Introduction
Chemical Structure and Biosynthesis
Major Dopaminergic Pathways in the Brain
Physiological Functions of Dopamine
Dopamine Receptors
Dopamine and Mental Health
Dopamine and Neurological Disorders
Dopamine in the Periphery
References
Further reading
Dopamine is a crucial neurotransmitter and neuromodulator that regulates mood, movement, reward, and various physiological processes in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. Disruptions in dopamine pathways contribute to neurological, psychiatric, and metabolic disorders, making it a key target for research and therapy.
 Chemical molecular formula hormone. Image Credit: GrAl / Shutterstock
Chemical molecular formula hormone. Image Credit: GrAl / Shutterstock
Introduction
Dopamine is a versatile catecholamine that functions as both a neurotransmitter and neuromodulator in the body. Within the central nervous system (CNS), dopamine regulates mood, motivation, and reward, in addition to its essential role for motor control. Its vasodilatory effects occur primarily in peripheral tissues via specific dopamine receptor subtypes.
Chemical Structure and Biosynthesis
Although dopaminergic neurons represent less than 1% of cell subtypes in the brain, dopamine embodies approximately 80% of catecholamines in the CNS, though this figure is an estimate and may vary depending on measurement methods1
Dopamine is a catecholamine that is primarily synthesized by dopaminergic neurons located in the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area (VTA) of the brain, where this chemical messenger primarily functions as a neurotransmitter. The hypothalamus and enteric nervous system of the gastrointestinal tract also produce small amounts of dopamine.2
The synthesis of dopamine begins with the conversion of tyrosine to levo-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) by the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase. L-DOPA is subsequently converted to dopamine by dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) decarboxylase.
Major Dopaminergic Pathways in the Brain
The substantia nigra within the brain is home to an estimated 135,000 dopaminergic neurons, although counts are species- and method-dependent, 35,000 of which are present in the ventral tegmental area (VTA). The release of dopamine can be further categorized as phasic or tonic, with phasic dopamine release leading to a rapid and transient increase in dopamine levels, whereas tonic dopamine release is a milder and less intense response.1
The dopaminergic system comprises four functionally and anatomically interconnected pathways, including the mesolimbic, nigrostriatal, mesocortical, and tuberoinfundibular pathways.2
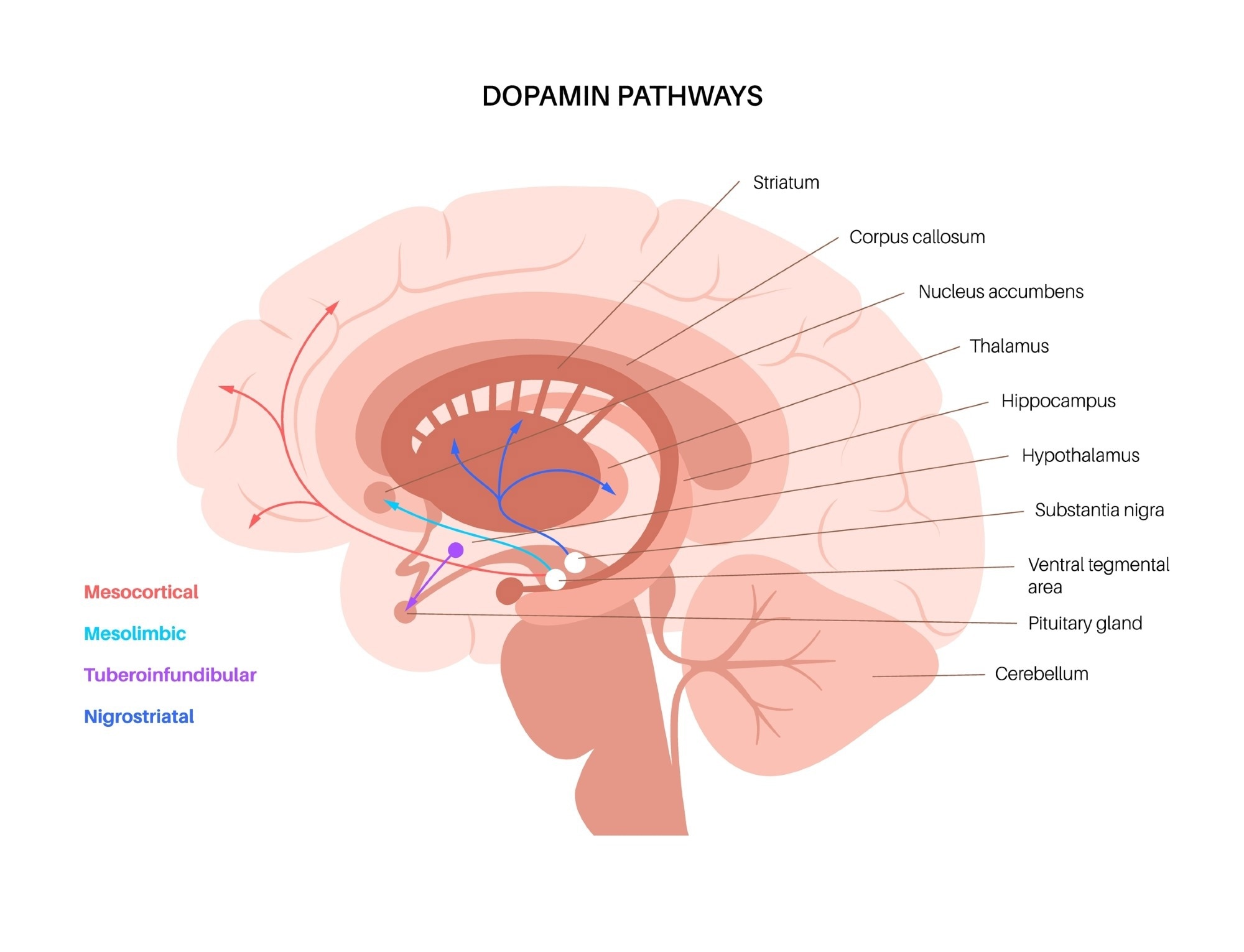 Dopamine pathways in the human brain. Image Credit Pikovit / Shutterstock
Dopamine pathways in the human brain. Image Credit Pikovit / Shutterstock
Mesolimbic Pathway
Originating from the VTA, the mesolimbic pathway projects to the amygdala, pyriform cortex, lateral septal nuclei, and nucleus accumbens (NAc). Primary reinforcers of dopamine release can include food and sex; however, ‘unnatural rewards’ like alcohol, drugs, and gambling can also facilitate a powerful release of dopamine.
Mesocortical Pathway
The mesocortical pathway originates from the VTA and projects to the frontal cortex and septohippocampal regions. The primary functions of the mesocortical pathway include modulating both cognitive and emotional behaviors.
Nigrostriatal Pathway
Dopaminergic signals are transmitted from the substantia nigra through the nigrostriatal pathway to reach the striatum of the forebrain. Although the nigrostriatal pathway is primarily involved in movement coordination, the release of dopamine through this pathway also affects cognition and sensory processing, including auditory discrimination.3
The degeneration of substantia nigra pars compacta neurons, a distinguishing feature of Parkinson’s disease, reduces dopamine release into the striatum, thereby disrupting the normal function of both direct and indirect dopamine pathways3.
Tuberoinfundibular Pathway
Originating from the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus, the tuberoinfundibular pathway eventually reaches the anterior pituitary gland to inhibit prolactin secretion. As a result, the tuberoinfundibular pathway regulates various neuroendocrine functions, including milk production in mammary tissues and stress responses4.
Physiological Functions of Dopamine
Dopamine is a key neurotransmitter involved in motor control, mood and emotional response modulation, as well as cognitive functions including attention, learning, and memory. Dopamine also exhibits neuroendocrine activity through its regulation of prolactin levels.
Disruptions in the dopamine pathway, from its synthesis and release to receptor binding and reuptake, have been implicated in several neuropathological conditions. In Parkinson’s disease, for example, the gradual degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the midbrain leads to tremors, stiffness, and slow movement.6
Dopamine Receptors
Dopaminergic receptors can be further characterized as autoreceptors or heteroreceptors. Whereas autoreceptors are located on the same cell that released the dopamine, heteroreceptors are present on neighboring neurons or target cells.4
In addition to location, dopaminergic receptors can also be classified by their function. D1-like receptors, of which include D1 and D5, activate the Gs signaling pathway to increase cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels. Comparatively, D2-like receptors D2, D3, and D4 couple to G inhibitory (Gi) proteins, thereby inhibiting adenylyl cyclase to reduce cAMP production. Notably, D2-like receptors have a 10- to 100-fold greater affinity for dopamine than D1-like receptors.1
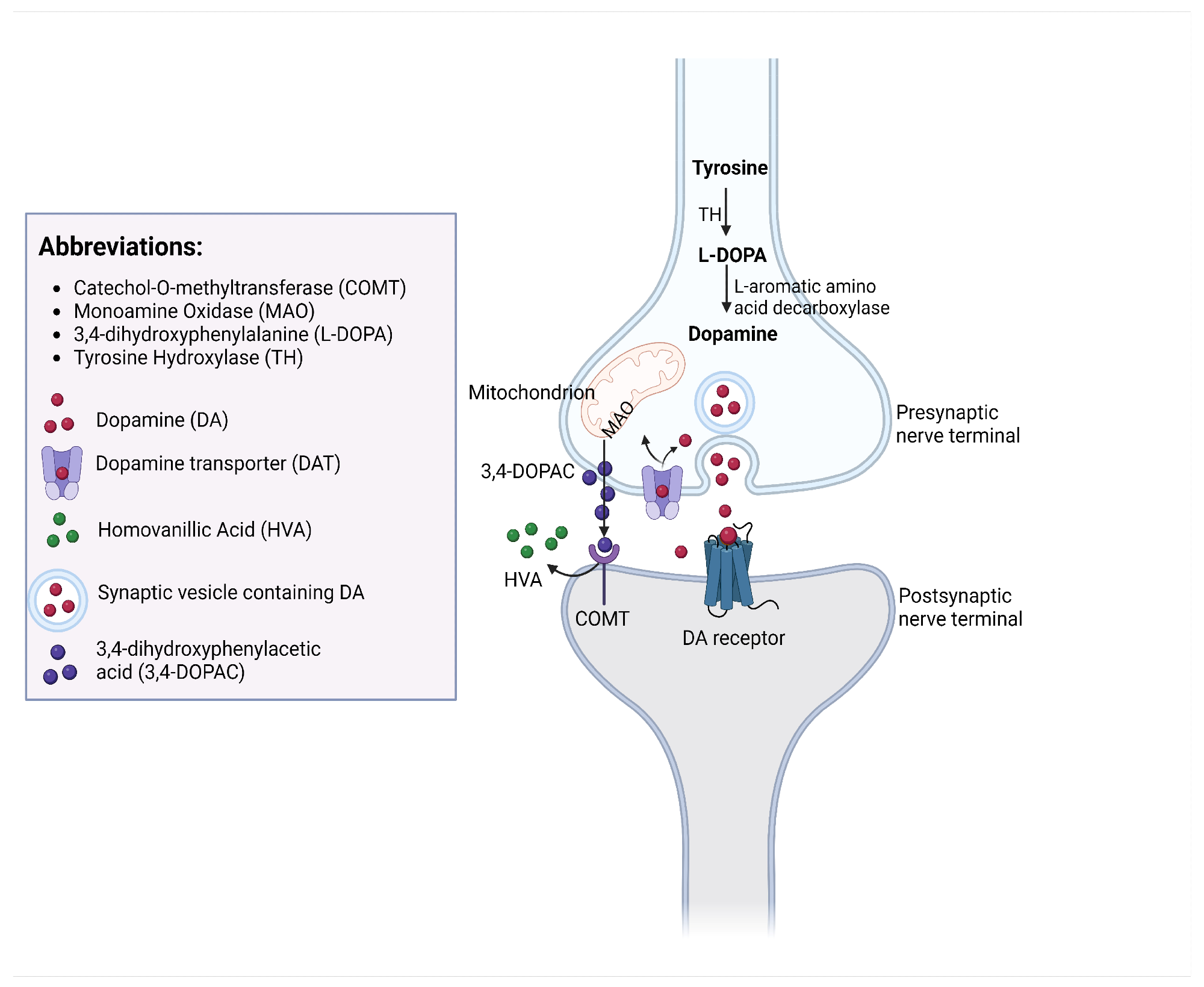 The processes of DA synthesis, reuptake, and metabolism occurring at a dopaminergic synapse.4
The processes of DA synthesis, reuptake, and metabolism occurring at a dopaminergic synapse.4
Dopamine and Mental Health
Dysregulated dopamine activity has been implicated in altered mood, cognition, and behavioral symptoms in schizophrenia, some of which include hallucinations, delusions, and cognitive impairment. As a result, dopamine D2 receptors are a primary target of many antipsychotic medications.6
Some schizophrenia patients are diagnosed with treatment-resistant schizophrenia (TRS), which may occur due to abnormal dopamine receptor activity, presynaptic synthesis and release of dopamine, and/or postsynaptic neurotransmission. Evidence for increased D2 receptor density in TRS is mixed and may vary by brain region, potentially limiting the effectiveness of conventional D2 antagonists.6
Chronic stress increases inflammation throughout the body, including dopaminergic pathways within the brain. Anhedonia, a stress-related psychological state in which the affected individual is unable to experience pleasure, is the product of chronic stress and increases the risk of addiction and depression. Prolonged dysregulation can lead to an 'anti-reward' brain state, characterized by reduced sensitivity to natural rewards and heightened vulnerability to compulsive behaviors.5
Reward-associated mechanisms explain why individuals search for initially positive stimuli again and again and why this can ultimately lead to compulsive behaviors and addictions that pose a threat to mental health.5
Dopamine and Neurological Disorders
In addition to the typical motor symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease, reduced cognitive flexibility has also been attributed to altered dopamine transmission patterns. When dopamine circuits within the medial prefrontal cortex (mpFC) and NAc are affected, anhedonia, apathy, and reduced goal-directed behaviors can arise.6
Current estimates suggest that up to 10% of the general adult population in both Europe and North America is affected by restless leg syndrome, a condition characterized by the irresistible restlessness and urge to move the legs, particularly at night. Whereas restless leg syndrome is associated with both an iron deficiency in the brain for genetically susceptible individuals and dopaminergic system dysfunction, potentially involving a presynaptic hyperdopaminergic state, in other patient populations.7
Huntington’s disease is an autosomal dominant disorder that is caused by the expansion of CAG trinucleotide repeats in the huntingtin gene6. Dysfunctional dopaminergic neurotransmission in Huntington’s disease contributes to psychiatric symptoms like depression, apathy, irritability, and aggression, as well as Parkinsonism-like features.9
Dopamine in the Periphery
Outside of the CNS, significant amounts of dopamine are produced in the gastrointestinal tract, spleen, pancreas, lungs, liver, cardiovascular system, kidneys, bones, and connective tissues. In the plasma, most dopamine circulates in sulfoconjugated form and acts primarily as a local autocrine/paracrine signal rather than a systemic hormone. In most peripheral tissues, D2-like receptors have anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic properties, whereas D1-like receptors regulate oxidative stress and infiltrating immune cell activity.8
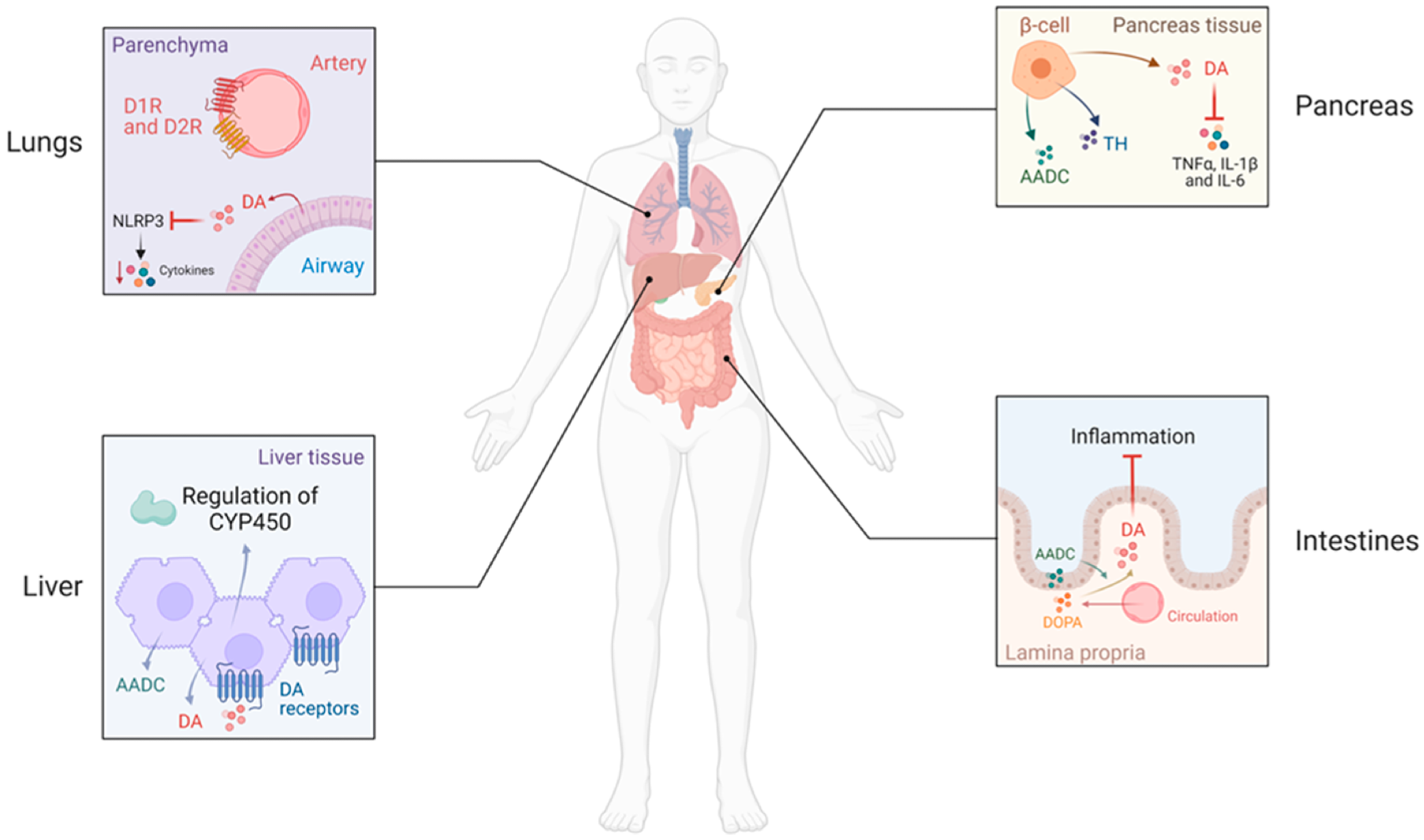 Peripheral dopamine (DA) production and actions. In the lung, alveolar type II epithelial cells can synthesize DA, which attenuates lung tissue injury, neutrophil infiltration, and inhibits inflammatory cytokine response through inhibition of NLRP3-signaling pathways. DA may also modulate ventilation by acting on dopamine D1 (D1R) and D2 (D2R) receptors in the arteries of the lung. In the liver, aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) is expressed, and DA is produced by hepatocytes. D2R can modulate the regulation of components of the cytochrome P450 (CYP450). Moreover, DA may protect the liver from acute injury. In the pancreas, DA is synthesized mainly in β-cells that intracellularly express TH and AADC and regulate insulin production in these cells. DA reduces the increased expression of inflammatory cytokines (TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6) induced by cholecystokinin in acute experimental pancreatitis. In the intestines, DA is abundant in the mucosal cell layer; the epithelial cells of the intestinal mucosa are rich in AADC and circulating DOPA is taken up to produce DA. DA reduces the inflammation in human inflammatory bowel disease.8
Peripheral dopamine (DA) production and actions. In the lung, alveolar type II epithelial cells can synthesize DA, which attenuates lung tissue injury, neutrophil infiltration, and inhibits inflammatory cytokine response through inhibition of NLRP3-signaling pathways. DA may also modulate ventilation by acting on dopamine D1 (D1R) and D2 (D2R) receptors in the arteries of the lung. In the liver, aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) is expressed, and DA is produced by hepatocytes. D2R can modulate the regulation of components of the cytochrome P450 (CYP450). Moreover, DA may protect the liver from acute injury. In the pancreas, DA is synthesized mainly in β-cells that intracellularly express TH and AADC and regulate insulin production in these cells. DA reduces the increased expression of inflammatory cytokines (TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6) induced by cholecystokinin in acute experimental pancreatitis. In the intestines, DA is abundant in the mucosal cell layer; the epithelial cells of the intestinal mucosa are rich in AADC and circulating DOPA is taken up to produce DA. DA reduces the inflammation in human inflammatory bowel disease.8
Within the gastrointestinal tract, dopamine mitigates inflammation by suppressing interleukin 1β (IL-1β), IL-6, tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), and NLRP3 inflammasomes. These effects can be tissue-specific and depend on dopamine concentration and receptor subtype activation. The anti-inflammatory effects of dopamine within the intestines, liver, and pancreas are crucial for protecting these organs from injury.8
Alveolar type II epithelial and pulmonary neuroendocrine cells in the lungs synthesize dopamine, with both D1- and D2-like receptors expressed on pulmonary arteries. The vasodilatory effects of dopamine have been utilized to treat bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
References
- Lauretani, F., Giallauria, F., Testa, C., et al. (2024). Dopamine Pharmacodynamics: New Insights. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25(10). DOI:10.3390/ijms25105293, https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/10/5293
- Khalil, B., Rosani, A., & Warrington, S. J. Physiology, Catecholamines. [Updated 2024 Dec 11]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507716/
- Chen, A. P. F., Malgady, J. M., Chen, L., et al. (2022). Nigrostriatal dopamine pathway regulates auditory discrimination behavior. Nature Communications 13(1). DOI:10.1038/s41467-022-33747-2, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-33747-2
- Qi-Lytle, X., Sayers, S., & Wagner, E. J. (2024). Current Review of the Function and Regulation of Tuberoinfundibular Dopamine Neurons. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25(1). DOI:10.3390/ijms25010110, https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/1/110
- Dresp-Langley, B. (2023). From Reward to Anhedonia—Dopamine Function in the Global Mental Health Context. Biomedicines 11(9):2469. DOI:10.3390/biomedicines11092469, https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/11/9/2469
- Speranza, L., Miniaci, M. C., & Volpicelli, F. (2025). The Role of Dopamine in Neurological, Psychiatric, and Metabolic Disorders and Cancer: A Complex Web of Interactions. Biomedicines 13(2):492. DOI:10.3390/biomedicines13020492, https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/13/2/492
- Bugnicourt, J.-M. (2024). Dopamine Agonists in the Treatment of Restless Legs Syndrome: Too Much of a Good Thing? Journal of Sleep Medicine 21(1):1–5. DOI:10.13078/jsm.230030, https://www.e-jsm.org/journal/view.php?doi=10.13078/jsm.230030
- Moore, S. C., Vaz de Castro, P. A. S., et al. (2023). Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Peripheral Dopamine. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24(18):13816. DOI:10.3390/ijms241813816, https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/24/18/13816
- Lauretani, F., Giallauria, F., Testa, C., et al. (2024). Dopamine Pharmacodynamics: New Insights. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25(10). DOI:10.3390/ijms25105293, https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/10/5293
Further Reading
Last Updated: Aug 17, 2025