From NuvisanReviewed by Olivia Frost
This article is based on a poster originally authored by Benjamin Bader, Volker Badock, Katrin Nowak-Reppel, Roman C. Hillig, Martin Lange, Jörg Weiske, and Holger Steuber, which was presented at ELRIG Drug Discovery 2024 in affiliation with Nuvisan.
This poster is being hosted on this website in its raw form, without modifications. It has not undergone peer review but has been reviewed to meet AZoNetwork's editorial quality standards. The information contained is for informational purposes only and should not be considered validated by independent peer assessment.

Successful drug discovery relies on advanced technology platforms and comprehensive expertise across all disciplines in the value chain. As indicated by increasing attrition rates in drug discovery over the recent decades, various risks contribute to the success or failure of a drug discovery campaign.
Potential liabilities could be linked to the validation of the target and disease hypothesis, low druggability, unsuitable assay systems, false hit selection, missing target engagement, toxicology and safety issues, or lacking efficacy. This study examines the essentials based on experience from a biochemical and a cell-based HTS project.
Target significance
RAS-SOS1
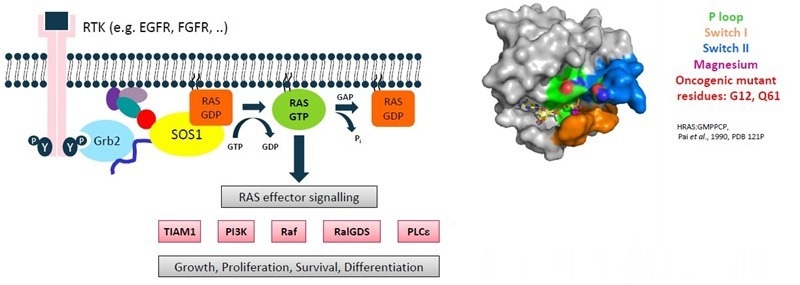
Figure 1. Target introduction. Image Credit: Benjamin Bader et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
- 3 RAS isoforms (H-, N-, K-RAS) act as molecular switches, oscillating between GDP- and GTP-state
- 30 % of human cancers feature RAS mutations (mainly positions 12 and 61) → render RAS constitutively active
- GxP binds with picomolar affinities, with millimolar concentrations in the cell → “undruggable target”
Hippo pathway (YAP1/TAZ)
- Physiological functions: Regulation of organ growth and size, cell proliferation and differentiation, embryogenesis, and tissue regeneration/wound healing
- Integration of upstream signaling, e.g., Wnt, GPCR, and RHO
- YAP1/TAZ are overexpressed in human cancers, interact with TEAD transcription factors, and activate target genes:
- Increased cell proliferation
- Resistance to apoptosis
- Induction of cell migration
- Therapeutic strategies that target dysregulated Hippo components could be promising approaches for the treatment of a wide spectrum of diseases
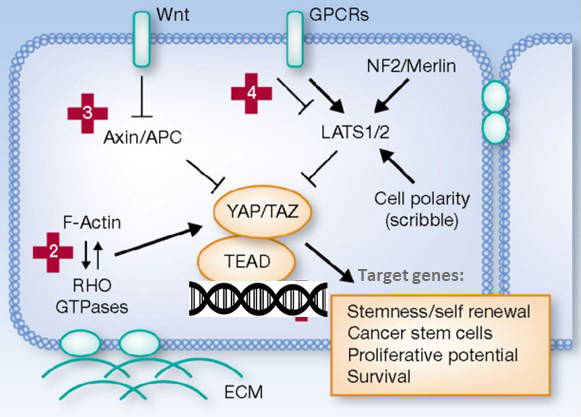
Image Credit: Adapted from Piccolo S et al., Clin Cancer Res, 2013
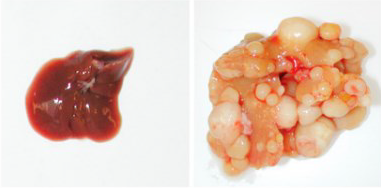
Induction of liver cancer by Yap1 overexpression in mouse. Image Credit: Liu-Chittenden Y et al., Genes Dev, 2012
Hit identification
Parallel hit finding: HTS and fragment screening
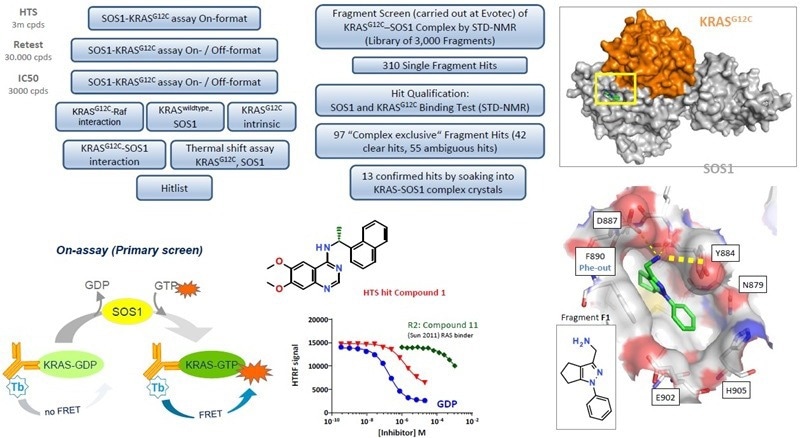
Image Credit: Benjamin Bader et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
Pathway screen with reporter cell line
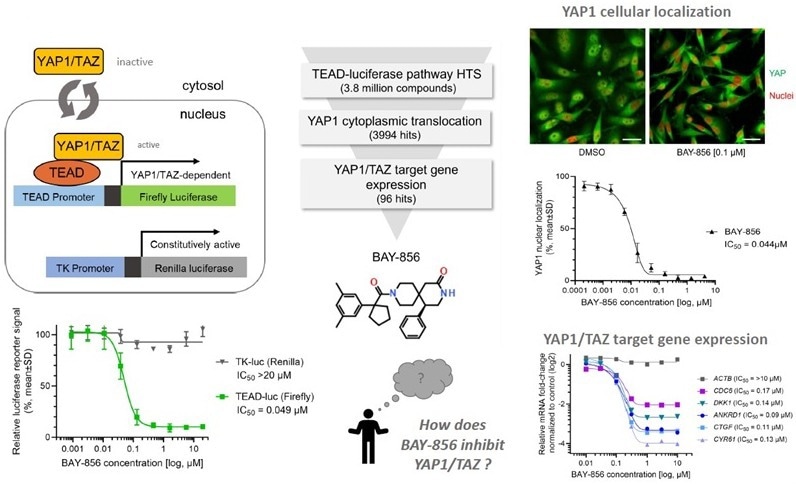
Image Credit: Benjamin Bader et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
Hit characterization & derisking
Target engagement & mode-of-action
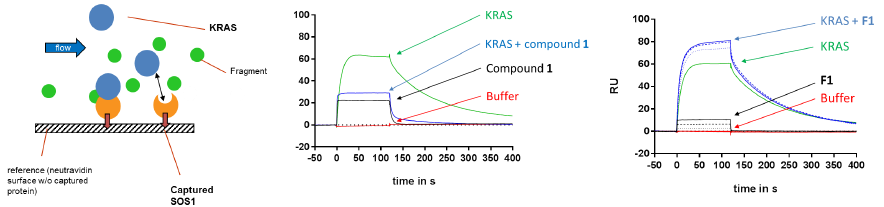
Surface-Plasmon-Resonance (SPR): Compound 1 is disrupting, but fragment 1 is stabilizing the KRAS-SOS1 interaction. Image Credit: Benjamin Bader et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
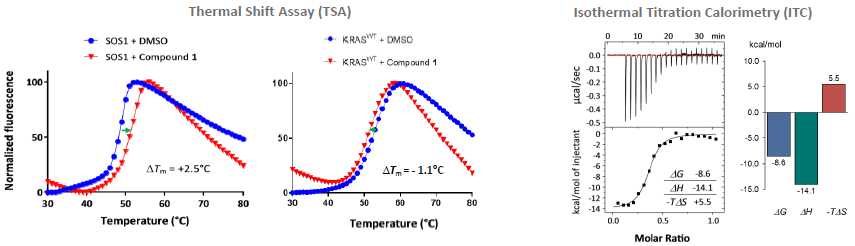
Thermal Shift Assay, Isothermal Titration calorimetry and native MS: Compound 1 identified as a SOS1 binder. Image Credit: Benjamin Bader et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
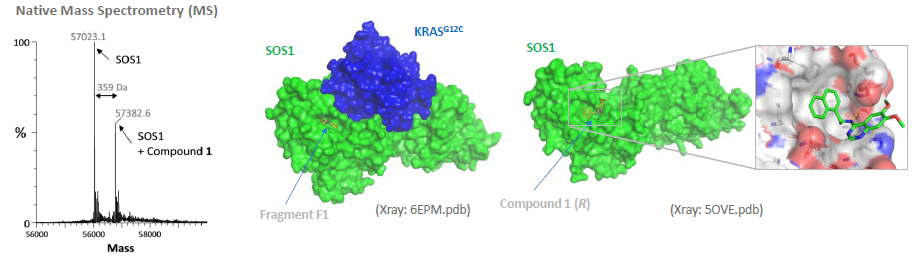
X-Ray: Fragment 1 and Compound 1 bind into same surface pocket of SOS1. Image Credit: Benjamin Bader et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
Target deconvolution: What is the direct target of BAY-856?
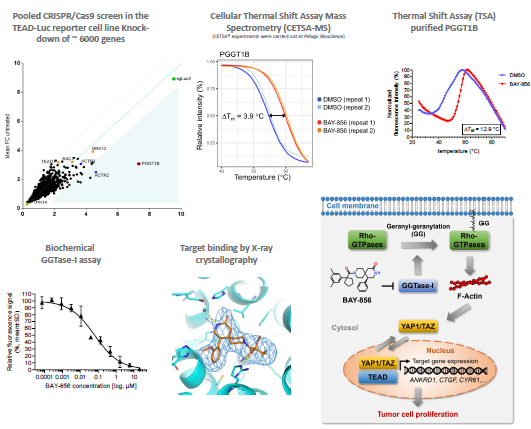
Image Credit: Benjamin Bader et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
Lessons
Success factors for biochemical screens:
- Employ multiple hit-finding approaches for targets with low druggability.
- Establish robust secondary and orthogonal assays for reliable hit validation.
- Confirm target engagement through biophysical methods.
- Integrate X-ray structural support early in the project.
Success factors for cell-based phenotypic/pathway screens:
- Include toxicity controls during primary and secondary HTS stages.
- Use well-established secondary and orthogonal assays for effective hit validation.
- Implement target deconvolution methods, such as CRISPR-KO, in silico models, and CETSA.
- Confirm target interaction with biochemical, biophysical, and X-ray techniques.
References
- Hillig, R.C., et al. (2019). Discovery of potent SOS1 inhibitors that block RAS activation via disruption of the RAS–SOS1 interaction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116(7), pp.2551–2560. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1812963116.
- Graham, Keith, et al. (2024). Discovery of YAP1/TAZ Pathway Inhibitors through Phenotypic Screening with Potent Anti-Tumor Activity via Blockade of Rho-GTPase Signaling. Cell Chemical Biology, March. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2024.02.013.
About Nuvisan
Your dedicated partner of choice
The NUVISAN group is a full-service contract research and development and manufacturing organization (CRO/CDMO) with state-of-the-art laboratories in Germany and France.
Our pharmaceutical, biotechnology, venture capital and non-profit clients partner with us because our high-quality end-to-end solutions and scientific expertise enable us to streamline and accelerate drug discovery and development – from ensuring target understanding to helping bring therapeutics to life.
Founded over 40 years ago by a team of pharma industry innovators, Nuvisan has built our reputation on a legacy of expertise and professionalism. Our team leaders have extensive experience in the biopharma industry, and our unique centres of excellence – for drug discovery in Berlin, topical dermatology in Sophia-Antipolis, and our bioanalysis hub in Neu-Ulm – enable our seasoned veterans to help guide and advance projects. We know how to discover, develop and bring the next generation of medicines to market. At the same time, we are committed to flexibility, transparency and collaboration in our approach, working closely with you to adapt to your individual needs, minimise risks, and help deliver your project.
About ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
The European Laboratory Research & Innovation Group (ELRIG) is a leading European not-for-profit organization that exists to provide outstanding scientific content to the life science community. The foundation of the organization is based on the use and application of automation, robotics and instrumentation in life science laboratories, but over time, we have evolved to respond to the needs of biopharma by developing scientific programmes that focus on cutting-edge research areas that have the potential to revolutionize drug discovery.
Comprised of a global community of over 12,000 life science professionals, participating in our events, whether it be at one of our scientific conferences or one of our networking meetings, will enable any of our community to exchange information, within disciplines and across academic and biopharmaceutical organizations, on an open access basis, as all our events are free-of-charge to attend!
Our values
Our values are to always ensure the highest quality of content and that content will be made readily accessible to all, and that we will always be an inclusive organization, serving a diverse scientific network. In addition, ELRIG will always be a volunteer led organization, run by and for the life sciences community, on a not-for-profit basis.
Our purpose
ELRIG is a company whose purpose is to bring the life science and drug discovery communities together to learn, share, connect, innovate and collaborate, on an open access basis. We achieve this through the provision of world class conferences, networking events, webinars and digital content.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.
Last Updated: Apr 4, 2025