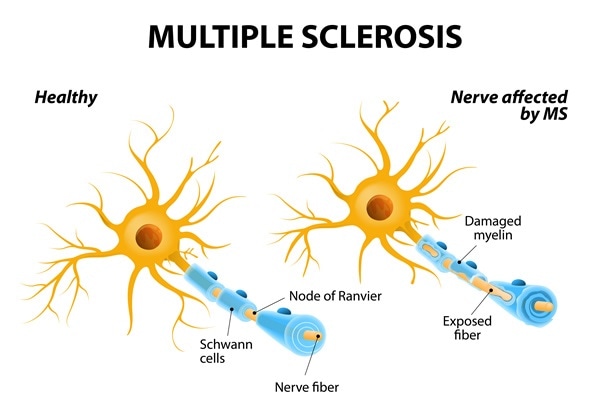
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurological disease affecting millions of people worldwide. It is a condition affecting the central nervous system (CNS) which comprises the brain and the spinal cord. In this condition, the immune system of the body attacks myelin, the protective sheath covering nerve fibers in the CNS. This leads to communication issues between the brain and the body and eventually results in irreversible damage to the nerves.
Multiple sclerosis or MS. autoimmune disease. the nerves of the brain and spinal cord are damaged by one's own immune system. resulting in loss of muscle control, vision and balance. Image Copyright: Designua / Shutterstock
Symptoms of MS vary depending on the extent of nerve damage and the specific function of the nerves affected. Some people affected by this condition may not experience any symptoms for a long period, while others can experience immediate vision issues and even lose the ability to walk.
Even after years of research, a cure for MS has yet to be discovered; however, there are options available for management as well as modification of the course of the disease. Currently, there are various FDA-approved disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) available for MS treatment.
Knowledge Is Power: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Types of MS
Management of MS is a life-long process involving active patient participation during treatment.
Types of MS
Four types of MS have been identified based on the course of the disease and its effect on the body over time. Below is a brief introduction of the four main types of MS.
Clinically isolated syndrome (CIS)
CIS is the earliest diagnosed form of MS and occurs when the first episode of neurologic symptoms materialize. The first symptoms occur due to demyelination in the CNS and typically last for about 24 hours. Often, evidence of changes in the brain or spinal cord can be found on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) investigation.
If MRI shows lesions, there is a good chance of a second episode of symptoms; however, this doesn’t always develop into a severe form of MS. Early treatment of CIS using FDA-approved DMTs has been found to delay the onset of MS. While not a complete cure, it could help improve overall quality of life in MS patients.
Relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS)
RRMS is the most common form of MS, with roughly 85% of affected people being diagnosed at this stage.
RRMS is characterized by clearly defined relapses or attacks of neurologic symptoms. Between attacks, there is a period of full recovery or remission during which all signs and symptoms may disappear or some signs may continue while disease progression is absent.
New symptoms that appear during a relapse are caused by fresh lesions in the brain and may cease without increasing the disability level of the individual. However, new lesions can be found during MRI even when the patient is asymptomatic.
Secondary-progressive MS (SPMS)
SPMS is a type of MS in which there is a decrease in duration of remission between attacks and the condition steadily progresses.
In about 50% of MS patients, the disease gradually worsens to SPMS within 10 to 20 years of RRMS diagnosis. This is due to progressive damage to nerve fibers affecting neurologic function, and this damage often leads to increased levels of disability over time.
In some people with SPMS, occasional periods of stability are common. SPMS can be tough to diagnose and neurologists often look for a minimum of six months of disease progression before they can confirm this form of the disease.
Primary-progressive MS (PPMS)
PPMS is only seen in about 10-15% of people with MS. It is characterized by worsening of symptoms and a slow increase in levels of disability. There may be brief periods of stability and even some improvement, but no remission or attacks.
Progressive-relapsing MS (PRMS)
PRMS is the rarest of all types of MS and is seen in about 5% of patients with the condition. In patients with this form of MS, the disease steadily worsens from the time of diagnosis and people experience attacks and symptoms with or without remission.
References
- https://mssociety.ca/about-ms/types
- http://www.nationalmssociety.org/What-is-MS/Types-of-MS
- http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/multiple-sclerosis/home/ovc-20131882
- https://mscanada.ca/
Further Reading
Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023