Skip to:
Fibroadenomas of the breast is considered to be one of the most commonly diagnosed benign breast tumors in women up to the age of 30.
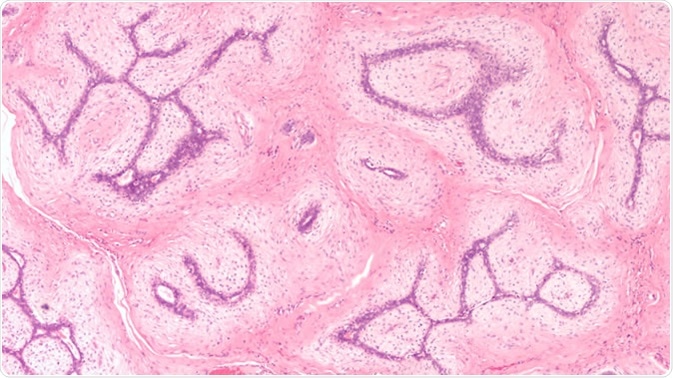
Breast Biopsy: Microscopic image (photomicrograph) of a fibroadenoma, a benign circumscribed tumor composed of both glandular and stromal tissue. - Image Credit: David A. Litman / Shutterstock
What are Breast Fibroadenomas?
Characterized as a non-fluid-filled solid lump, fibroadenomas of the breast are benign tumors that are typically painless and unilateral in form. They are most prevalent in women aged between 14 to 35 years old and are considered to be one of the most common breast masses in young people.
The lumps are made up of stromal and epithelial components found just beneath the breast’s skin and typically measure between 2-3cm in size. However, in some cases, they can grow in excess of 10cm, and as a result, hypertrophy or asymmetry of the breast may occur.
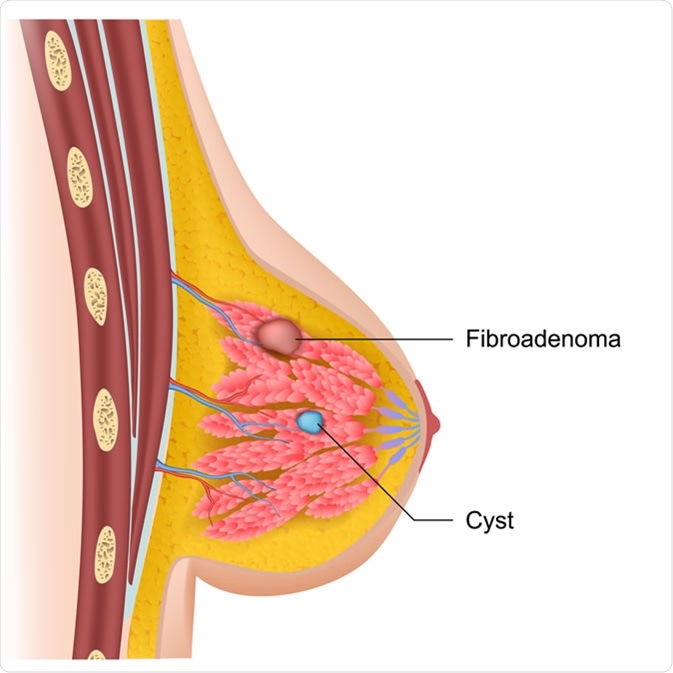
Breast cysts and fibroadenoma medical illustration. Credit: medicalstocks / Shutterstock
Types of Breast Fibroadenomas
There are three main types of fibroadenomas; cellular, juvenile, and giant. Cellular fibroadenomas grow rapidly and can be diagnosed upon review of the patient’s breast tissue biopsy results. Research suggests that between 70-90% of all fibroadenomas are cellular.
Juvenile fibroadenomas are most prevalent in those aged between 10-18 years old, and despite having a quicker rate of growth, they will often reduce in size over time.
Giant fibroadenomas are larger in size than cellular and juvenile masses, and patients with this form typically undergo surgery to remove the tumor.
Some women may just have one breast fibroadenoma, while others may have multiple. The size of the fibroadenoma may fluctuate spontaneously or change in response to the varying hormone levels associated with the menstrual cycle.
The level of pain can also vary between cases. Some women may experience high levels of pain while others may be asymptomatic.
Causes of Breast Fibroadenomas
Research is yet to conclusively pinpoint one singular cause of breast fibroadenomas. However, one popular notion links to the female hormone, estrogen. This is backed by research that found that breast fibroadenomas typically reduce in size in menopausal women and get larger during pregnancy. During menopause, estrogen levels typically decline and the inverse is seen during pregnancy. Due to this relationship, medical professionals believe that etiology is linked to estrogen levels. Similarly, research has found that changes in the size of the masses often align with changes in the menstrual cycle.
Research has also found a potential genetic link. The gene MED12 is thought to play a roll in the developed of breast fibroadenomas.
Other risk factors identified include a history of benign breast disorders, being young, and self-breast examination. In contrast to this, the number of births and the consumption of the combined pill prior to menopause are thought to reduce the prevalence of breast fibroadenomas.
Fibroadenoma Definition And Cancer Risk
Diagnosis of Breast Fibroadenomas
In order to diagnosis breast fibroadenomas, patients should typically undergo a physical examination as well as a review of their family and medical history.
A physical examination should aim to assess the consistency of the lump, whether it moves or is fixed in one place, and its size. Further examination of the lymph nodes that protrude into the armpit is also recommended as well as noting whether there is discharge from the nipple or skin.
The patient may be questioned about how long they have had the mass, its location, if it has changed in size and if this occurs in line with their menstrual cycle, as well as any experience of pain. It is also suggested that the fibroadenoma is observed over the course of at least one menstrual cycle.
Depending on the age of the woman, either one of the following imaging options may be used to examine the mass further and enable diagnosis; MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), mammography, or ultrasound. In cases of adolescent breast fibroadenomas, ultrasounds are often the preferred option due to the structure of the adolescent breast.
Management of Breast Fibroadenomas
Management of fibroadenomas of the breast can range from observing potential changes over time to surgical removal of the mass.
Observation of Breast Fibroadenomas
Observation of the fibroadenomas may be recommended in instances where the masses are not causing deformity, are asymptomatic and not rapidly increasing in size. The patients may undergo annual ultrasounds to check the progress of the fibroadenomas as well as engaging in regular self-examinations.
Surgical Removal of Breast Fibroadenomas
For large fibroadenomas or ones that pose a risk of malignancy, patients may undergo surgery to remove the mass. Particularly large or multiple fibroadenomas may necessitate reconstruction of the breast due to deformity.
There is also a range of less invasive procedures that patients can undergo to remove slightly smaller fibroadenomas that measure up to 3 cm. These include cryotherapy and vacuum-assisted percutaneous biopsy.
Sources
- Greenberg, R., Skornick, Y., & Kaplan, O. (1998). Management of Breast Fibroadenomas. Journal of General Internal Medicine. DOI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1497021/
- Peacock, K., & Ketvertis, K. M. (2019). Menopause. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507826/
- Tal, R., Taylor, H. S., Burney, R, O., et al. (2015). Endocrinology of Pregnancy. Endotext. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278962/
- Ajmal, M., & Van Fossen, K. (2018). Breast Fibroadenoma. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535345/
- Cerrato, F., & Labow, B. I. (2013). Diagnosis and Management of Fibroadenomas in the Adolescent Breast. Seminars in Plastic Surgery. DOI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3706050/
Further Reading
Last Updated: Oct 9, 2019