Introduction
Factors that raise the risk of acne
What does not cause acne?
References
Further reading
The most important cause of acne or pimples is an infection of the hair follicles. As a child attains puberty, the levels of sex hormones begin to rise. These stimulate secondary sexual characteristics like the development of hair in the armpits and groin and the deepening of the voice.
The hormones also bring about significant changes in the skin. These hormones stimulate several glands in the skin called sebaceous glands to produce more oil, also called sebum. Sebum is primarily released through the hair shaft onto the skin. Its main function is to lubricate and protect the skin.
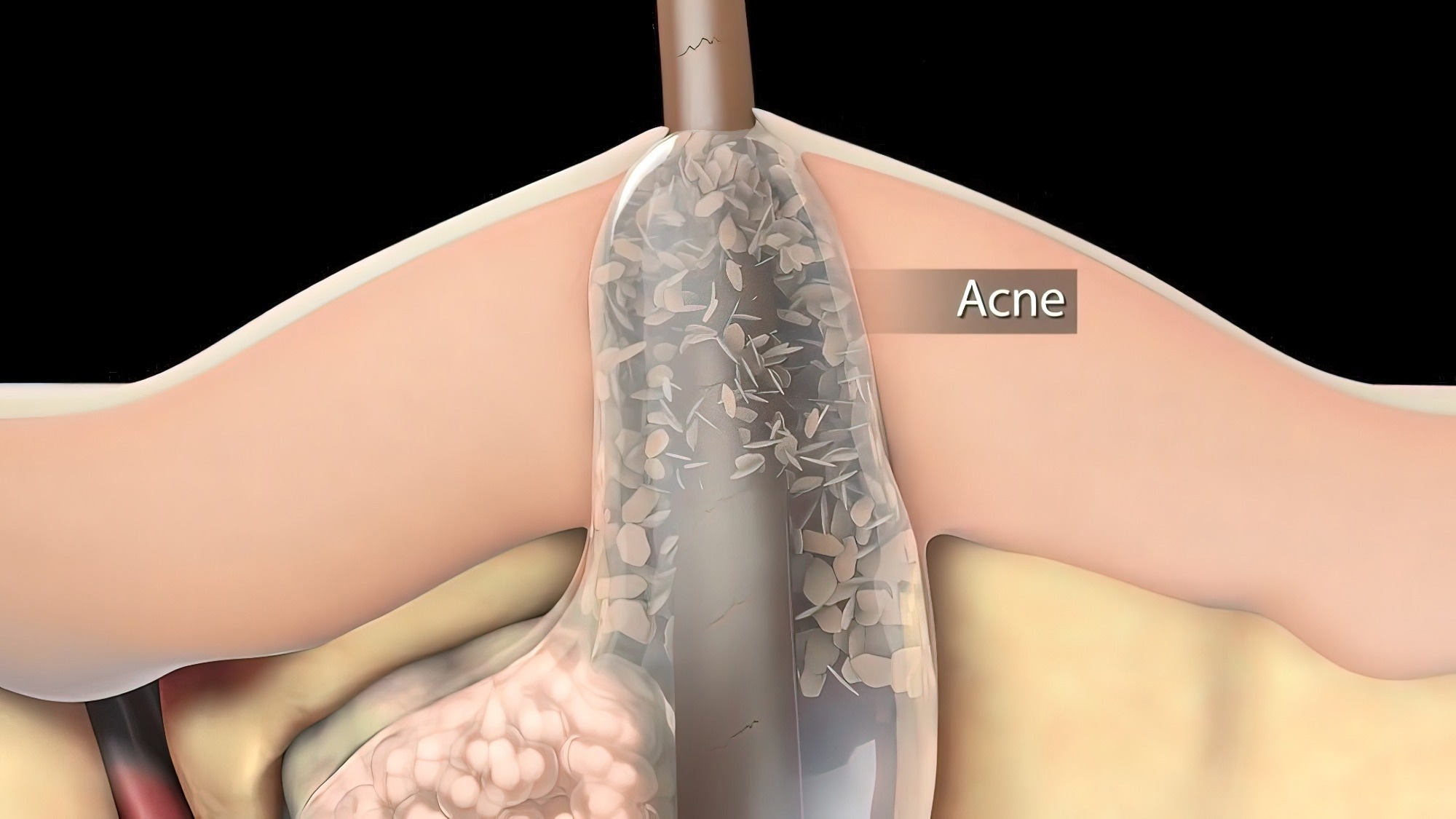
Image Credit: picmedical/Shutterstock
The skin and hair follicles contain several harmless bacteria. These are generally called commensal organisms. Their presence is not infective in a normally healthy person. When there is excessive sebum production, it combines with the dead cells and is regularly shed from the top layer of the skin. This combination forms a plug in the skin pore called a comedone.
A comedone or plugged follicle eventually ruptures. This leads to the leakage of sebum into the surrounding skin, causing inflammation. The commensal bacteria on the skin can break down the fatty parts of the sebum into fatty acid substances. These also leak into the surrounding skin, causing inflammation.
The result of this pathological process is the formation of a solid bump or a pustule over the skin's surface or
forming a cyst (fluid-filled sac) within the skin. The solid bump over the skin is called a whitehead.
Alternatively, the plugged follicle can be open to the skin, creating a blackhead. Bacterial infection of the whitehead or blackhead may give rise to papules, pustules, nodules, or cysts.
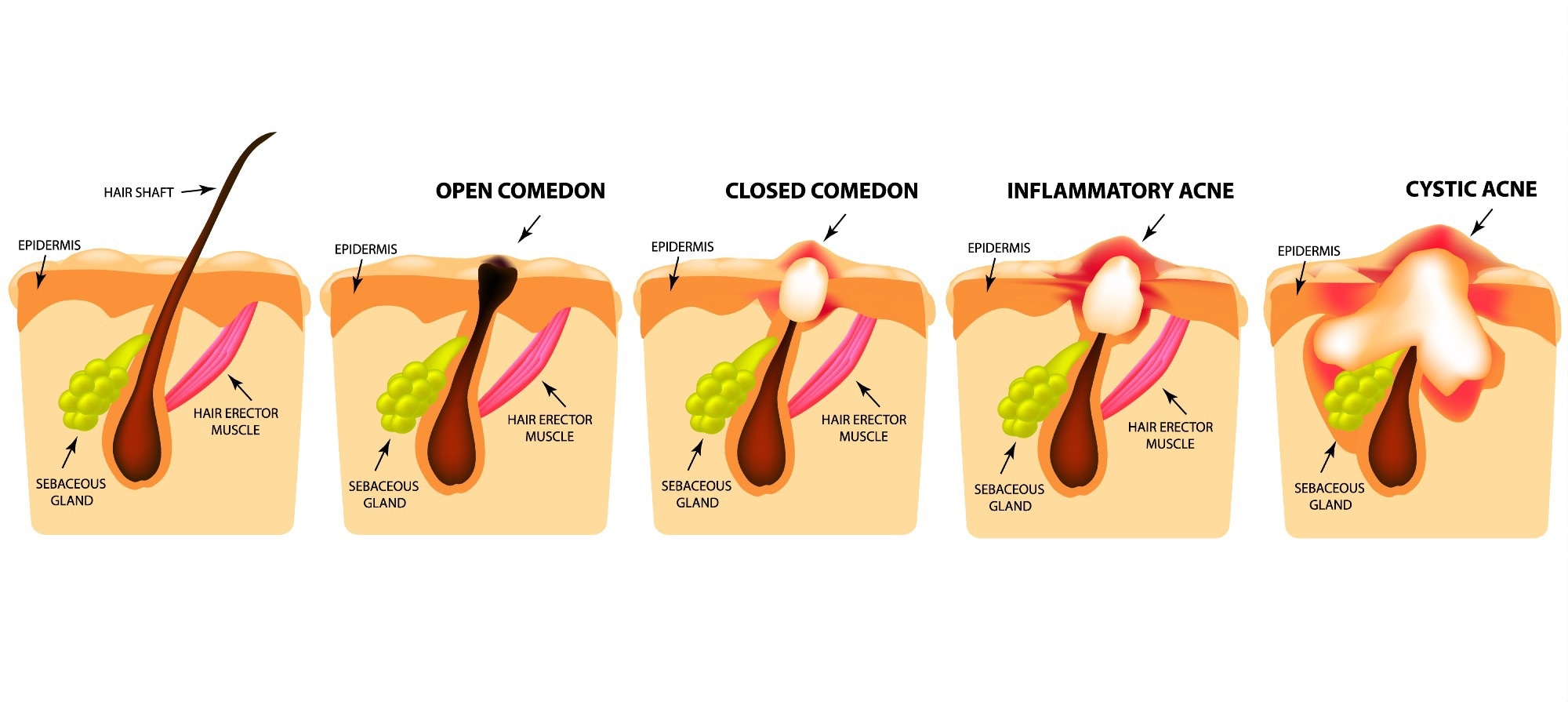
Image Credit: Timonina/Shutterstock
Factors that raise the risk of acne
Age
Adolescence or puberty is a risk factor for developing acne. The sebaceous glands are particularly sensitive to hormones. Raised levels of testosterone (male sex hormone) lead to secondary sexual changes and reproductive development of the boys. In girls, testosterone levels also rise during puberty but to a much lower extent. This helps in bone and muscle growth. Increased testosterone levels cause the glands to produce much more sebum than the skin needs.
Familial traits
Those with parents who have suffered from acne are more likely to get acne.
Oily skin
Increased skin oiliness is most likely the result of increased sebum secretion.
Hormonal changes
Some women have a flare-up of acne just before their periods. This indicates a hormonal association. Similarly, acne may be more severe in some pregnant women, especially during the first three months of their pregnancy.
Hormonal disorders
Women with a hormonal disease like Polycystic ovary syndrome are more likely to get acne
Acne may also result from side effects of certain drugs like steroids and lithium (taken for bipolar disorder or depression).
What Causes Acne? | Earth Science
What does not cause acne?
Acne is not caused by a poor diet or a diet rich in spices and oils. Eating a healthy, balanced diet is recommended, however. A lack of cleanliness does not cause acne. Although not cleaning the affected or prone areas leads to the accumulation of sebum and dirt in susceptible persons, raising the risk of acne.
Moreover, acne is also not caused or worsened by sunbeds and sunlamp exposure. Artificial tanning beds, however, should be avoided as they raise the risk of skin cancer.
References
Last Updated: Nov 9, 2022