Diverticulitis is a common condition of the large intestine that refers to the infection and inflammation of diverticula, bulges which can form in the lining of the colon as a person ages.
These diverticula are thought to form as a result of hard stools passing through a colon that has become weakened over time. When the diverticula cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, a person is said to have diverticular disease, while infection and inflammation of the diverticula is referred to as diverticulitis.
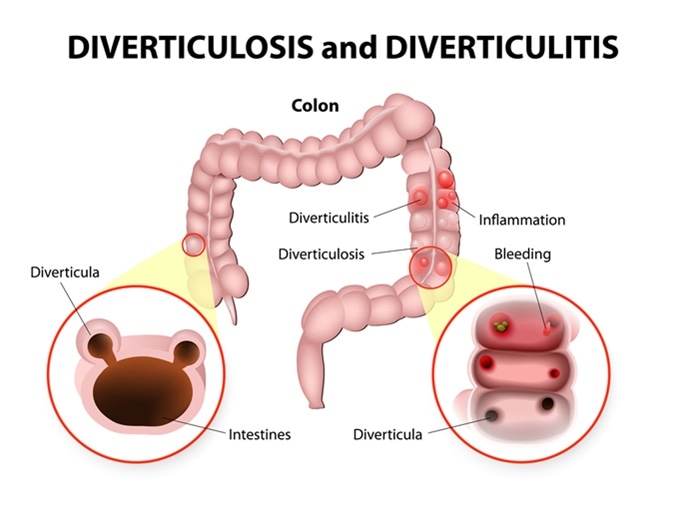
Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis. Image Credit: Designua / Shutterstock
Symptoms
Some of the symptoms of diverticulitis include:
- Intermittent stomach pain
- Abdominal bloating
- High fever of 38ºC (100.4ºF) or above
- Rectal bleeding
- Diarrhea and constipation
Causes and pathology
Diverticula are more common among older individuals and are estimated to affect around 50% of those aged 50 years and around 70% of those aged 80 years.
A lack of fibre is thought to be the main cause of diverticula, as hard stools require the intestine to exert more pressure to push them through the body. Straining to pass hard, small stools causes weak spots to develop in the muscular layer of the intestine.
The inner layer of the intestine then pushes through these weak spots to form diverticula. Diverticulitis is thought to occur when a piece of food becomes trapped in one of the bulges and bacteria start to multiply, triggering infection and inflammation. This causes the pain associated with diverticulitis and can also lead to further complications such as the formation of an abscess or fistula.
Diverticulitis is more common in western countries where diet tends to be lower in fibre than in African or south Asian countries, where the condition is almost unheard of.
Treatment
The pain associated with diverticulitis can be relieved using paracetamol or ibuprofen and bowel infection can be cleared up using antibiotics. Recurring cases or complications such as fistula or abscess may require hospitalization and surgery to remove the diseased part of the intestine.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jun 10, 2023