Micromanipulation refers to the microscopic-level manipulation of cellular organelles using specific tools that can move an object with high precision. Microinjection refers to a technique wherein substances are injected into single cells using a very thin needle. These methods are used in several fields, including semiconductors, genetic engineering, in vitro fertilization, cell biology, virology etc.
 Phonlamai Photo | Shutterstock
Phonlamai Photo | Shutterstock
Microinjection
Microinjection was first introduced in the 1900s with the injection of large macromolecules into cells. The method was subsequently adapted to inject DNA, RNA, enzymes, proteins, metabolites, ions and organelles into cells. Xenopus eggs and animal embryos have been used extensively in the development of microinjection techniques due to their large size.
Microinjections usually necessitate an inverted microscope wherein the objective lens is located below the stage and the light source is placed above. The working distance of the condenser (i.e. the distance between the bottom of the condenser and stage) is one of the critical parameters during microinjection. This distance should be long to ensure no obstructions while performing microinjections.
A camera or a TV can be additionally attached if the technique is to be used for teaching purposes. A micromanipulator precisely positions the injection needle near the tissue that has to be manipulated and is positioned at 45-degree angle to the injection dish.
The micromanipulator has to be highly stable to achieve accuracy. Microinjection pipette uses capillary tips that are heated until the glass liquefies; this liquefied glass is then stretched to create a very fine tip that measures approximately 0.5 millimeters in diameter.
Microinjection needle
Producing a microinjection needle requires experience and careful handling. A borosilicate glass capillary is heated and drawn out, then bent using forceps to produce a needle tip of around 10-30 micrometers. In cases where very small volumes need to be injected (less than 2 nanoliters), gas-pressure regulated microinjectors may be used.
One of the most widely used applications of microinjections is injecting DNA into the pronucleus of a newly fertilized egg to create transgenic organisms. Initially, this method was applied in mice, but today this is being applied in several different organisms.
Another area is introducing genetically altered stem cells into blastocyst to invoke the contribution of the stem cells. Enucleating and then transplanting a somatic cell are methods used to produce genetically identical copies of an animal.
Micromanipulation
Micromanipulation techniques evolved to manipulate a specimen delicately or precisely. Different micromanipulators include holding pipettes, injectors, and cutting tools. There is a need in the field to accurately and precisely move in different x, y, and z directions at a resolution of sub-microns.
This has led to the creation of several mechanical, hydraulic, and electric devices to provide smooth and controlled movement. Micromanipulation is applied in diverse fields such as electrophysiology, in vitro fertilization (IVF), transgenics, and adherent cell research. Specifically, optical tweezers are used to monitor the movement and properties of cells, metal particles, and colloids.
Micromanipulation pertinent for in vitro fertilization (IVF)
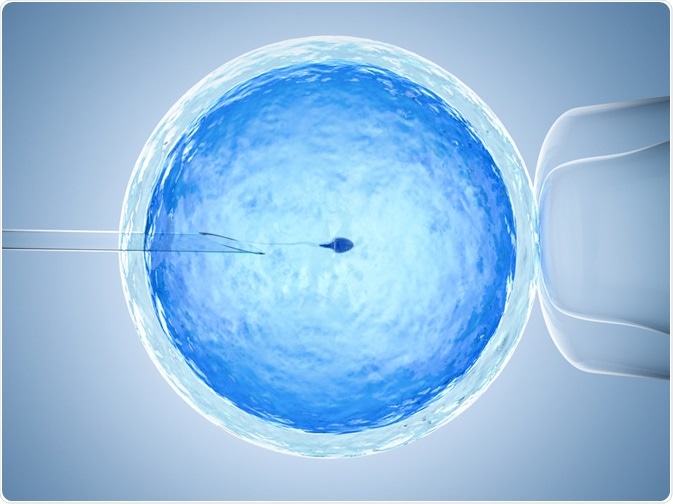
One of the widely applied fields of micromanipulation is during IVF. Various micromanipulation methods - such as zona dissection, sub-zonal insemination, and direct injection of a spermatozoon into the cytoplasm (ICSI) - are extensively used in assisted reproduction.
ICSI involves micromanipulating male and female gametes. Another method is opening the zona pellucida using lasers during different stages of preimplantation to help in hatching, or to remove cells for genetic diagnosis. Blastocysts are also sometimes micromanipulated to shrink the blastocoel, which in turn facilitates its survival.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jan 18, 2019