 Prescription medicines such as antibiotics require regulatory approval in the countries in which they are sold, but recent evidence indicates unapproved antibiotics are being distributed and are associated with increasing antibiotic resistance.
Prescription medicines such as antibiotics require regulatory approval in the countries in which they are sold, but recent evidence indicates unapproved antibiotics are being distributed and are associated with increasing antibiotic resistance.
 Credit: Fahroni/Shutterstock.com
Credit: Fahroni/Shutterstock.com
The central issue
Antibiotic resistance is on the rise globally, and can be of serious health concern. Since antibiotic introduction in the 20th century, they’ve been used successfully to curb the spread of bacterial diseases and saved countless lives. However, bacteria are very adaptable and some have become resistant to the actions of antibiotics. This has been acknowledged as a global crisis.
One cause for the rise in antibiotic resistance is that more antibiotics are being distributed. In the first decade of the 21st century, sales of antibiotics rose by 36% in 71 countries. Most of this increase (76%) was accounted for by five countries with rapid population growth, including India where consumption per capita was the highest. Unfortunately, some areas lack access to effective water treatment and improved sanitation, leading to antibiotics occasionally being used when a major source of the infection has not been taken care of.
Fixed-dose combination (FDC) formulations are combinations of two or more drugs in a fixed ratio of doses which are available in a one-off dosage form. FDCs can be a viable option when combinations of antibiotics are known to be effective against a particular infection, when the doses remain the same during the entire treatment time, and when the combined drugs are pharmacologically compatible. However, some antibiotic FDCs approved in India have been found to be unhelpful, and other FDCs have been marketed despite not being approved by India’s national regulator (the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization, CDSCO).
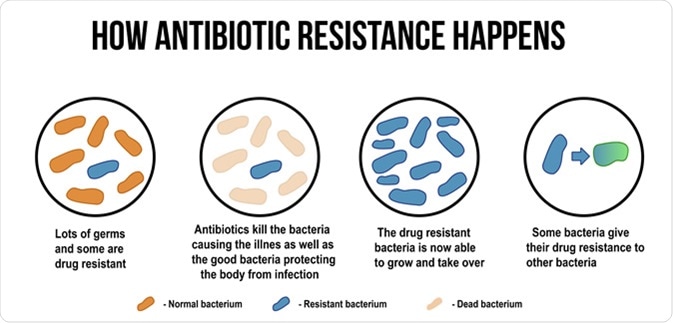
How antibiotic resistance happens diagram. ducu59us / Shutterstock
Unapproved antibiotics in India
A study looking at FDCs of antibiotics on the Indian market and their regulatory approval status in India, the UK, and the US found that 64% of the FDC formulations used in India had no record of approval by India’s CDSCO and only 3.4% were approved in the UK and US.
This study tied the rising trend in antibiotic consumption to the sale of FDC antibiotics, most of which were unapproved by regulatory bodies. Perhaps most worrisome, multinational companies are among those selling unauthorized antibiotic formulations in India.
The study also found that antibiotics not used in formulations, but used concomitantly with another antibiotic, were approved by the CDSCO and by UK and US regulators, for the most part. In this light, it appears that most of the sale of unauthorized antibiotics is in the form of FDC formulations, which increase exposure to unnecessary antibiotics and can contribute to a rise in resistance.
Comparisons also revealed that FDC sales are several magnitudes larger in India than the UK per population, comprising more than one third of antibiotic sales in India by 2011-2012, compared to 5% in the UK. FDC sales in India increased by 38% from 2007 to 2012, an increase of 18% more than single antibiotics.
Selling unapproved, unscrutinized antibiotics undermines measures in India to control antimicrobial resistance. Multinational companies should explain the sale of products in India that did not have the approval of their own national regulators and, in many cases, did not even have the approval of the Indian regulator."
Dr. Patricia McGettigan, Clinical Senior Lecturer at Queen Mary University of London
Global significance
Because of the issues with antibiotic formulations in India, both in terms of FDC sales and overall increase in antibiotic prescriptions, initiatives aiming to reduce antimicrobial resistance will likely be unsuccessful.
A rise in antibiotic resistance due to currently ineffective control systems in India will be dangerous to the entire Indian population and other international hubs to which resistance spreads. Like India, many low and middle income countries with large populations are at risk due to increased sale, and combined effects from both issues can compromise antibiotic efficacy locally and worldwide. This issue affects the use of and resistance to broad spectrum antibiotics, such as penicillins, as well as more targeted therapies and last-resort therapies.
Penicillium, ascomycetous fungi are of major importance in the natural environment as well as food and drug production. Image Credit: Rattiya Thongdumhyu
Several global initiatives are in place to try to curb the spread of antimicrobial resistance, such as the World Health Organization’s five-point antimicrobial resistance global action plan. As a major hub for business and travel and with one of the world’s largest populations, ineffectiveness in this area of the world will have significant knock-off effects on global plans to decrease resistance.
For global initiatives of tackling antimicrobial resistance to be successful, it seems that global initiatives need to focus on adherence to regulatory bodies by those selling and dispensing antibiotic formulations. Particularly, inappropriate antibiotic formulations can undermine otherwise successful initiatives to prevent antimicrobial resistance and international collaboration should focus on tackling this.
Sources
- McGettigan, P. et al. (2018). Threats to global antimicrobial resistance control: Centrally approved and unapproved antibiotic formulations sold in India. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.13503
- Van Boeckel, T.P. et al. (2014). Global antibiotic consumption 2000 to 2010: an analysis of national pharmaceutical sales data. Lancet Infectious Diseases. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70780-7
Further Reading
Last Updated: Nov 16, 2021