Guillain-Barré syndrome is an autoimmune condition that can result in rapid and severe muscle weakness in a patient.
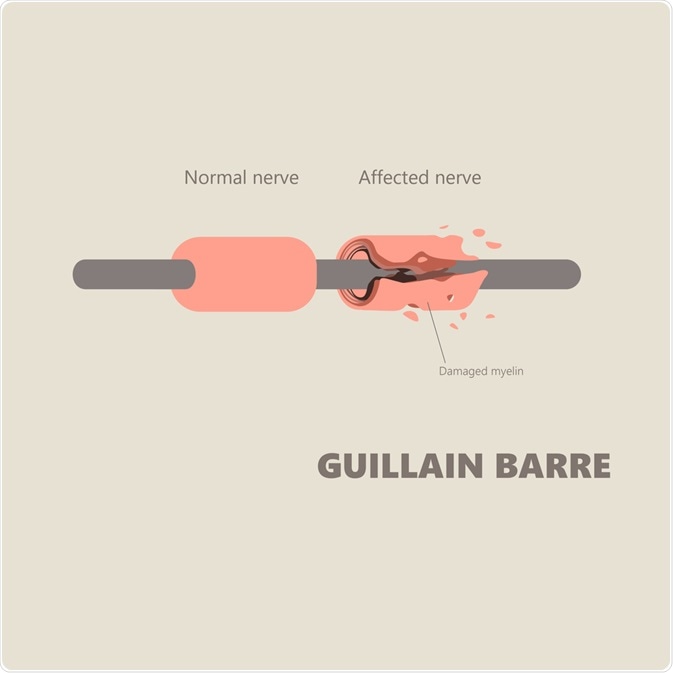
Image Credit: visona29 / Shutterstock.com
Incidence and diagnosis
This condition can affect people of all ages across the world. More specifically, both men and women can be affected by the condition equally, although the incidence of Guillain-Barré is higher in older people. The condition presents itself differently in patients and, depending on the subtype that affects each patient, their symptoms will vary.
Diagnosis of the syndrome can be difficult, as muscle weakness can be a symptom of many diseases. However, the onset of muscle weakness in Guillain-Barré syndrome is very quick.
Medical teams can carry out specific tests to help diagnose or rule out this syndrome. A lumbar puncture helps draw and test the cerebrospinal fluid of patients for their protein levels and white blood cell (WBC) counts. Additionally, a nerve conduction study can also be used by medical staff to assess the function of the nerve, whereas electromyography (EMG) helps to determine the health status of a muscle. The results of these tests help physicians in the diagnosis of Guillain-Barré syndrome.
A dedicated medical team uses various recovery techniques to improve the health of patients affected by Guillain-Barré syndrome. Recovery will take into account the fact that the syndrome is an autoimmune condition with the body attacking itself.
Plasmapheresis and intravenous immunoglobulins
Plasmapheresis and intravenous immunoglobulin administration are two types of immunotherapies that are used to treat Guillain-Barré.
The process of plasmapheresis involves removing the substances that are attacking the peripheral nervous system from the patient’s blood. The patient is connected to a device that removes some of their blood, extracts the plasma, and then puts the filtered blood cells back into the body. The blood cells go on to make more healthy plasma to replace the plasma that was removed. This process is useful for patients in the first four weeks of developing symptoms of the disease.
Comparatively, during intravenous immunoglobulin administration, immunoglobulins from blood donors are introduced into the bloodstream of patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. The introduction of these antibodies helps these patients to fight and eliminate the harmful antibodies that attack their bodies. The patient is given immunoglobulin injections for five consecutive days in order to treat the syndrome.
Both these immunotherapy techniques have similar effects on patients and encourage the patient’s immune systems to fight the syndrome.
Guillain Barre Syndrome: Mayo Clinic Radio
Breathing
If the patient’s breathing has been compromised by the syndrome affecting the muscles that help them to breathe, they can have the assistance of a mechanical respiratory machine inserted into the windpipe. This helps by performing breathing on the patient’s behalf and by keeping oxygen levels up, as low O2 levels can be fatal.
The patient may need to have an extended stay in the hospital to recover from their disease. This may also involve some periods in intensive care. Treatment can take months, depending on how severely a patient has been affected.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Dec 22, 2022