Modifying the diet and nutritional intake of individuals with motor neuron disease (MND) is paramount in managing the disorder. Symptoms of muscle weakness and stiffness of the muscles of the hands, arms, face, jaw and those used for swallowing, lead to difficulty with eating sufficient food. In addition, the increased energy expenditure caused by twitching muscles requires a 10-20% higher calorie consumption. This higher metabolic demand, combined with a compromised calorie intake, commonly leads to malnutrition and weight loss.
Malnutrition can exacerbate the breakdown of muscles, increase vulnerability to infection, and reduce the life expectancy. Dietary supplements are therefore important in ensuring that patients maintain a healthy weight. Supplements can be used as sustenance, to maintain sufficient calorie and nutrient intake. They can also be taken as a treatment, to prolong the progression of the disorder.
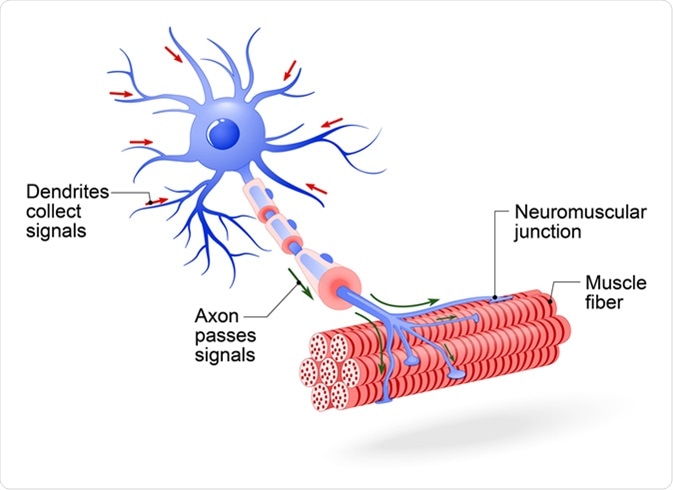
Structure of motor neuron. Image Credit: Designua / Shutterstock
Supplements for Nutritional Sustenance
A dietician can assess the nutritional needs of an individual with MND. This helps formulate recommendations on how to minimize weight loss and improve the individual’s nutrient intake in a way that is manageable. A healthy diet enriched with carbohydrates, fats and proteins is advised to achieve the required caloric intake.
Supplements may be advised for those who have lost weight, or have difficulties swallowing, chewing, or eating enough food. These can be taken in place of, or in addition to food, and include:
- Tablets
- Liquids: milk- or juice-based
- Powders: protein or glucose powders
- Energy bars
Supplements for Treatment
Supplements are often taken over the counter for treatment within the MND population; around 75% of patients report taking them. Despite the absence of clinical research evidence, many individuals continue to do so, based on anecdotal reports of their potential efficacy. The ease of availability of these supplements and the progressive nature of the disease entices individuals with MND to pursue them as a therapeutic avenue.
The supplements used often claim to combat some specific causes of motor neuron cell death, including:
- Oxidative stress
- Inflammation
- Mitochondrial dysfunction
- Neuron excitotoxicity (the death of neurons caused by over activation by the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate)
Vitamin E
This antioxidant is one of the most popular supplements used among individuals with MND. It reduces free radicals which cause neuron cell damage, a possible cause for MND. It has been suggested that Vitamin E is neuroprotective and reduces the chance of developing the disorder.
B Vitamins (Folic Acid, B6, B12)
Individuals with MND have elevated levels of homocysteine, which is involved in the formation of free radicals and oxidative stress. Folic acid and vitamin B12 convert homocysteine into methionine, while vitamin B6 converts it into sulfur amino acids, reducing homocysteine levels.
Creatine
It is suggested that creatine, a nitrogenous organic acid that takes part in cellular energy production, has neuroprotective properties, limits the uptake of glutamate into neurons, and stabilizes the mitochondrial membrane.
Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10 is a component of the mitochondrial electron transport chain and important in cellular energy production. It is an antioxidant which reduces free radical oxidation damage in cells.
Other potential supplements with antioxidant properties include:
- Zinc
- Melatonin
- L-Carnitine
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D (which also has anti-inflammatory properties)
- Catechins
While there is a large amount of anecdotal evidence for the use of these supplements, there is a lack of clinical data supporting their efficacy as a treatment for MND. Further research should also aim to investigate the effect of taking several supplements simultaneously, like many patients do. It is critical that any individual with MND consults a physician or neurologist prior to adjusting their diet.
Last Updated: Jul 17, 2023