAZYR if:
you are suffering from angina (reduced blood flow to the heart muscle)
you have recently suffered a stroke
Tell your doctor before using FIRAZYR if you are taking a medicine known as an Angiotensin
Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitor (for example: captopril, enalapril, ramipril, quinapril,
lisinopril) which is used to lower your blood pressure or for any other reason.
Tell your doctor if you have allergies to:
any other medicines
any other substances, such as foods, preservatives or dyes.
If you are pregnant or plan on becoming pregnant, discuss this with your doctor before
using FIRAZYR.
Your doctor will discuss the possible risks and benefits of using FIRAZYR during pregnancy.
Tell your doctor if you are breastfeeding. You should not breastfeed for 12 hours
after you have used FIRAZYR.
It is not known whether FIRAZYR passes into your breast milk.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including any
that you get without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food
shop.
FIRAZYR can interact with other medicines, e.g. ACE inhibitors (as previously discussed).
Food and drink have no effect on the action of FIRAZYR.
How to use FIRAZYR
FIRAZYR is intended for subcutaneous injection (under the skin). FIRAZYR is injected
into the fatty tissue under the skin in the abdomen (tummy).
FIRAZYR comes in a ready-to-use syringe. A needle is packed separately which you need
to attach before use. Each syringe should only be used once.
The medicine inside your FIRAZYR pre-filled syringe should be clear and colourless.
Do not use your FIRAZYR if the solution contains particles, is cloudy, or has an unusual
colour.
Please see step-by-step instructions for injecting FIRAZYR at the end of this leaflet.
Adults:
FIRAZYR injections are usually administered by healthcare professionals. If you wish
to inject FIRAZYR yourself and the doctor agrees it is appropriate (e.g. if you have
a lot of HAE attacks or if you live far from a hospital or doctor), you will be trained
on how to give yourself an injection.
You or your caregiver must be trained on subcutaneous injection technique before you
self-inject or your caregiver injects you with FIRAZYR.
Immediately after you self-inject FIRAZYR or your caregiver injects you with FIRAZYR
while you are experiencing a laryngeal attack (obstruction of the upper airway), you
must seek medical care in a medical institution.
The following information is for patients who have been trained to inject themselves:
As HAE attacks can often be serious, it is best to contact your doctor or hospital
when you experience an attack.
If the HAE attack involves your face, lips, throat, or voice box, or if you have any
difficulty breathing, you should always contact your doctor or hospital.
If your HAE attack has not shown signs of improvement within 2 hours of the injection
of FIRAZYR; or if the attack spreads to your face, lips, throat, or voice box, or
you develop any difficulty breathing, you should contact your doctor or hospital immediately.
It is possible to have further injections of FIRAZYR if you do not have relief from
the HAE symptoms following the first injection; however, this should be done by your
doctor or in hospital (see below) - or following the advice of your doctor.
Children and adolescents aged 2 to 17 years:
FIRAZYR injections are usually administered by healthcare professionals, or by the
caregiver of the child.
The caregiver must be trained on subcutaneous injection technique before administering
FIRAZYR to the child.
Immediately after administering FIRAZYR to the child while he/she is experiencing
a laryngeal attack (obstruction of the upper airway), the child must seek medical
care in a medical institution.
As HAE attacks can often be serious, it is best to contact your doctor or hospital
when the child experiences an attack.
If the HAE attack involves the face, lips, throat, or voice box, or if the child has
any difficulty breathing, contact the doctor or hospital.
If the HAE attack has not shown signs of improvement within 2 hours of the injection
of FIRAZYR; or if the attack spreads to the face, lips, throat, or voice box, or the
child develops any difficulty breathing, contact the doctor or hospital immediately.
No more than one injection was given to a child for each HAE attack in clinical studies.
How much and when it is given
Your doctor will determine the exact dose of FIRAZYR and will tell you how often it
should be used.
Adults:
The recommended dose of FIRAZYR is one injection (30 mg in 3 mL) given subcutaneously
(under the skin) as soon as you develop symptoms of an angioedema attack (e.g. increased
skin swelling, particularly affecting the face and neck, increasing tummy pain).
If the HAE symptoms are still present, or return after initial relief, an additional
injection of FIRAZYR (3 mL) may be given after 6 hours.
If after a further 6 hours you still experience symptoms you may need a third injection
of FIRAZYR (3 mL).
You should have no more than 3 injections in a 24-hour period and no more than 8 injections
in a month.
Children and adolescents aged 2 to 17 years:
The recommended dose of FIRAZYR is one injection of 1 mL up to a maximum of 3 mL based
on body weight given subcutaneously (under the skin) as soon as you develop symptoms
of an angioedema attack (e.g. increased skin swelling, particularly affecting the
face and neck, increasing tummy pain).
The dose will be determined by your doctor based on your child's body weight. The
dose will increase over time as your child grows and the doctor will need to periodically
review that the dose is appropriate.
The decision to initiate caregiver or self-administration of icatibant should be made
by a physician experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of HAE. FIRAZYR may be administered
by a healthcare professional.
Please see step-by-step instructions for the dose to inject in children and adolescents.
If you are not sure which dose to inject, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
You must seek immediate medical help if your symptoms get worse or do not improve.
If you use too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or the Poisons Information Centre (Australia: 13
11 26; New Zealand: 0800 POISON or 0800 764766) for advice, or go to Accident and
Emergency at the nearest hospital if you think that you or anyone else may have used
too much FIRAZYR. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning.
When high doses have been given, patients have experienced a drop in blood pressure.
While you are using FIRAZYR
Things you must do
Tell your doctor immediately if you notice that your symptoms of the attack get worse
after you use FIRAZYR.
Some of the side effects connected with FIRAZYR are similar to the symptoms of your
disease.
If you are about to be started on any new medicine, remind your doctor and pharmacist
that you are using FIRAZYR.
Tell any other doctors, dentists, and pharmacists who treat you that you are using
this medicine.
If you become pregnant while using this medicine, tell your doctor immediately.
Things to be careful of
Do not drive or operate any machinery if you feel tired or dizzy as a result of your
HAE attack or after using FIRAZYR.
Side effects
Tell your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you
are using FIRAZYR.
Like all medicines, FIRAZYR can cause some side effects. Sometimes they are serious,
most of the time they are not. You may need medical attention if you get some of the
side effects.
Do not be alarmed by the following lists of side effects. You may not experience any
of them.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist to answer any questions you may have.
Almost all patients receiving FIRAZYR will experience a reaction at the site of the
injection. The reaction may include burning sensations, reddening of the skin (erythema),
pain, swelling, feeling of warmth, and itching (pruritus). These effects are usually
mild and clear up by themselves without the need for any additional treatment.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice any of the following symptoms and they
worry you:
nausea
pain in the abdomen (tummy)
weakness
dizziness
headache
blocked nose
rash
vomiting
fatigue
fever
sore throat
weight gain
asthma
cough
itching
redness of the skin
hot flushes
muscle spasm
hives
abnormal liver function test (symptoms may include yellowing of the skin and eyes
(jaundice)).
These are the more common side effects of FIRAZYR. Mostly, these are mild and short-lived.
Tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist if you notice anything that is making you feel
unwell.
Other side effects not listed above may also occur in some people.
After using FIRAZYR
Storage
Keep your medicine in the pack until it is time to use it.
If you take the medicine out of the pack it may not keep well.
Keep the medicine in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 25°C. Do not
freeze it.
Do not store FIRAZYR or any other medicine in the bathroom or near a sink. Do not
leave it on a window sill or in the car.
Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep it where children cannot reach it.
A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place
to store medicines.
Disposal
If your doctor tells you to stop using this medicine or the expiry date has passed,
ask your pharmacist what to do with any medicine that is left over.
Product description
What FIRAZYR looks like
FIRAZYR is supplied in one single-use pre-filled glass syringe with a grey plunger
stopper. The solution is clear and colourless and free from visible particles. A hypodermic
needle (25 G; 16 mm) is included in the package.
Ingredients
Active ingredient:
Icatibant acetate (equivalent to 30 mg of icatibant) in 3 mL solution for injection
in each pre-filled syringe.
Other ingredients:
sodium chloride
acetic acid - glacial
sodium hydroxide
water for injections.
The injection solution contains less than 1 mmol (23 milligrams) of sodium so it is
essentially 'sodium-free'.
FIRAZYR does not contain lactose, sucrose, gluten, tartrazine or any other azo dyes.
Sponsor
Australia:
Takeda Pharmaceuticals Australia Pty Ltd
Level 39
225 George Street
Sydney NSW 2000
Australia
Telephone: 1800 012 612
New Zealand:
Takeda New Zealand Limited
Level 10
21 Queen Street
Auckland 1010
New Zealand
Telephone: 0508 169 077
This leaflet was prepared in July 2023.
Australian Registration Number:
AUST R 160313
FIRAZYR® is a registered trademark of Shire Orphan Therapies GmbH, a Takeda company.
TAKEDA® and the TAKEDA Logo® are registered trademarks of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited.
Step-by-step instructions for injecting FIRAZYR
1.General information
Clean the work area (surface) to be used before beginning the process.
Wash your hands with soap and water.
Open the blister tray by peeling back the seal.
Remove the pre-filled syringe from the blister tray.
Remove the cap from the end of the pre-filled syringe by unscrewing the cap.
Put down the pre-filled syringe after unscrewing the cap.
2a). Preparing the syringe for children and adolescents (2-17 years) weighing 65 kg
or less
For patients who have not previously received FIRAZYR, initial treatment should be
given in a medical institution or under the guidance of a physician. The decision
to initiate caregiver or self-administration of FIRAZYR should only be made by a physician
experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of HAE.
FIRAZYR may be administered by a caregiver only after training in subcutaneous injection
technique by a healthcare professional.
Important information for healthcare professionals and caregivers:
Where the dose is less than 30 mg (3 mL), the following equipment is required to extract
the appropriate dose (see below):
a) FIRAZYR pre-filled syringe (containing icatibant solution)
c) 3 mL graduated syringe
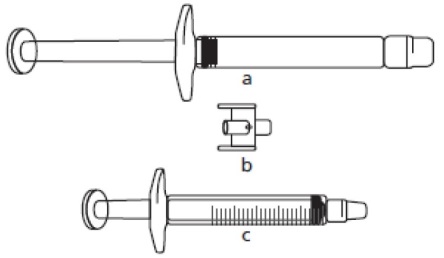
The required injection volume in mL should be drawn up in an empty 3 mL graduated
syringe (see table below).
Table 1. Dosage regimen for children and adolescents:
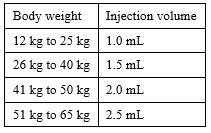
Patients weighing more than 65 kg will use the full contents of the pre-filled syringe
(3 mL).
If you are not sure which volume of solution to extract, ask your doctor, pharmacist
or nurse.
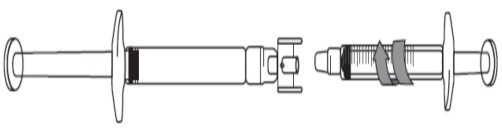
Preparing to extract dose less than 3 mL:
Remove the caps on each end of the adapter.
Avoid touching the ends of the adapter and syringe tips, to prevent contamination.
Screw the adapter onto the pre-filled syringe.
Attach the graduated syringe to the other end of the adapter ensuring that both connections
fit securely.
Transferring FIRAZYR solution to the graduated syringe:
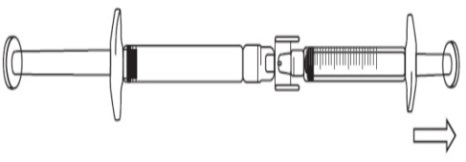
To start transfer of FIRAZYR solution, push the pre-filled syringe plunger (on far
left of the below image).
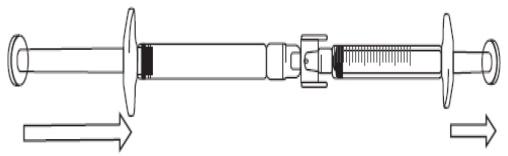
If the FIRAZYR solution does not begin to transfer to the graduated syringe, pull
slightly on the graduated syringe plunger until the FIRAZYR solution starts to flow
into the graduated syringe (see below image).
Continue to push on the pre-filled syringe plunger until the required injection volume
(dose) is transferred to the graduated syringe. See Table 1 for dosage information.
If there is air in the graduated syringe:
Turn the connected syringes so that the pre-filled syringe is on top (see below image).
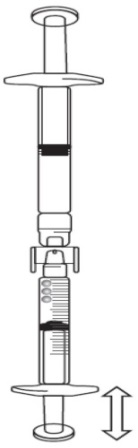
Push the plunger of the graduated syringe so that any air is transferred back into
the pre-filled syringe (this step may need to be repeated several times).
Withdraw the required volume of FIRAZYR solution.
After transfer of FIRAZYR solution to the graduated syringe:
Remove the pre-filled syringe and adapter from the graduated syringe.
Discard the pre-filled syringe and adapter into the sharps container.
2b). Preparing the syringe and needle for injection: All patients (adults, adolescents
and children)
Remove the needle cap from the blister tray.
Twist the lid of the needle cap to break the seal (the needle should be still in the
needle cap).
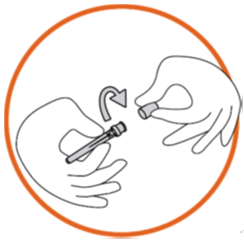
Grip the syringe firmly. Carefully attach the needle to the syringe containing the
colourless solution.
Screw the syringe on the needle still fixed in the needle cap.
Remove the needle from the needle cap by pulling the syringe. Do not pull up on the
plunger.
The syringe is now ready for injection.
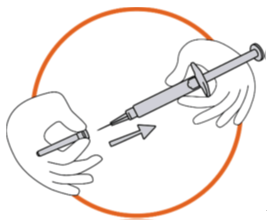
3. Preparing the injection site
Choose the injection site. The injection site should be a skin fold on your abdomen
(tummy), approximately 5 to 10 cm below your navel (belly button) on either side.
This area should be at least 5 cm away from any scars. Do not choose an area that
is bruised, swollen, or painful.
Clean the injection site with an alcohol wipe and allow it to dry.
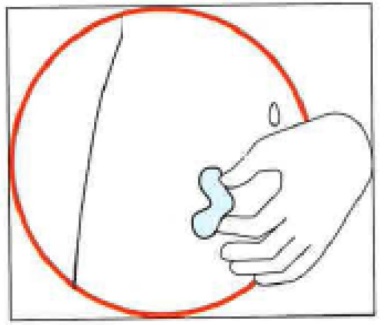
4. Injecting the solution
Hold the syringe in one hand between two fingers with your thumb at the bottom of
the plunger.
Make sure that there is no air bubble in the syringe by pressing the plunger until
the first drop appears on the tip of the needle.
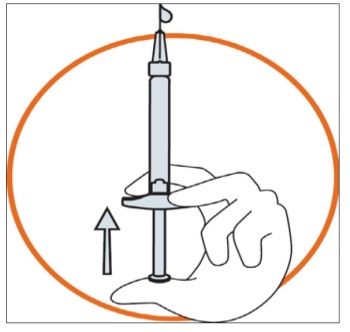
Hold the syringe between a 45 to 90 degrees angle to your skin with the needle facing
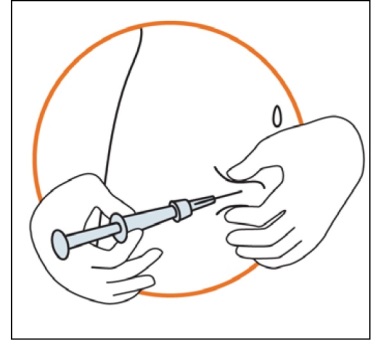
the skin.
Keeping the syringe in one hand, use your other hand to gently hold a fold of skin
between your thumb and fingers at the previously disinfected injection site.
Hold the fold of the skin, bring the syringe to the skin and quickly insert the needle
into the skin fold.
Slowly push the plunger of the syringe with a steady hand until all the solution is
injected into the skin and no liquid remains in the syringe.
Press slowly so that this takes approximately 30 seconds.
Release the skin fold and gently pull the needle out.
5. Disposal of the injection material
Discard the syringe, needle and needle cap into the sharps container.
Ask your pharmacist if you are not sure about the right way to throw away used syringes
and needles.