Axillary lymph nodes are kidney bean-shaped organs in the underarm area and are part of the lymphatic system. The interior of the lymph nodes contain lymphocytes and macrophages in abundance. The lymph nodes receive an extracellular fluid called lymph that circulates in the body and helps cleanse the blood vessels and tissues.
Lymph nodes act as filters of the lymph. Lymph from different tissues enters and drains away through the lymph nodes, where the macrophages and T-lymphocytes attack and destroy the tumor cells and pathogens. Post filtration, the lymph is returned to the blood stream for circulation as blood plasma. Thus, the lymph nodes function as filters in the lymphatic system and eliminate harmful substances from our body.
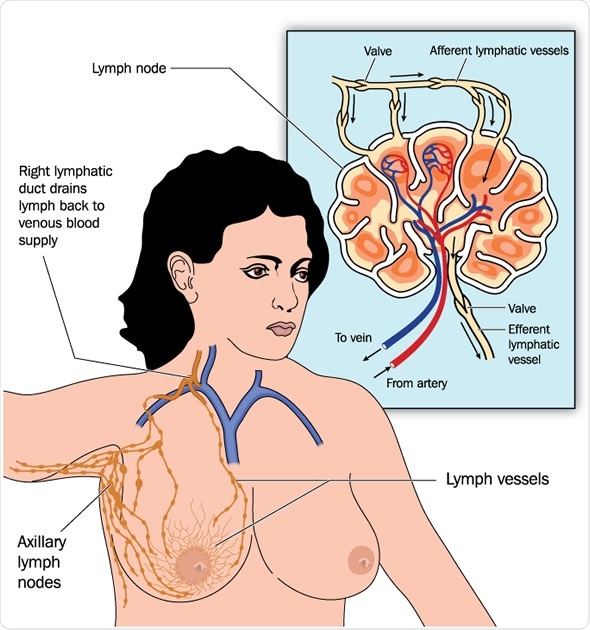
Drawing of female breast lymph drainage - Image Copyright: Blamb / Shutterstock
Role of Lymph Nodes in Cancer
Breast cancer often spreads to the axillary lymph nodes, thus taking the cancer cells to other parts of the body. Since the lymph nodes filter out harmful substances, they are usually examined to detect the presence of cancer cells that have passed through the node on their way to reach other parts of the body. During breast removal surgery, the lymph nodes are often dissected by surgeons to study the extent that cancer has spread. This is known as axillary lymph node dissection.
Axillary lymph node dissection was first used as part of breast cancer treatment in the 18th century. Since then axillary dissection has become a standard procedure used for staging of the axilla and treatment of breast cancer patients.
Positive and negative lymph nodes indicate the presence and absence of tumor cells in the lymph nodes and are one of the key indicators of the type of treatment required for a particular patient. Lymph node dissection helps remove cancer cells from the nodes, thus preventing cancer metastasis to a great extent. Patients in the early stages of breast cancer have a 30-40% chance of having positive axillary nodes.
If the cancer has spread to the axillary lymph nodes, the surgeon will recommend an axillary node dissection. The number of affected nodes varies from one patient to another, and so the decision is largely based on site of the cancer and not the number of positive nodes.
Many studies proved that axillary lymph node dissection helps in local control of the disease, thus improving overall survival of cancer patients. The cancer recurrence rate post axillary dissection was shown to be less than 2%. Hence, the staging of the axilla is an important step in the treatment of breast cancer. The status of axillary lymph node is a key prognostic variable in individuals with early stage breast carcinoma. The number of positive nodes also has prognostic importance.
Although removal of lymph nodes reduces the risk of cancer spreading to other body parts, it cannot destroy the cancer cells that may have already spread to other parts. However, the involvement of lymph nodes gives important insights into the nature and stage of the cancer and thus aids doctors in developing a customized treatment plan for a patient.
Levels of Axillary Nodes and Dissection
Axillary lymph nodes are classified into three levels including low axilla, mid axilla, and high axilla. Based on which level of axillary nodes is affected, the surgeon performs various levels of axillary dissection. In a majority of cases, level I or II nodes are removed if the sentinel node is positive or if there is a cancerous node present in the armpit. Women with invasive breast cancer usually undergo axillary dissection along with a mastectomy.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Feb 26, 2019