Chromosome 5 is the fifth largest chromosome of the 23 chromosomal pairs in humans and represents nearly 6% of the total DNA. Despite being one of the largest chromosomes, chromosome 5 has a low gene density due to a significant proportion of the chromosome having non-coding gene regions.
Chromosone 5 contains approximately 1700 genes and approximately 180 million base pairs, of which over 95% have been determined. Image Credit: NIH
Structure
Chromosome 5 is submetacentric. This means that the centromere that usually forms the central point of a chromosome, lies away from the centre, making one arm of the chromosome longer than the other. The chromosome shares a 99% similarity with chromosome 5 found in chimpanzees.
Human Genome Project
Chromosome 5 is the 12th chromosome to have completed gene sequencing in the Human Genome Project. It comprises 9 million base pairs that make up 923 genes. Sixty-six of the genes are known to be involved in human disease if they are mutated. Chromosome 5 also contains clusters of genes that code for the immune signalling molecules, interleukins.
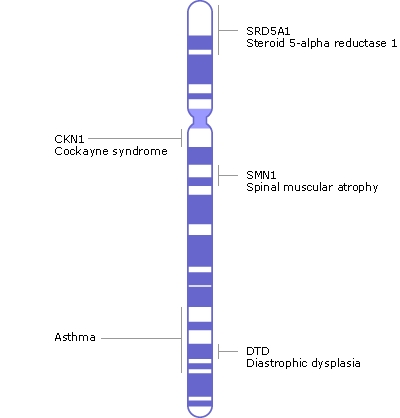
Chromosome 5 genes
Some of the genes present on chromosome 5 include:
- ADAMTS2 that codes for metallopeptidase with thrombospondin motifs-2
- APC that stands for adenomatosis polyposis coli or colonic polyps
- EGR1 that codes for early growth response protein 1
- DTDST that codes for diastrophic dysplasia sulfate transporter
- ERCC8 that codes for excision repair cross-complementing rodent repair deficiency, complementation group 8
- FGFR4 that codes for fibroblast growth factor receptor 4
- GM2A that codes for GM2 ganglioside activator
- HEXB that codes for hexosaminidase B (beta polypeptide)
- MCCC2 that codes for methylcrotonoyl-Coenzyme A carboxylase 2 (beta)
- MTRR that codes for 5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase reductase
- NIPBL that codes for Nipped-B homolog (Drosophila or fruit fly)
- NSD1 that codes for nuclear receptor binding SET domain protein
- SLC22A5 that codes for solute carrier family22, member 5
- SLC26A2 that codes for solute carrier family 26, member 2
- SMN1 that codes for survival motor neuron 1
- SMN2 that codes for survival motor neuron 2
- SNCAIP that codes for synuclein, alpha interacting protein
- TGFBI that codes for transforming growth factor, beta-induced
- TCOF1 that codes for Treacher Collins-Franceschetti syndrome 1
- FGF1 that codes for fibroblast growth factor 1
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jun 17, 2023