In most cases, seborrheic keratosis is not harmful to the health of the individual and treatment is not required. However, removal of the keratosis may be indicated in some circumstances, such as if it becomes irritated or bleeds when rubbed. Patients may also sometimes wish for it to be removed if they do not like the way they appear on their skin.
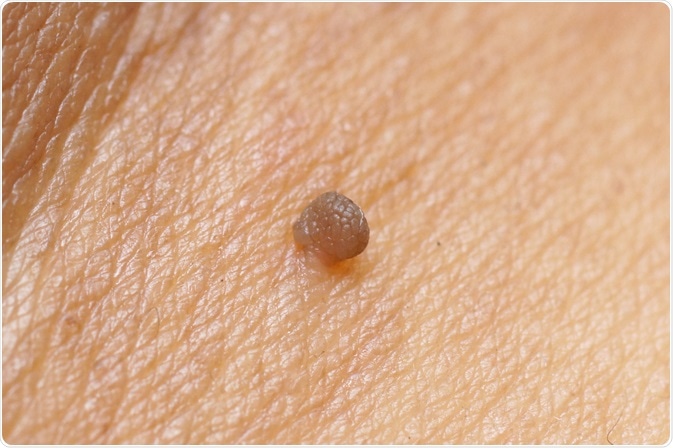
Image Credit: wk1003mike / Shutterstock
There are various options that may be used in the treatment and removal of seborrheic keratosis. Some of the most common techniques are discussed in more detail below.
Topical Agents
Topical creams can sometimes be used to reduce the height of bumps resulting from seborrheic keratosis. Examples of topical agents include:
- Ammonium lactate
- Alpha hydroxyl acids
- Tazarotene cream
There are currently drugs in development that may be effective to completely remove smaller lesions. These act by inhibiting the Akt kinase activity, thereby causing the growths to self-destruct.
Cryosurgery
Cryosurgery is a technique that involves freezing the keratosis with liquid nitrogen. It can effectively remove many seborrheic keratoses, although it is most effective for smaller, thinner growths. Additionally, it may cause some lightening of the skin in the treated area. This technique can sometimes also be used in conjunction with curettage, which generally yields a more positive outcome.
Curettage
Curettage involves scraping of the skin surface with a curette to remove small or thin growths. It can also be used in conjunction with other techniques, such as cryosurgery or electrocautery, to burn and then remove the growth.
Electrocautery
Electrocautery involves burning the growth with an electric current. It is often followed by curettage to remove the seborrheic keratosis. In general, this technique can take more time than other methods of removal and it may also leave a scar if it is not carried out correctly.
Laser Ablation
Laser ablation involves the vaporization of the growth with a laser beam. There are different types of laser treatments that may be used. For example, a topical pigment may be applied to the growth to direct the laser beam towards it, in this way, increasing the efficacy.
Treatment Outcomes
After the successful removal of a seborrheic keratosis, it is unlikely for the growth to reappear in the same place. However, patients should be aware that they are more likely to be affected by new growths in other areas of the body.
Additionally, this skin, at the removal site, may be a shade lighter than the healthy skin in the same area. In most cases, this difference fades with time, although it can be permanent.
Follow-Up
It is important for patients who have had seborrheic keratosis to continue monitoring their skin for any changes that may present in the future. This is because they are at an increased risk for the development of malignant skin tumors in other areas of the body.
Therefore, patients should be encouraged to perform regular skin checks of their own accord, in addition to annual skin checks with a dermatologist to assess changes to the skin.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Apr 9, 2021