The vocal cords comprise two thin flexible bands of muscle tissue that are stretched across the inside of the voice box. Lesions on these vocal cords are a common cause of voice disorders. Benign lesions of the vocal cords are non-cancerous, whereas abnormal growths fall into three main categories including nodules, polyps, and cysts.
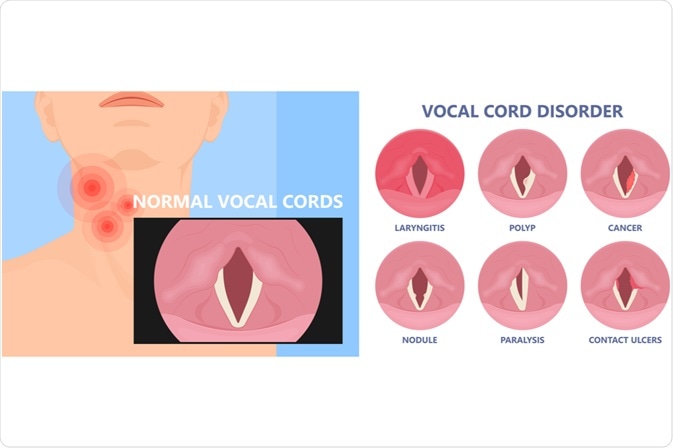
Image Credit: rumruay / Shutterstock.com
Vocal cord lesions often occur as a result of the voice being misused or overused by screaming, shouting, or trying to talk during an attack of laryngitis. Many of these lesions occur in people who rely on their voice such as professional singers, cheerleaders, or salespeople.
Symptoms
The earliest symptoms of a lesion on the vocal cord often include a change in the voice quality and persistent hoarseness. Depending on the size of the lesion and where it is located, signs and symptoms can vary significantly.
Some additional examples of the signs and symptoms associated with vocal cord lesions include:
- Unpredictable voice failure
- A delay before the voice emerges
- A downward change in the pitch of the voice
- A low raspy or rough voice
- Vocal fatigue, where the voice tires quickly with its use
- Frequent clearing of the throat
- The need for increased effort while speaking
- A loss of the ability to reach a high note, especially when singing softly
Diagnosis
When a person develops hoarseness or other symptoms of a voice cord lesion, the individual may be referred to an otolaryngologist, which is a specialist in disorders of the ear, nose, and throat. Diagnosis of the problem requires a full history of the voice problem and the way the voice is used, as well as an evaluation of the way the patient speaks.
The following are important factors that the doctor will take into consideration:
- Time of onset of symptoms
- Other symptoms or signs that accompany the onset of hoarseness, such as a respiratory tract infection
- The presence or absence of vocal fatigue
- Whether there is waxing or waning of the symptoms with the time of day
- Pain during speaking or singing
- Limitations of the singing range
- The presence of voice breaks especially while singing a particular note
- Previous medical history
- The use of any medications
In addition, a thorough examination will be made of the vocal cords, usually with the help of a laryngoscope and a stroboscopic light source. This involves the use of an endoscope being passed through the patient’s mouth and into the throat so that the voice box can be visualized. The light source enables the vibration of the vocal cords to be assessed.
The appearance and location of the vocal cord lesions will be carefully noted and, if required, a biopsy may be taken from the lesion.
Other investigations may be ordered to rule out the presence of exacerbating factors such as hypothyroidism or allergies.
Sometimes, the patient is advised to completely rest the voice, which means no singing, talking, or even whispering before undergoing a second examination to determine if this has led to any improvement in the lesion. The otolaryngologist will also ensure that other problems which may be affecting the voice, such as acid reflux, medication use, allergies, or hormonal balances, are also addressed.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Nov 2, 2022