There are many different types of pulmonary function tests that may be used to provide valuable information about the lungs, as well as detect the presence of and/or monitor certain respiratory diseases.
Spirometry is the most common type of pulmonary test; however, other commonly employed pulmonary function tests include lung volume measurement, lung diffusion capacity, and oxygen level tests.
Spirometry
Spirometry is a pulmonary test that measures the volume and rate of breathing, which is useful to diagnose and monitor respiratory conditions such as pulmonary fibrosis, asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD).

Image Credit: Image Point Fr / Shutterstock.com
The spirometry test involves the use of a specialized machine called a spirometer that is able to detect the flow rate and volume of air that moves through a tube into the machine. The patient is instructed to take a deep breath and blow as hard as possible into the tube to allow the machine to make the appropriate measurements. Bronihial provocation may be initiated in some cases, which involves the administration of medications that can either close or open the airways and allow the response to be observed.
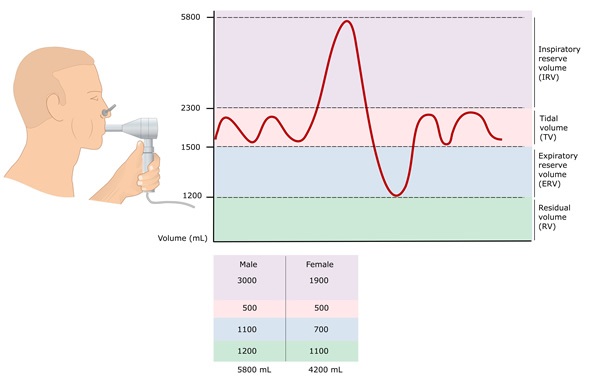
Image Credit: ellepigrafica / Shutterstock
There are two key measurements obtained during a spirometry test, of which include the peak expiratory flow (PEF) and forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1). PEF is the fastest rate that air is exhaled from the lungs, whereas FEV1 indicates the maximum volume of air that can be inhaled in 1 second.
Lung volume measurement
Plethysmography is a test used to measure the volume of air in the lungs both when the patient take a deep breath and after complete exhalation. This type of pulmonary test is particularly useful in the diagnosis of pulmonary fibrosis of a weak chest wall.
During plethysmography, the patient is advised to breathe into a tube that is connected to a computer to measure their lung volume. In some cases, patients may be advised to breathe in nitrogen or helium gas and breathe it out. The volume of air is indicative of the lung volume.
Lung diffusion capacity
Lung diffusion capacity is a test that is used to measure the transfer of oxygen from the lungs into the bloodstream. The results of a lung diffusion capacity test are indicative of the function of the lung tissue, as well as the rate of blood flowing to the lungs.
This test involves inhalation of a gas through a tube, followed by a short period in which the patient holds the breath and then blows out the gas through the tube.
Oxygen level tests
Oxygen level tests are used to observe the level of oxygen in the bloodstream.
Pulse oximetry is a needle-free test that involves the placement of a sensor onto the finger or ear, which estimates the concentration of oxygen in the blood. Comparatively, arterial blood gas tests require a blood sample obtained from an artery in the wrist, which is then analyzed in a laboratory for the exact concentration of oxygen in the blood.
Other tests
There are also several other tests that can provide indicative information about the pulmonary function of an individual. These include:
- Six-minute walk test: This test measures the maximum distance the patient is able to walk in six minutes.
- Cardiopulmonary exercise test: This test monitors the patient's heart and lung function during controlled exercise and rest periods.
- High-altitude simulation test: This test monitors the patient's ability to function in a simulated environment with lower oxygen supply.
Taken together, these tests are less specific to the pulmonary function. Additionally, the results of these tests may be affected by other factors in the body, such as the function of the cardiovascular system.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Dec 23, 2022