Radiation therapy is a technique often used in the treatment of cancer, particularly when the tumor is confined to a certain area in the body that can be physically targeted.
The mechanism of radiation therapy is effective as a treatment for cancer, as it damages the DNA or genes that are responsible for the replication or growth of cells. This is an important aspect of treatment, due to the specific characteristics of cancer pathophysiology.
 Woman receiving radiation therapy for cancer treatment. Image Credit: Mark_Kostich / Shutterstock.com
Woman receiving radiation therapy for cancer treatment. Image Credit: Mark_Kostich / Shutterstock.com
Cell cycles and cancer pathophysiology
In the normal cell cycle, there a five phases of cell replication which are as follows:
- G0 phase, the normal resting state
- G1 phase, RNA and proteins are produced in preparation for cell division
- S phase, DNA is produced in preparation for cell division
- G2 phase, cell structurally prepares to divide
- M phase, mitosis occurs as the cell splits in half to form two identical cells
These phases exist in most types of cells, both those normally found in the body and cancerous cells that cause tumors in the body.
Cancer cells have mutations that make them behave differently from normal cells and tend to divide more often, as they move through the replication phases more quickly. As a result, these cells have a tendency to grow out of control and take over the body where normal cells usually reside.
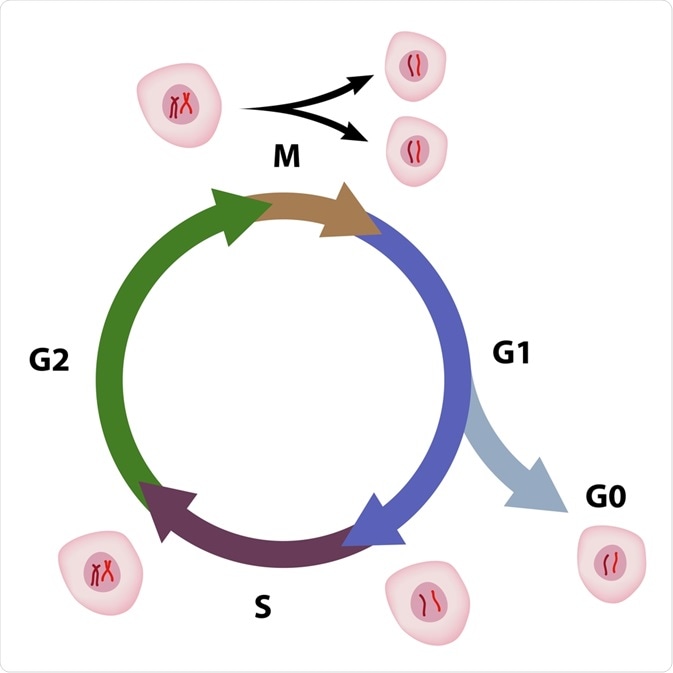 The cell cycle. Image Credit: Alila Medical Media / Shutterstock.com
The cell cycle. Image Credit: Alila Medical Media / Shutterstock.com
Mechanism of action
Radiation therapy uses particles or waves moving at a high frequency to target the DNA of cells in the body and change the way they are able to replicate. If the DNA required for mitosis and replication is damaged, the cells are unable to replicate as usual and the growth of a cancerous tumor is inhibited.
This type of therapy manipulates the fact that cancerous cells usually replicate more quickly than normal cells in the body. As the DNA can only be damaged when the cells are undertaking the replication process – not in the G0 phase – the majority of normal cells that take longer to replicate are less affected than the cancerous cells.
There are two main types of radiation therapy: photon radiation and particle radiation. Each of these works in a specific way, which will be covered in more detail below.
Photon radiation
This is the most common form of radiation used in the treatment of cancer and involves a beam of high-energy photons. The radiation is produced from a radioactive source such as cobalt or cesium, or with the use of a linear accelerator machine.
The photon beam is then directed towards the location of the tumor in the body, passes through the cancerous cells and exits from the other side of the body. The high energy of the photons that pass through the body allows them to break the DNA bonds and inhibit the replication of cells.
What is radiotherapy and how does it work? | Cancer Research UK
Particle radiation
Electron, proton and neutron particle beams can also be used to irradiate areas of the body and damage the replication process of cancerous cells.
Electron beams produced by a linear accelerator can effectively treat tumors and lymph nodes that are near the surface of the body, as their low energy level doesn’t allow them to penetrate deep within the body.
Proton beams are believed to emit their energy to tissue at the end of their path, without causing great damage to the tissues they previously travelled through. This is less commonly used in practice, as it needs more research to determine the optimal method of use and requires highly specialized medical equipment.
Neutron beams can be a useful alternative when standard radiation therapy does not work effectively. It is often used in cancer of the head, neck and prostate, however is not usually the first line choice of therapy as it is difficult to target the beam and surrounding tissues can easily be affected.
Additionally, alpha and beta particles can be used in the treatment of cancer, although they are more commonly used in medical imaging. Radiation with carbon ions provides an option for tumors that do not respond to conventional radiotherapy. This is a heavier particle and can therefore do more damage than other radiation types, particularly on the cancer cell where it finishes its path but also on the surrounding tissues.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Feb 3, 2021