The pancreas is an organ that sits in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach and plays a role in both the digestive and endocrine system.
In the endocrine system, it is responsible for producing several hormones, such as insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide. Additionally, its exocrine function involves the secretion of digestive enzymes that aid the digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine.
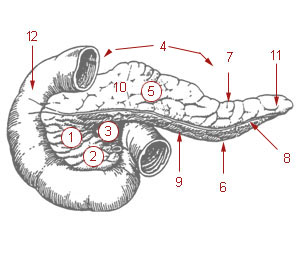 |
-
Head of pancreas
-
Uncinate process
-
Pancreatic notch
-
Body of pancreas
-
Anterior surface
-
Inferior surface
-
Superior margin
-
Anterior margin
-
Inferior margin
-
Omental tuber
-
Tail of pancreas
-
Duodenum
|
Endocrine Function
There are many cell clusters in the pancreas referred to as islets of Langerhans that are responsible for the endocrine function of the organ. The islets are composed of groups or chains of endocrine cells, woven together to form a dense network. There are four types of cells in these islets, including:
- α alpha cell that secrete glucagon
- β beta cells that secrete insulin
- Δ delta cells that secrete somatostatin
- γ gamma cells that secrete pancreatic polypeptide
Each of these hormones plays an important role in the body and is essential for normal bodily functions to occur.
Of particular note, glucagon and insulin work together to maintain adequate glucose levels in the blood. Glucagon is secreted when there is low blood sugar concentration to increase the glucose content, whereas insulin is secreted when there is excess sugar to decrease the glucose in the blood.
For example, after a meal that causes the concentration of glucose in the blood to spike the pancreas produces insulin, which encourages the insulin to be broken down and used in the body. Conversely, when the glucose concentration falls such as during the night without eating, the pancreas produces glucagon to signal to the liver, muscle or fat cells to release sugar from the stored form.
Exocrine Function
The pancreas also plays a significant role in the digestive system as an exocrine gland. It secretes a fluid that is rich in enzymes needed to aid digestion in the small intestine. The digestive enzymes help to break down different nutrients from the diet, such as carbohydrates, lipids and proteins.
The part of the pancreas responsible for exocrine function consists of ducts in several clusters, known as acini. The secretions from the lumen of the acini build up in the intralobular duct and eventually drain into the duodenum, via the main pancreatic duct.
Several hormones including gastrin, cholecystokinin (CCK) and secretin regulate the process of digestive enzyme secretion. Cells in the stomach or duodenum release these hormones when sensory information detects the need for pancreatic juices.
For example, secretin initiates the release of bicarbonate ions, which are alkaline (pH >7) and assist the neutralization of stomach acid and chyme. Conversely, CCK hormone leads to the secretion of digestive enzymes that help to break down food, including:
- protease for the digestion of protein
- amylase for the digestion of carbohydrates
- lipase for the digestion of lipids.
Together, the digestive enzymes released in the pancreatic juice aid in the process of breaking food down and absorption from the small intestine to be used in cells throughout the body.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jul 8, 2023