Endometrial scratching is a technique used to improve the ability of an embryo to implant in the uterus after in-vitro fertilization. It involves superficially wounding the lining of the womb, in order to improve the receptivity of the uterus to the embryo.
Why is Endometrial Scratching Used?
In 2005, the number of cycles of assisted reproductive techniques in the USA, Australia, New Zealand and Europe was more than 600,000, however, only ̴30% of these were successful. Embryo implantation is thought to be the most important factor influencing pregnancy.
Endometrial scratching is offered to women who fail to become pregnant after several failed rounds of IVF, despite transfer of good-quality embryos and without clear reason for their lack of success.
Although some studies suggest that endometrial scratching may double the chances of getting pregnant, conclusive scientific evidence on its benefits and knowledge of the underlying mechanisms is limited. Therefore, medical opinion is divided, and its use in patients undergoing IVF for the first time is not supported.
Endometrial biopsy. Image Credit: Corbac40 / Shutterstock
How Does Endometrial Scratching Work?
The endometrium is the layer of tissue that lines the inside of the womb. In order for a woman to fall pregnant, an embryo must attach to this lining (termed implantation). Implantation failure is considered to be the primary factor influencing human fertility and is usually attributed to a lack of uterine receptivity.
It is not clear exactly how endometrial scratching works, but it is thought that scratching the uterine lining may induce an inflammatory response, similar to that of a scratch to the skin. The subsequent repair process may improve the chances of implantation by:
- The release of growth factors, hormones and proinflammatory cytokines, which make the newly-formed lining more receptive to an implanting embryo
- Activating genes that are important for preparation of the endometrium, which may not otherwise be turned on, at the time of attempted implantation.
Mechanical disruption to the endometrium has been shown to modulate the genetic expression of factors important for implantation, including laminin alpha 4, integrin alpha 6, matrix metalloproteinase 1 and glycodelin A.
When is Endometrial Scratching Performed?
The optimum time for a woman to undergo this procedure is during the second of the cycle before IVF treatment begins.
The Procedure
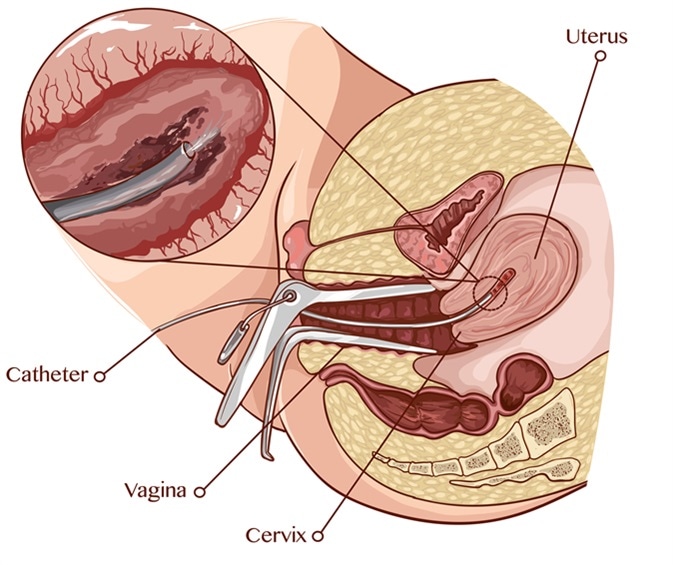
Endometrial scratching is simple, low-cost, minimally invasive, and only takes 15-20 minutes. It is performed at an outpatient appointment and is the same method used to gain a sample from an endometrial biopsy.
A flexible catheter, 3mm wide, is inserted through the cervix, into the cavity of the uterus then moved back and forth and rotated in order to cause some disruption to the uterine lining.
Potential Adverse Effects
In general, endometrial scratching is a safe procedure. It does not require anaesthetic. Potential side effects include:
- Mild bleeding
- Abdominal cramps for a short time after
- Pelvic infection or uterine perforation, in rare cases
- Disruption of an early pregnancy, particularly if conducted in the second half of the menstrual cycle
Pelvic infection results from the spreading of an infection from the cervix to the uterine cavity. This may become apparent up to 10 days following the procedure. It is recommended that women are screened for chlamydia prior to endometrial scratching.
Evidence for Performing Endometrial Scratching
Animal studies have shown an enhancement of endometrial receptivity from endometrial scratching. Human trials, on the other hand, have shown conflicting results.
This is probably due to differences in the population studied, the device used for scratching, timing of injury (luteal or follicular phase), and frequency. Each of these factors may impact the success or failure of implantation attempts.
A Cochrane review of nine randomized trials including 1512 women with unexplained subfertility suggested an overall benefit from endometrial scratching. However, the review also stated significant limitations to the included studies, and cautioned against drawing confident conclusions from these findings. The authors also emphasised the importance of balancing the possible benefits against the potential risks. More research is needed in order to determine whether endometrial scratching significantly improves the chances of pregnancy with IVF.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jul 21, 2023