Tinnitus or “ringing of the ears” is a symptom of an underlying condition rather than a disease in itself.
Patients complain of hearing sounds or noises even when there are no actual sounds in the background.
Anatomy of the ear
In the normal course sounds pass through the ear canal and fall on the ear drum that marks the end of the outer ear and beginning of the middle ear.
The middle ear amplifies and passes on the sound information to the inner ear.
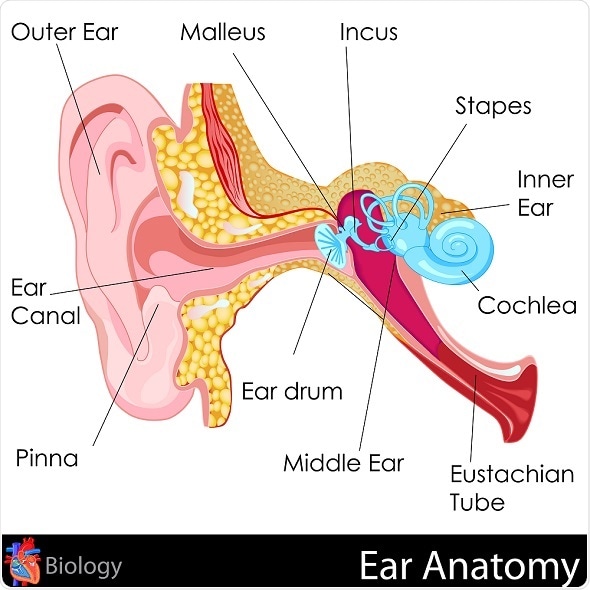
The inner ear contains the cochlea and the auditory nerve.
The cochlea looks like a sea shell and is a coiled, spiral tube that contains a large number of sensitive hair cells.
The nerve picks up sound information and relays it to the brain.
If some parts of the cochlea are damaged the brain tries to seek out information from other healthy parts of the cochlea.
This over-representation of sounds leads to the symptoms of tinnitus.
Cause of temporary Tinnitus
Tinnitus could be temporary or a chronic annoying or distressing condition. A temporary tinnitus is caused by exposure to a loud noise like being in a sports arena or loud concert.
Sometimes a bout of cold or flu or a blow to the head may also lead to tinnitus.
Cause of prolonged or recurring Tinnitus
Prolonged or recurring tinnitus may occur due to (1, 2, 3, 4, 5): –
- Ear infections – Infections of the inner ear called Acute otitis media or Chronic otitis media
- Foreign bodies or wax impaction in the ear
- Ear injury caused by loud noises may lead to tinnitus
- Meniere's disease - a disease of the inner ear that is characterized by loss of hearing, dizziness and tinnitus
- Alcohol, caffeine and certain drugs like aminoglycoside antibiotics (like gentamycin, amikacin etc.), aspirin, loop diuretics, cancer chemotherapeutic agents etc. especially when taken in an overdose
- Underlying disease like high blood pressure, allergy or anemia
- Sometimes there may be no cause for the tinnitus wherein it is termed “idiopathic tinnitus”
- Presbyacusis – This is basically age related hearing loss. Tinnitus is often accompanied with hearing loss in the elderly.
- A severe head injury, whiplash injury etc.
- Some disease like multiple sclerosis or brain tumors like cerebellopontine-angle tumors
- Brain infections like meningitis, syphilis, Lyme disease etc. may lead to tinnitus
- Temporomandibular-joint (the joint connecting the lower jaw to the skull at the base of the ears) dysfunction and dental disorders
- A rapid change in environmental pressure while travelling to high altitudes
- Psychosocial stress and noise exposure
Deeper causes of Tinnitus
Tinnitus may be a primary sign of a deeper problem like a tumor of the inner ear called acoustic neuroma or an aneurysm that is a deformity of a blood vessel within the inner ear.
This deformity leads to ballooning of the blood vessel that carries a risk of rupture.
If there is hearing loss in one ear, difficulty in understanding speech and dizziness, there is a chance of an acoustic neuroma that is also known as vestibular schwannoma.
There is also a risk of a meningioma – a brain tumor.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jun 8, 2023