A neuron is a cell that can transmit electrical and chemical signals. Neurons are considered the building blocks of the nervous system and make up the major nerve pathways responsible for communicating information throughout the body.
Structure
The neuron comprises a cell body called the soma, branched projections called dendrites, and an axon, which is the long, slim nerve fiber that transmits information to muscles, glands, and other neurons. Signals are received at the dendrite, processed in the soma's nucleus, and transmitted away from the soma along the axon.
3d illustration of the scientific function of a synapse or neuronal connection with a nerve cell. Image Credit: Christoph Burgstedt / Shutterstock
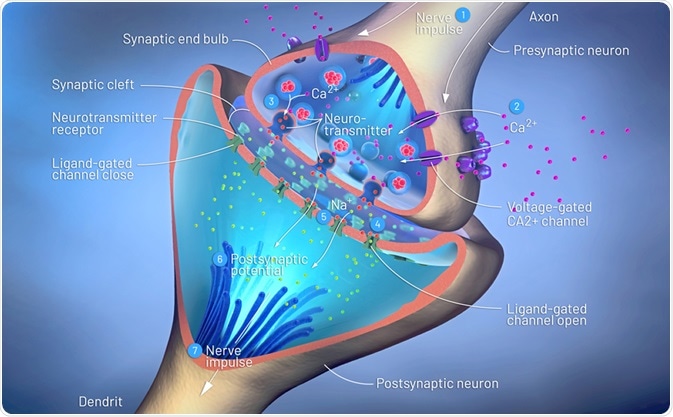
Other important structures include the neuronal membrane, the synapse, and the myelin sheath. Composed of a double layer of lipids and proteins, the neuronal membrane surrounds the nerve cell. These proteins act as transporters for the chemicals that enter and leave the neuron. The synapse is the gap between two neurons where they connect. Most of the important signal transmission and drug actions occur at the synapse. The myelin sheath is a protective covering composed of fatty tissues surrounding the axons of neurons, providing insulation and aiding the conduction of electrical impulses. Diseases that involve damage to the myelin sheath have severe effects on the nervous system, slowing the transmission of neuronal signals across the body. These devastating diseases are termed demyelinating diseases.
Neurons can be categorized based on their function as follows:
- Sensory neurons send information from sensory receptors in the skin, eyes and nose to be interpreted by the brain as touch, sight, and smell.
- Motor neurons send information away from the central nervous system to control the muscles or glands.
- Interneurons are the cells that send information between the motor neurons and the sensory neurons.
Neurons can also be categorized depending on their shape as follows:
- Neurons with multiple processes arising from the cell body are called multipolar neurons. One of the processes is the axon, and the rest are dendrites.
- A neuron with two processes (one axon and one dendrite) arising from the stoma is called a bipolar neuron.
- A neuron with one projection that includes both the dendrite and the axon is described as unipolar.
How Neurons Communicate
Last Updated: Feb 17, 2023