Uveitis is a common condition involving inflammation of the uvea in the eye, which can present alone as an isolated illness or as a symptom secondary to a number of underlying health conditions. These conditions can be divided into two main groups of autoimmune disease and inflammatory disorders.
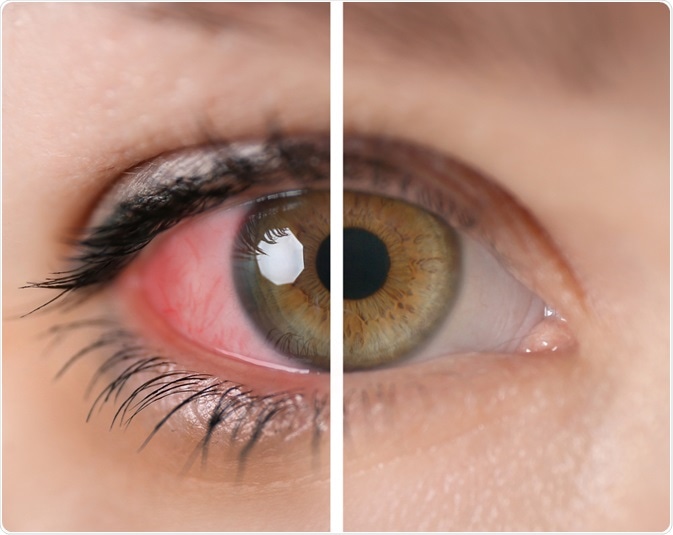
Image Credit: Pixel-Shot / Shutterstock.com
Autoimmune diseases
Autoimmunity refers to when the body’s immune system attacks its own cells. The immune reaction results in inflammation and, if localized to the eye area, may also cause symptoms of uveitis.
These autoimmune conditions include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Behcet’s syndrome
- Psoriasis
- Reactive arthritis
- Ulcerative colitis
- Kawasaki disease
- Crohn’s disease
- Sarcoidosis
- Multiple sclerosis
Infections
There are several types of infections that may reside within the eye area and cause symptoms of uveitis. These include several viral, bacterial, parasitic, and fungal infections.
Some of the specific types of infections that may cause uveitis include:
- Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- Viral herpes zoster infection
- Viral cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis infection of the eye
- Bacterial syphilis infection
- Parasitic toxoplasmosis infection
- Bacterial tuberculosis infection
- Fungal histoplasmosis infection
- West Nile viral infection
Other related conditions
In addition to the aforementioned autoimmune diseases and infections that are associated with uveitis, there are several other conditions that may cause uveitis that do not fit into either of these categories. These include:
- Exposure of a toxin to the eye
- Physical trauma or injury to the eye
- Medications such as rifabutin and moxifloxacin
Unrelated conditions
Some health conditions may cause symptoms that are mistakenly diagnosed as uveitis but are not, in fact, due to inflammation of the uvea.
These unrelated health conditions include:
- Retinis pigmentosa
- Foreign body inside the eye
- Juvenile Xanthogranuloma
- Detachment of the retina
- Retinoblastoma neoplasia
- Lymphoma neoplasia
- Malignant melanoma
- Leukemia
- Reticulum cell sarcoma
These conditions are not believed to be related to uveitis; however, they may cause disturbances to the eye area that are not due to an inflammatory response.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: May 17, 2023