Why are bleeding gums important?
Which medical conditions may cause bleeding gums?
Bleeding gums due to HIV infection
Anemia-related bleeding gums
Herpes infection
Stress-induced bleeding gums
Leukemia and gum cancer
Deficiency of Factor V
Which dental diseases can cause bleeding gums?
Gingivitis
Periodontitis
Bleeding gums during pregnancy
Other conditions
How are bleeding gums treated?
References
Why are bleeding gums important?
Understanding the primary cause of bleeding gums can help to treat and cure the condition.
Coarse brushing, trauma, injury, gingivitis, or initial stages of periodontal gum disease could cause bleeding gums. Some symptoms which are usually observed in such conditions include:
- Persistent halitosis or bad mouth odor
- Painful gingival ulceration (gum sores)
- Excessive gingival pain or discomfort
- Inflamed gums and oral mucosa
- Dental sensitivity
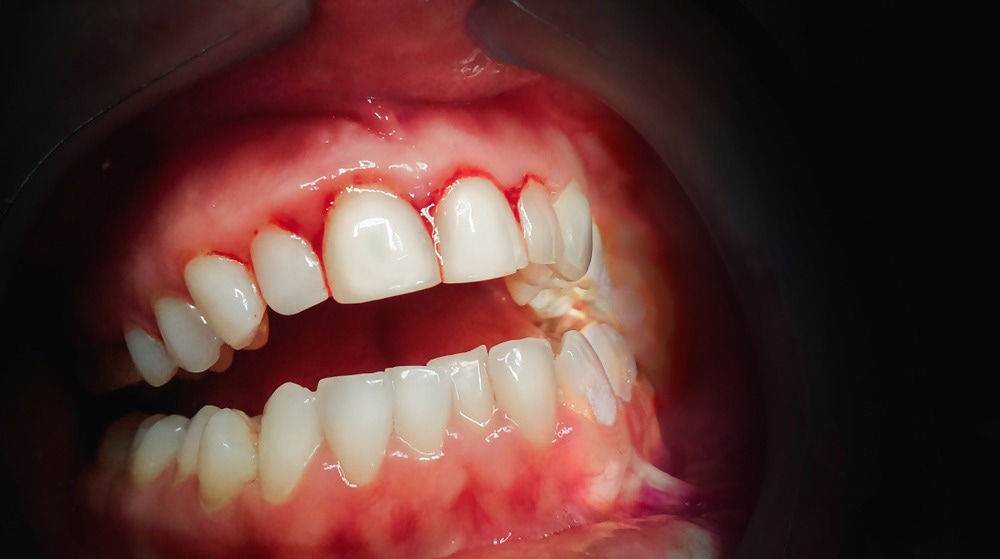
Image Credit: Algirdas Gelazius/Shutterstock.com
Which medical conditions may cause bleeding gums?
Most of the time, it is challenging to recognize the exact cause of bleeding gums. However, underlying medical conditions should be ruled out. A list of various disorders requiring immediate medical treatment and whose manifestations could include bleeding gums include:
Bleeding gums due to HIV infection
HIV is a condition that results in serious infections due to a compromised immune system. This infection is transmitted via blood contact or having direct sexual contact with an HIV-positive individual or from an infected mother to the baby.
Various medical issues may arise following HIV infection. This includes dental problems such as bleeding gums and soreness in the oral cavity, including the tongue, lips, or mouth. However, this cause can be confirmed only by serologic testing.
Anemia-related bleeding gums
Anemia is a medical condition caused by the lack of red blood cells. One form of anemia is pernicious anemia, associated with Vitamin B12 malabsorption, which also causes bleeding from the gums.
Herpes infection
Herpes simplex virus infection can cause severe pain, soreness of the oral mucosa, and bleeding from the gums if involved.
Stress-induced bleeding gums
Stress may result in gingival inflammation, making the gums more susceptible to trauma. Stress also induces an immunosuppressed state, encouraging bacterial infection and inhibiting normal coagulation processes.
Leukemia and gum cancer
Oral cancer usually manifests in painless eruptions on the surface of the gums, the inner parts of the cheeks, or the tongue, often associated with gum bleeding.
Leukemia can also cause bleeding from the gums, producing immature or non-functional leukocytes and platelet deficiency. Other characteristic signs and symptoms include enlargement of the spleen, liver, and lymph nodes.
Deficiency of Factor V
Factor V deficiency is a bleeding disorder with typical symptoms like bleeding gums, bleeding underneath the skin surface, frequent bruising, or nose bleeds.
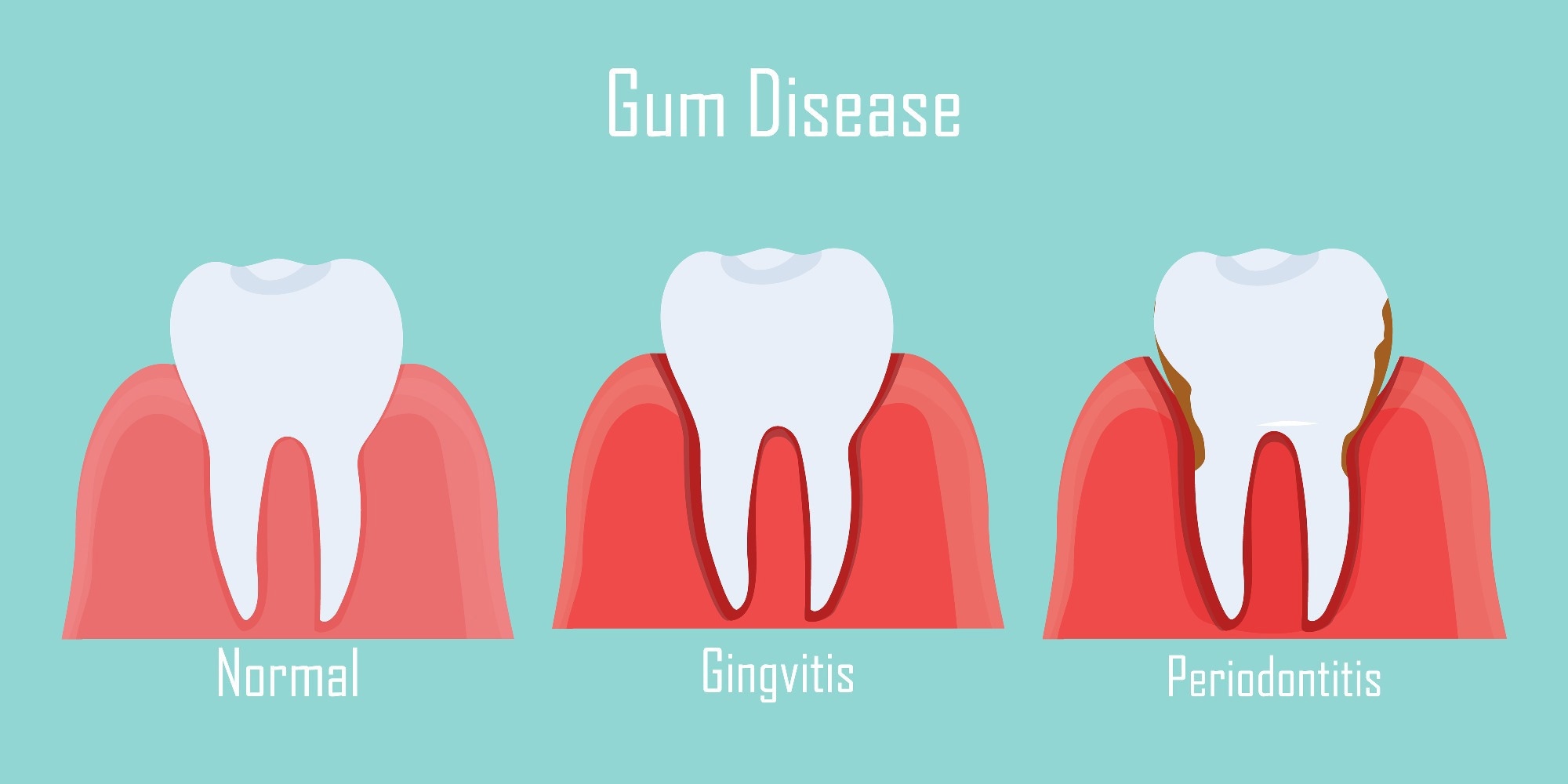
Image Credit: AlyonaZhitnaya/Shutterstock.com
Which dental diseases can cause bleeding gums?
Gingivitis
Gingivitis refers to inflammation of the gums and is associated with gum bleeding. However, this condition is treatable if diagnosed early. It is also preventable with proper oral hygiene. Risk factors for gingivitis should be ruled out. These include smoking, diabetes, periods of hormonal fluctuations, especially in females, and dry mouth.
Periodontitis
This condition can also cause bleeding gums and is one sequel of untreated gingivitis. This condition results in the loosening of the gum sockets around the teeth, which results in bleeding gums.
Bleeding gums during pregnancy
Pregnancy is a condition that is associated with hormonal fluctuations. Such hormonal changes may result in inflammation and sore gums. Good hygiene methods can prevent bleeding gums during this time. However, dental consultation is important to avoid complications if the condition flares up.
Other conditions
Some other conditions like deficiency of Vitamin C and Vitamin K can also cause bleeding gums. Gum trauma is one obvious cause of bleeding from the gums.
How are bleeding gums treated?
Understanding and eliminating the root cause of bleeding gums is fundamental to treatment. Appropriate dental treatment is mandatory if the gum bleeding is due to dental causes. However, if the root cause of bleeding gums is an underlying medical illness, this should be identified and treated.
Good oral hygiene methods will generally prevent the most typical causes of bleeding gums.
References:
Further Reading
Last Updated: Sep 19, 2023