Many techniques have been explored to detect breast cancer in women in a timely and accurate manner. Recently, research has been carried out on microwave imaging (MWI) of the breast.
 Xray Computer | Shutterstock
Xray Computer | Shutterstock
The basis of microwave imaging is the difference in the resistance to electrical current through normal and tumorous tissue. Many studies have focused on the ability of microwaves to pick out the difference between a cancerous area and normal breast tissue using dielectric properties, using simulations. They have been found to produce a clear and adequate reconstruction of breast tissue in most situations.
How does microwave imaging compare to mammography?
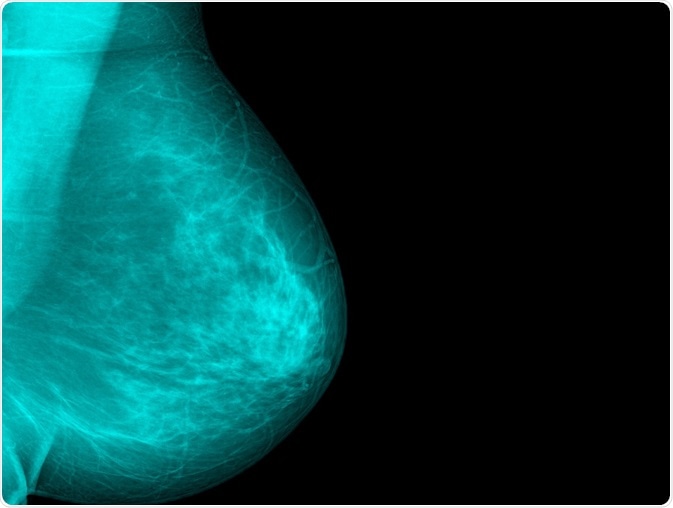
Mammography achieves good resolution in breast imaging, and is therefore the most sensitive way to detect a tumor which is non-palpable, but at the cost of using radiation at higher frequencies.
In the case of microwave imaging (MWI), the wavelength used is much longer, with frequencies of 1-30 Hz. Though this reduces the resolution as compared to X-ray mammography, MWI is not associated with tissue damage.
MWI is performed by using antennas that generate microwave energy. These are arranged in a specific array around the breast, so that they can pass through the breast tissue. The difference in the ease of passage of electric current through the healthy breast tissue vs malignant tissue is significant enough to generate sufficient contrast in the images to detect cancers.
Another advantage of microwave imaging is that microwave energy can be scattered by the dielectric contrast, which enables it to be sensed by the same set of detectors, dispensing with the need for a separate sensor. This allows the breast tissue to be mapped according to its reflectivity, and this leads to tumor identification. The challenge lies in refining the technology to achieve greater precision and contrast as well as higher resolution, which would make it a go-to technology in this field.
What happens in microwave imaging?
In the current prototypes, the patient does not have to undergo breast flattening to ensure better imaging, which is an often-cited reason for reluctance to undergo X-ray mammography. Instead, after informed consent is obtained, the patient is placed in a prone position on a specially designed bed, which has a cup-shaped depression into which the breast is inserted. The posture not only makes it easier to image the breast, but reduces the appearance of artefacts due to respiratory movements.
Before the examination begins, the imaging system is prepared and calibrated, and a carefully chosen liquid coupling material is used to provide a seamless interface between the microwaves and the skin overlying the breast. Coupling fluid may also be dispensed without any major reduction in imaging quality.
One challenge that remains to be overcome by new prototypes is the irregular outline of the human female breast as compared to the regular models used in simulation studies. It is thought that this issue could be overcome by using a low level vacuum to make sure the breast is in contact with multiple sensors around the examination cavity, and this in turn ensures that the imaging will be complete and uniform.
Significant differences in human breast size may be overcome by a cylindrical arrangement of antennas which can be adjusted to any size, besides obviating the use of complex devices to change antenna alignment.
Once the patient and the equipment are ready, a computerized data acquisition is performed while an operator observes the process from a nearby room. This takes only a few minutes. The data is then transmitted to a secure software server for reconstruction and image analysis, before a diagnosis is made.
Such devices are being clinically tested and show that MWI is an efficient alternative to X-ray mammography for breast cancer screening, as well as being more comfortable for the patient.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Feb 13, 2023