Staphylococcus aureus is a type of bacteria. It stains Gram positive and is non-moving small round shaped or non-motile cocci. It is found in grape-like (staphylo-) clusters. This is why it is called Staphylococcus.
Who does Staphylococcus aureus affect?
Staphylococcus is one of the five most common causes of infections after injury or surgery. It affects around 500,000 patients in American hospitals annually. It is abbreviated to “S. aureus” or “Staph aureus” in medical literature. S. aureus was discovered in Aberdeen, Scotland in 1880 by the surgeon Sir Alexander Ogston in pus from surgical abscesses.
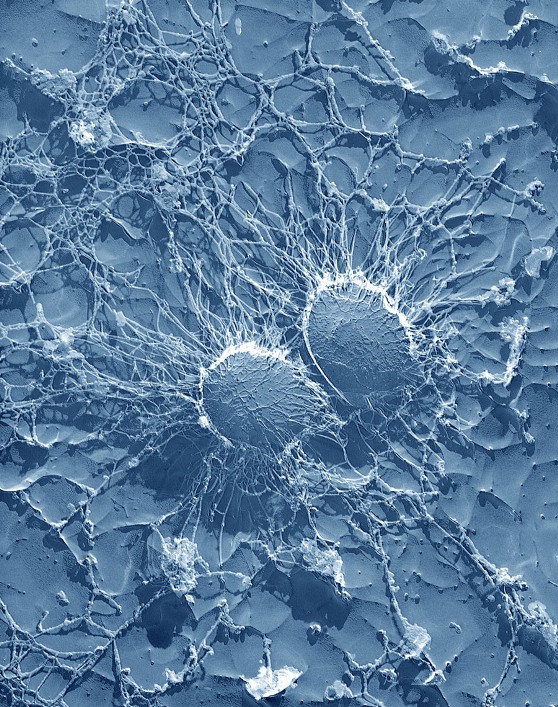
Bacterial cells of the bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) which is one of the causal agents of mastitis in dairy cows. Its large capsule protects the organism from attack by the cow’s immunological defenses. Magnified 50,000X. Image Credit: arsusda.gov
Staphylococcaceae Family
Staphylococcus aureus belongs to the family Staphylococcaceae. It affects all known mammalian species, including humans. Further due to its ability to affect a wide range of species, S. aureus can be readily transmitted from one species to another. This includes transmission between humans and animals.
Transmission of Staphylococcus aureus
S. aureus may occur commonly in the environment. S. aureus is transmitted through air droplets or aerosol. When an infected person coughs or sneezes, he or she releases numerous small droplets of saliva that remain suspended in air. These contain the bacteria and can infect others.
Another common method of transmission is through direct contact with objects that are contaminated by the bacteria or by bites from infected persons or animals. Approximately 30% of healthy humans carry S. aureus in their nose, back of the throat and on their skin.
Clinical manifestation of infection
Around one third of healthy individuals carry this bacteria in their noses, pharynx and on their skin. In normal healthy and immunocompentent person, S. aureus colonization of the skin, intestinal tract, or nasopharynx does not lead to any symptoms or disease.
When S. aureus is isolated from an abscess or boil or other skin lesion, it is usually due to its secondary invasion of a wound rather than the primary cause of disease. S. aureus may similarly be isolated from abscesses, breast absecesses or mastitis, dermatitis or skin infections and genital tract infections.
S. aureus is considered the classic opportunist in this way since it takes advantage of broken skin or other entry sites to cause an infection.
In animals and humans that are immunocompromised or immunodeficient, this bacteria may be life threatening. It may lead to pyogenic (abscessing) infections of the skin, eyes and genital tract.
What does S. aureus cause?
Of the variety of manifestations S. aureus may cause:
- Minor skin infections, such as pimples, impetigo etc.
- It may cause boils (furuncles), cellulitis folliculitis, carbuncles
- It is the cause of scalded skin syndrome and abscesses
- It may lead to lung infections or pneumonia
- Brain infections or meningitis
- Bone infections or osteomyelitis
- Heart infections or endocarditis
- Generalized life threatening blood infections or Toxic shock syndrome (TSS), bacteremia and septicaemia
Diagnosis
Presence of S. aureus in culture is normally insignificant since this bacteria is normally present on the skin, nose and pharynx of many humans and animals. The organism is readily cultured from nasopharynx or skin, or by culture of suspicious lesions.
On culture the bacterial colonies a characteristic glistening, opaque, yellow to white appearance on blood agar.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jun 21, 2023