Fibromyalgia is a condition that is characterized by widespread pain, whereas bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa (small, fluid-filled sacs in joint spaces. While the two conditions are distinct from one another, they are sometimes seen concomitantly. In some cases, the conditions can be confused for one another.

Credit: Zerbor / Shutterstock
What is fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition that causes widespread pain that can feel like aching or burning and fatigue that can range from tiredness to exhaustion similar to that brought on by flu. Fatigue can set in suddenly, and the pain can vary in severity over time. Stress levels can affect how severely symptoms present themselves.
The symptoms of fibromyalgia include:
- Widespread pain, including extreme sensitivity to touch
- Not feeling refreshed from sleep
- Headaches and migraines
- Irritable bowel
- Frequent diarrhea or constipation
- Tendency to mix up words
- Difficulties concentrating
- Memory problems
- Dizziness
- Clumsiness
- Sensitivity to noise, bright lights, smoke, and changes in weather.
Other symptoms can include painful periods in women, anxiety, depression, restless leg syndrome, paresthesias of the hands and feet (pins and needles), and difficulties in regulating body temperature.
Fibromyalgia is much more common in women than men.
The exact cause of fibromyalgia is unknown. However, several factors have been identified that may contribute to the development of the syndrome. Changes in chemicals in the central nervous system, and the way the central nervous system sends pain messages throughout the body could be the reason for the widespread pain experienced by those living with the condition.
Low levels of the hormones serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine may also play a part in the condition, as these hormones are responsible for regulating mood, appetite, sleep, and stress responses.
Additionally, genetics could explain why certain people are more susceptible to developing the condition.
What is bursitis?
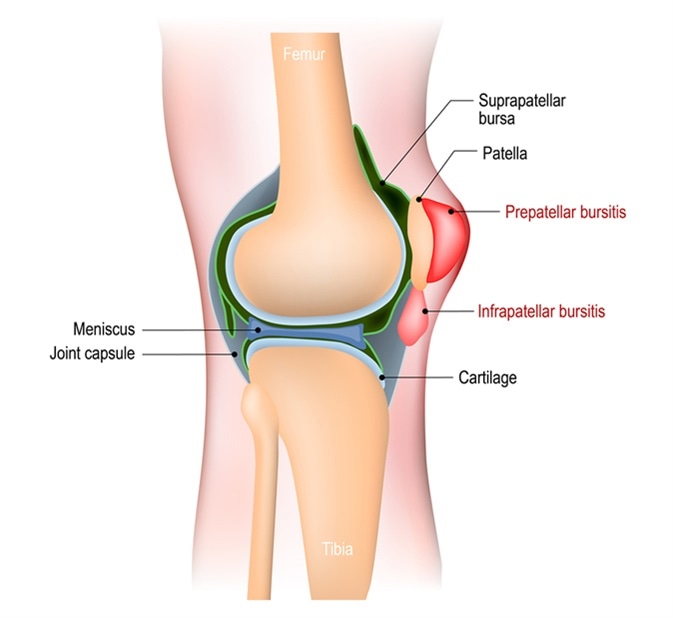
Bursitis is a condition affecting the fluid-filled sacs (bursae) found between the bones and soft tissues of the joints, which help to reduce friction in the joints. The synovial membrane, the outer lining of the bursae, becomes inflamed. Bursitis can affect any joint in the body. The most commonly affected joints include the shoulders, hips, elbows, knees, and heel.
Bursitis is characterized by warm, swollen, red, and painful joints. It can be caused by injury to the joint, repetitive use of the joint, over-exertion, and infection. Bursitis tends to be limited to single joints or a few joints, in contrast to fibromyalgia.
Bursitis. inflammation of bursae (synovial fluid). Image Credit: Designua / Shutterstock
Treatments for bursitis include rest, heat and ice packs, corticosteroid injections, NSAID medication to reduce pain and inflammation, and in the cases of septic bursitis, antibiotics. In rare cases, surgery is required to correct the problem.
Fibromyalgia-related bursitis
There have been reports of bursitis occurring in association with fibromyalgia. There are a number of painful soft-tissue conditions that are seen alongside fibromyalgia. Rotator cuff tendonitis, pes anserinus bursitis, and lateral epicondylitis are particularly common in patients with primary and secondary fibromyalgia, according to research.
Types of bursitis that have been reported in patients with fibromyalgia include:
- Olecranon bursitis – elbow bursitis affecting the bursa found at the tip of the elbow.
- Pes anserinus bursitis – bursitis affecting the bursa found beneath the knee on the inner side of the leg
- Subacromial bursitis – shoulder bursitis causing pain in the upper shoulder or upper third of the arm, limiting shoulder movement without pain
- Trochanteric bursitis – bursitis affecting the hip bursae.
Trochanteric bursitis is a common condition in patients living with fibromyalgia. Trochanteric bursitis develops when two particular bursae in the hip become inflamed. One bursa is located on the greater trochanter and the other, called the iliopsoas bursa, is found on the inside of the hip in the groin.
Typically, olecranon bursitis is seen less commonly in conjunction with fibromyalgia.
In one study of 554 patients with fibromyalgia, it was found that the patients reported a higher incidence of bursitis.
Summary
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread pain, and can exist in conjunction with additional soft tissue conditions like bursitis. Sometimes, the two conditions are confused for one another as they present similar symptoms. However, symptoms of bursitis are limited to pain in the affected joints, while fibromyalgia presents cognitive symptoms as well as difficulties with fatigue.
There is evidence that patients with fibromyalgia are more likely to experience soft tissue conditions like bursitis as an additional symptom of their primary syndrome. However, there is a lack of clinical studies investigating a link between the two conditions.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Mar 27, 2019