Lyme disease is caused by Borrelia burgdorferi, a bacterium carried in the gut of certain ticks. When these infected ticks attach to the human body (often in armpits, groin, scalp, or other hairy, hidden body areas), they slowly feed, and within 36-48 hours they may transmit B. burgdorferi to their human host. Young ticks are especially abundant and are seeking hosts in late spring and early summer, although adult ticks can transmit infection as well.
Lyme disease occurs in temperate forested regions of Europe and Asia and in the northeastern, north central, and Pacific coastal regions of North America. Transmission has not been documented in the tropics. In the eastern United States, Lyme disease is transmitted by the bite of the blacklegged tick Ixodes scapularis. The life cycle of the blacklegged tick progresses through four stages: eggs, larvae, nymphs, and adults. Larval and nymphal ticks become infected by feeding on infected small animals like white-footed mice. Nymphal and sometimes adult ticks feed on humans and if infected, may transmit the bacterium that causes Lyme disease. Tick larvae are not thought to be important in the transmission of Lyme disease to humans. Transmission from infected ticks does not occur until a tick has been attached and feeding for at least 24-36 hours. Person-to-person spread of Lyme disease does not occur. Transmission from an infected pregnant woman to her fetus is extremely rare.
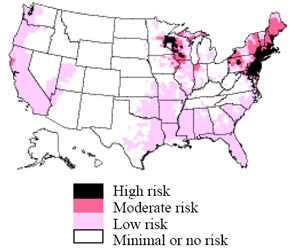 |
| This map demonstrates an approximate distribution of predicted Lyme disease risk in the United States. The true relative risk in any given county compared with other counties might differ from that shown here and might change from year to year. |
Lyme disease is still mistaken for other ailments, and it continues to pose many other challenges, including the following;
- It can be difficult to diagnose
- It can be troublesome to treat in its later phases
- A number of different ticks can transmit diseases with symptoms similar to Lyme disease
- Deer ticks can transmit diseases other than Lyme disease
Borrelia burgdorferi
Borrelia burgdorferi bacterium belongs to a group of bacteria, called spirochetes, whose appearance resembles a coiled spring. Borreliae are very small and can not be seen without a microscope.
 |
| Borrelia burgdorferi |
Ixodes scapularis
Three diseases, Lyme disease, caused by Borrelia burgdorferi, human babesiosis, caused by a protozoan, Babesia microti, and human granulocytic ehrlichiosis (a bacterial infection) are spread by the bite of Ixodes scapularis. This tick is found from coastal Maine through the mid-Atlantic states and in several north central states, particularly Wisconsin and Minnesota. This tick is also found throughout the southeastern United States. In the southeast, few Ixodes scapularis have been found infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. On the Pacific coast, particularly northern California, Lyme disease is spread by the western blacklegged tick, Ixodes scapularis.
 |
| Left to right: larva, nymph, male and female Ixodes scapularis, and male and female of Dermacentor variabilis. |
 |
| Actual sizes with addition of engorged female Ixodes |
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jun 25, 2019