RNA interference (RNAi) is a rapidly developing and potent method of gene silencing.
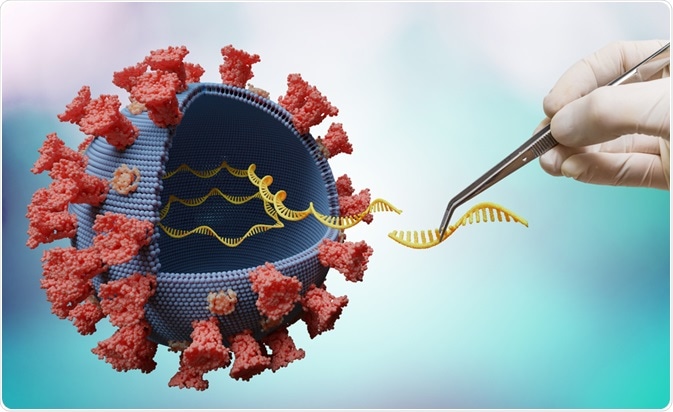
Image Credit: vchal/Shutterstock.com
RNAi is a fundamental and potent phenomenon in which a short double-strand RNA (dsRNA) deters the specific gene expression by creating disintegration in the chain sequence of particular target messenger RNA in the cytoplasm.
It allows the creation of more advantageous features in plants that are subjected to genetic modification (GM). RNAi-based genetically modified plants are more efficient in silencing the targeted gene expressions rather than modifying the novel protein expressions.
Functions of RNA interference in the field of biotechnology include managing pests and diseases caused by bacteria, fungi, and viruses, improving crop yield, and generating plants with novel traits (PNTs).
RNA interference involves specific tissue gene silencing with suitable promoters to simultaneously deactivate numerous genes, which enhances crop protection against detrimental pathogens. Hence, the application of RNA interference has successfully controlled many plant diseases.
RNAi for resistance to plant diseases
Pathogens in plants massively decrease crop yield, and often have an immense negative economic impact; they also support the annihilation of complete plant species.
Even though there are various methods available for improving genotype resistance in plants, the RNAi gene silencing method is considered to be one of the best ways to improve disease resistance.
In RNAi, the double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) initiates homologous mRNAs to hinder the transcription and translation of susceptibility genes, deactivating them. The RNAi approach reveals new pathways in the advancement of an eco-friendly system for the improvement of plants by silencing the specific genes that cause stress and novel gene expression for plant disease resistance.
Host gene silencing—hairpin RNAi (HGS-hpRNAi) is considered to be a more stable method of gene silencing in plants. The technique is used to increase resistance to diseases caused by bacteria and fungi, by altering the gene expression against the pathogens in host plants.
RNA interference utilizes a virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) system to improve resistance to viral diseases in plants. This method relies on the viral-mediated replication of the target protein into a viral-mediated dsRNA intermediate, which is then processed into viral-mediated siRNAs (vsiRNAs).
Later, the vsiRNAs target and conceal gene expression and protein translation of the viral and target genes.
RNAi for resistance to insects or pests
RNAi is one of the most widely used methods in biotechnology and plant breeders for genetically engineering resistance to various insects/pests. RNAi is utilized for improving nematode resistance and is believed to be a unique tool in plant-parasitic nematode control.
Genetically engineered plants can generate double-stranded RNAi’s (dsRNAs) that have the capacity to turn off target genes in the body of nematodes. The dsRNAs within the plant cytoplasm are ingested by the nematode, where they insert into the genome and silence the target genes.
DsRNA reduces the impact of nematode predation and allows the growth and development of plants. Efficient control demands recognition of nematode-responsive plant promoters.
RNAi can be used to reduce parasitism, and also supports the identification of unique targets that are crucial for nematode survival, furthering research into effective control mechanisms.
RNAi for improvement of crop quality
RNA interference offers a unique opportunity to enhance the quality and nutritional value of various crops. It can also be used to modify crops to suit an individual’s nutritional requirements.
This technique aids the development of trajectories of RNAi constructs for the modification and evaluation of lines for examining quality traits.
RNA interference can be employed as a metabolic engineering technique for the synthesis and production of economically important plant products, including alkaloid productions (such as scopolamine, quinine, codeine, vincristine), flavoring agents, and essential oil biosynthesis.
RNAi for abiotic stress tolerance
Abiotic stress is a life-threatening factor, especially for plants in which their yield and growth are largely affected. It is considered to be a major contributor to crop devastation, affecting both crop quantity and quality.
Transgenic methods that include gene detection and functional genomics have allowed the innovation of numerous procedures and gene families to assure higher production and adaptability to abiotic stresses.
Other applications of RNAi
Male sterility
RNA interference can be used to create male sterility, which is important in the industry of hybrid seeds. It can be used to target genes in specific cells, such as those responsible for the production of pollens.
Sources:
Further Reading
Last Updated: Apr 22, 2021