Bursitis and osteoarthritis are two conditions which cause significant joint pain and can reduce your ability to perform physical activities or everyday tasks. The conditions share many similarities in terms of their symptoms and treatment. This can make it hard to distinguish between them, as people with either condition may describe a near identical experience. Despite this, the conditions have very different reasons for causing pain.
This article will cover:
Symptoms
The symptoms of bursitis and arthritis overlap considerably. Both cause aching pain, tender or warmth, stiffness, swelling, and redness in the joint. However, bursitis differs from osteoarthritis in that the pain is generally more acute following repetitive movements, whereas, pain in osteoarthritis is worst following a period of inactivity. Despite this, both conditions can be triggered by certain movements.
Any joint can be affected by either condition, however, osteoarthritis most often affects the knees, hips, and small joints of the hands. Whereas, bursitis is most common in the shoulders, hips, elbows, and knees.
Bursitis can occur suddenly, last for a few days or longer, and usually resolves with rest or treatment. In comparison, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are progressive and degenerative conditions which generally become worse over time.
What is the difference between bursitis and arthritis of the hip?
Pathology
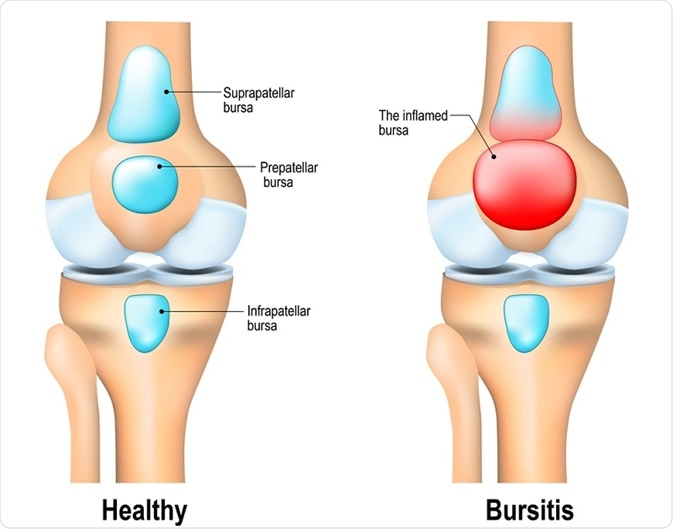
The most pertinent difference between arthritis and bursitis are their underlying pathologies. Bursitis results from the inflammation of the bursa - a fluid-filled sac that works as a cushion and gliding surface to reduce friction between tissues of the body.
There are over 150 different bursae in the human body, with the major ones being located next to the tendons of large joints, such as the hips, knees, elbows and shoulder.
There are many different types of bursitis, the variety depends on which particular bursa has become inflamed. For instance, retromalleolar tendon bursitis is caused by inflammation of the bursa located near the Achilles, whereas, trochanteric bursitis can be considered bursitis of the hip.
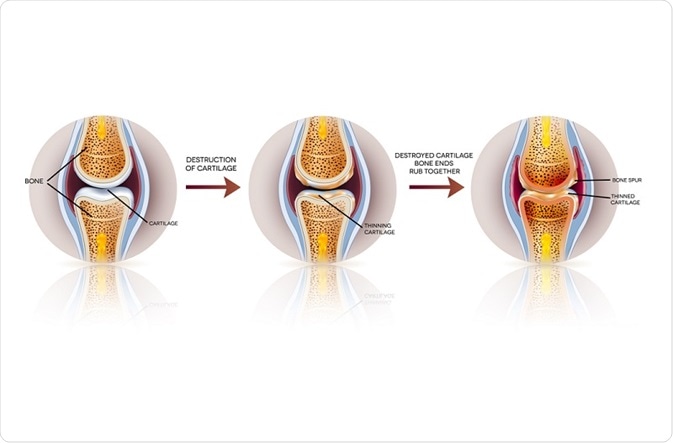
In contrast, someone with osteoarthritis is experiencing symptoms caused by the protective cartilage at the ends of their bones breaking down. The cartilage can either become thin or disappear completely causing bone-on-bone contact and joint deformity.
Cartilage is found in joints throughout the body. It is usually smooth and slippery, enabling a joint to move freely. However, during osteoarthritis it becomes rough. This forces the ligaments and tendons to work harder, resulting in inflammation and the formation of bony spurs called osteophytes.
 Designua | Shutterstock
Designua | Shutterstock
Risk factors
Both bursitis and osteoarthritis can be caused by injury to a joint. This can occur via sports, overuse injuries, or any prolonged stress to a joint. This can include repetitive movements or stress caused from abnormally positioned joints or bones (such as joint deformities or differences in leg length).
Obesity, which places excess strain on your weight-bearing joints, can also be a risk factor of both conditions. Certain systemic conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, diabetes, and ankylosing spondylitis, can also increase your risk of developing bursitis or osteoarthritis.
Bursitis may also result from a joint infection and existing osteoarthritis can be a risk for septic arthiritis. Unlike bursitis, certain types of osteoarthritis may run in families. Research studies have identified multiple genes associated with the development of osteoarthritis.
 Tefi | Shutterstock
Tefi | Shutterstock
Treatment
Treatment procedures for bursitis and osteoarthritis are designed to reduce the amount of inflammation in and around the joint.
For bursitis, conservative measures of treatment are often recommended first. This includes taking rest from strenuous activities which may place stress on the joint, reducing inflammation by elevating the joint to encourage blood flow and frequently placing a bag of ice the affected area.
In contrast, mild osteoarthritis can sometimes be managed by making lifestyle changes to increase activity levels. Your health professional may recommend regular exercise or losing weight if you are overweight, to help manage your symptoms of osteoarthritis.
Pain relieving and anti-inflammatory medication may be recommended for both bursitis and osteoarthritis. In more moderate cases, corticosteroids may be injected into the bursa or joint to help reduce inflammation and pain. If bursitis has been caused due to infection, antibiotic medication may be prescribed by your physician to help reduce the inflammation.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jul 9, 2019