The root canal treatment procedure, also known as endodontic treatment, is a common procedure in modern dentistry that is used to remove inflamed or infected tissue from inside a tooth.
Beneath the enamel and dentin layer of teeth, a type of soft tissue referred to as pulp is found inside each tooth. The pulp contains blood vessels, nerves and connective tissue. This pulp is essential for the growth and development of a tooth, although it is possible for a fully developed tooth to exist without it because it can obtain nourishment from the surrounding tissues.
A root canal procedure involves the removal of pulp that is infected or inflamed. The pulp chamber and root canal are completely cleaned out and refilled to protect the area from further damage.
Root canal treatment. Image Credit: Alila Medical Media / Shutterstock
Indications for Root Canal Treatment
The root canal treatment procedure is a good solution with many potential benefits for patients who have significant inflammation or infection in the pulp of a tooth. Without treatment, the infection may progress to cause significant pain or cause the formation of an abscess underneath the tooth, which affects the strength and function of the tooth.
Root canal treatment can help to maintain the function of the teeth so that patients may continue to chew effectively using normal biting force. It also helps to maintain the natural aesthetic appearance of the tooth, in contrast to alternative options, such as dental implants. Additionally, root canal treatment can help to protect other teeth in the mouth from excessive strain and possible damage, as may occur if only one side of the mouth is used.
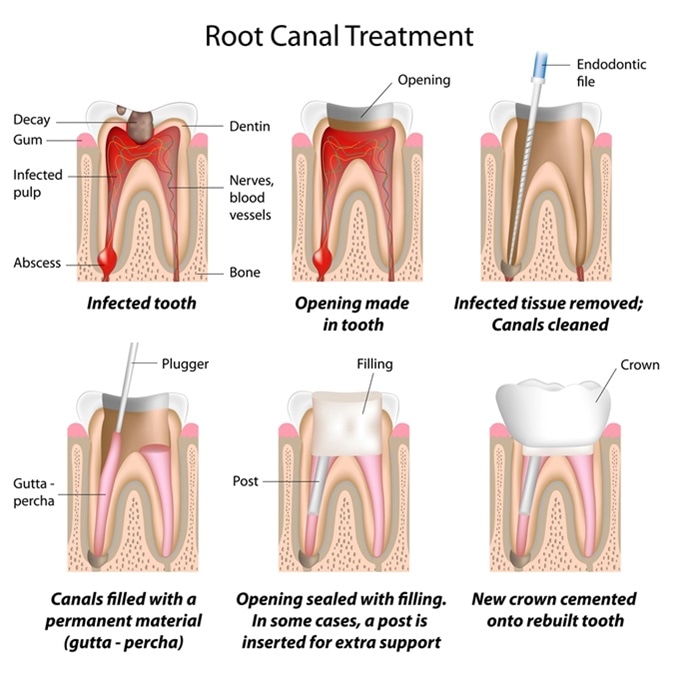
Step-by-Step Root Canal Procedure
The first step in the root canal treatment is making an examination of the tooth so that the dentist understands the nature of the problem and is able to treat it effectively. This typically involves a physical examination of the inside of the mouth, in addition to X-ray imaging of the tooth to visualize the pulp chamber.
Molar Root Canal: Start to Finish
Next, a local anesthetic is administered to numb the tooth and increase the comfort of the patient during the procedure. A “dental dam” – a small protective sheet – is then put in place over the affected area to isolate the tooth and keep saliva and other substances away from it while the work is completed.
The dentist is then able to drill into the crown of the tooth to open it. This allows specialized dental instruments to be inserted into the pulp chamber and root canals to clean the inflamed or infected pulp from the area. The remaining space is then cleaned completely and shaped to make space for a filling, which will replace the pulp in the tooth.
The root canal can then be filled with a suitable biocompatible material, such as gutta-percha. Adhesive dental cement is also usually used to ensure that the root canal is properly sealed and to prevent future infections in the area.
Once the root canal has been filled, a temporary filling is usually put in place over the opening to seal it. Eventually, a crown is usually placed over the tooth to protect it over the long-term, but there is usually a waiting period between dental appointments while the crown is constructed. A temporary filling is useful during this time. At the subsequent dental appointment, the temporary filling can be removed and the tooth restored with a crown or other restoration.
Pain During the Procedure
The techniques used to perform a root canal have progressed significantly over recent decades. As a result, most patients now find that they are relatively comfortable while the procedure is being carried out and do not experience significant pain.
This is in large part due to the local anesthesia used during the procedure to numb the area. It may, in fact, bring relief to the patient, particularly if the pulp inflammation caused significant pain and thus brought about the need for a root canal treatment.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Feb 27, 2019