A digital rectal examination (DRE) is one of the simplest methods for assessing the state of the prostate gland. This may be performed as part of a routine check of the prostate gland or in the case of symptoms such as severe constipation, bleeding or pain from the anus or bowel incontinence.
The DRE process
Although the procedure is not usually painful, it can be uncomfortable and a local anesthetic may be applied in the form of a gel or a cream to numb the area. In the case of particularly apprehensive individuals, a sedative may be administered.
The test is performed by a nurse or doctor. The patient is asked to remove their lower garments and lie on their left side with their knees drawn up to the chest. Women who undergo the procedure may be asked to lie on their backs with their legs raised.
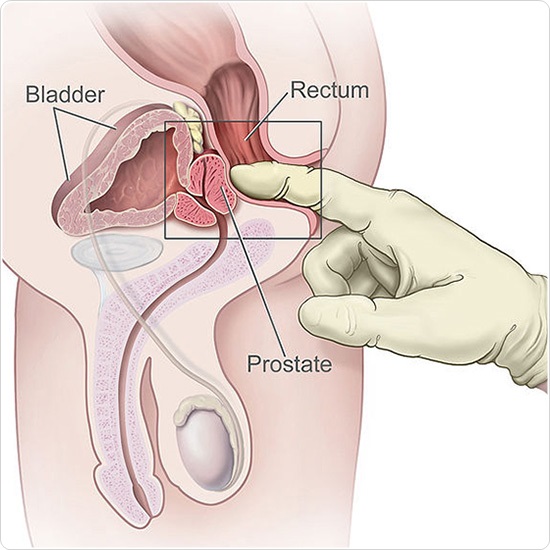
The examination begins with a careful check of the area and skin around the anus to check for symptoms such as rashes, bleeding, warts, tearing or fissures and swollen blood vessels. The nurse or doctor then inserts a gloved and lubricated finger, usually the index finger, into the rectum and the patient is asked to squeeze their anus to test the strength of their anal sphincter muscles. The finger is then pressed against the front wall of the rectum to feel the prostate gland.
If the prostate is healthy, it feels smooth, while an enlarged prostate may be felt as a bulge. If the prostate is enlarged, it will still feel smooth in the case of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) but if cancer is present, the gland may feel hard and lumpy. The prostate may be painful when squeezed if it is inflamed or infected. The whole test may take around five minutes.
DRE only forms part of the testing performed in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. The examination is not specific for prostate cancer and is used in combination with a blood test to check for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level, a biomarker for prostate cancer, as well as a biopsy to check prostate tissue for the presence of cancer cells. DRE is also performed as a way of monitoring individuals who have already been diagnosed with prostate cancer, to check for changes that may indicate recurrence of the cancer after treatment.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jan 2, 2023