A brain (cerebral) aneurysm is a weak spot in an artery in the brain that swells and fills with blood.
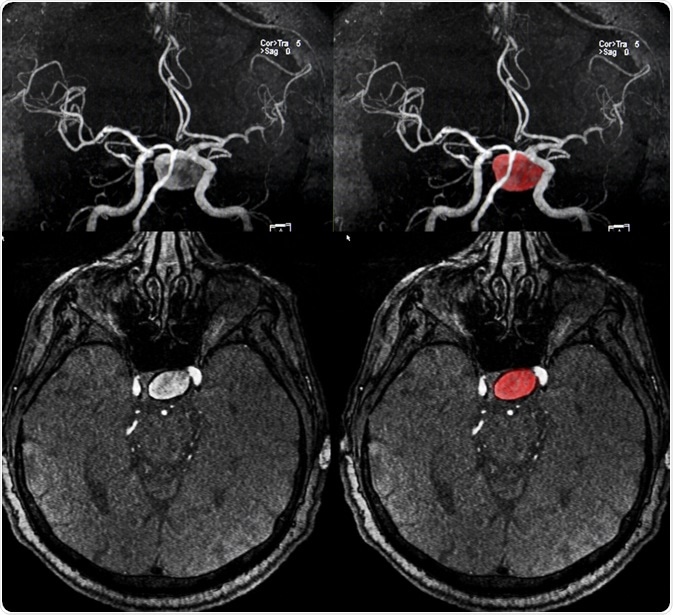
Image Credit: Semnic / Shutterstock.com
What is a cerebral aneurysm?
The bulging area within a cerebral aneurysm can put pressure on surrounding tissue or a nerve. The aneurysm can also rupture, spilling blood into the brain tissue. This is referred to as a subarachnoid hemorrhage.
In most cases, a cerebral aneurysm does not cause any symptoms and goes unnoticed; however, in rare cases, the aneurysm ruptures, causing a hemorrhage and stroke. Depending on how severe the hemorrhage is, a person may suffer brain damage or even die. Cerebral aneurysms can occur anywhere in the brain, but the most common location is a loop of arteries found at the base of the brain, referred to as the circle of Willis.
Treatment
A cerebral aneurysm is usually only treated if the aneurysm has ruptured or is at risk of rupturing. In the majority of cases, aneurysms do not burst and only high risk patients are treated, owing to the fact that the surgery itself is associated with the risk of complications such as damage to other blood vessels, likelihood of aneurysm recurrence and rupture, and the risk of post-operative stroke or brain damage.
Decisions regarding the best treatment option for a patient with a brain aneurysm are based on careful comparison of the risk of rupture and the risk of intervention. When deciding on a treatment option, doctors take several factors into consideration. These include the following:
- Patient’s age
- Patient’s health
- Size, shape and location of the aneurysm
- Patient’s neurological condition
- Other medical conditions
- Previous history of familial aneurysm
- Risk of rupture
- Risk of treatment
If it is decided that the risk of aneurysm rupture is low, then active observation may be the recommended approach and the patient’s aneurysm is regularly monitored. The patient may also be put on blood-lowering medication and asked to make changes to their lifestyle, such as quitting smoking or losing weight.
If the patient is at a high risk of aneurysm rupture, one of two main surgical procedures may be recommended that include neurosurgical clipping or endovascular coiling. These procedures cut off the blood flow to the aneurysm to prevent rupture using either a clip or a coil.
Brain Surgery (Cerebral Aneurysm) | Inside the OR
Neurosurgical clipping
Under general anesthesia, an incision is made in the skull and a small piece of bone is removed to allow access to the brain so that the aneurysm can be located. Using a microscope, the neurosurgeon isolates the vessel that is feeding the aneurysm and places a metal clip on the neck of the aneurysm to stop its blood supply.
The clip stays inside the patient and prevents the risk of any bleeding in the future. The bone segment is then replaced to close the scalp and the incision is stitched back up.
In cases where the aneurysm is particularly large, the artery in which the aneurysm has formed may be clipped instead. This is referred to as occlusion. In this case, a simultaneous bypass may also need to be performed and a blood vessel from another part of the body is used to direct blood flow around the clamp. Clipping has been shown to be very effective and, in general, clipped aneurysms do not return.
There have been significant advances in the fields of neurology, neurosurgery, and endovascular surgery. As a result, many surgeons can now carry out mini craniotomies or eye-brow incisions in order to place a clip on an aneurysm. Here, s small incision is made over the eyebrow, and a small window is made in the bone over the eye. A small clip is passed through the incision and is placed on the neck of the aneurysm.
Endovascular coiling
This procedure is also performed under general anesthesia. A thin tube or a catheter is passed through a blood vessel, usually in the groin, and guided towards the aneurysm in the brain. Tiny platinum coils are then used to fill the aneurysm until blood can no longer enter it, which prevents the aneurysm’s growth and rupture.
Additional devices such as a stent or balloon may be needed to hold the coils in place. In stent-assisted coiling, a stent is permanently placed in the vessel alongside the aneurysm to provide a support that holds the coils in place inside the aneurysm. For balloon remodelling, a removable balloon is temporarily placed next to the aneurysm while the coils are placed inside the aneurysm.
Patients who undergo treatment for an aneurysm need to stay in bed until the bleeding has stopped. Other conditions such as hypertension also need to be treated. Other treatments for the aneurysm include analgesics to prevent headaches and anticonvulsants to prevent seizures.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Feb 17, 2023