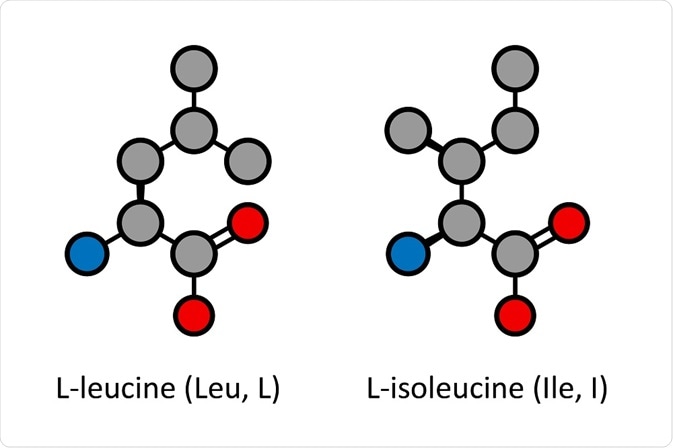
Leucine and isoleucine are among the 20 amino acids found naturally in the human body. They are very similar in structure but have small differences which change their physiological properties.
 molekuul_be | Shutterstock
molekuul_be | Shutterstock
Both of these amino acids are non-polar and aliphatic and have a four-carbon side chain emerging from the basic amino acid structure. The skeletal structure of leucine is shown below.
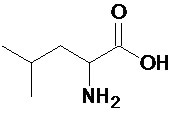
The skeletal structure of isoleucine is shown below.
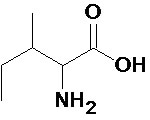
Both contain the same carboxyl and amino functional groups and are of a similar size, but they have a different side chain layout. These are an example of structural isomers, where the carbon atoms are in different positions.
Role of leucine in the body
Both these amino acids have many essential roles in the body, but despite their similar structure, these roles tend to differ. Leucine is important for the general health of muscle. It can stimulate protein synthesis and reduce protein breakdown, especially of muscle protein following physical trauma.
Leucine also increases the levels of insulin in the blood, which leads to a similar effect on the proteins in muscle tissue.
Leucine is also important in the regulation of blood sugar levels since it acts as a source for gluconeogenesis (the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrates) in the liver. This helps the body and the muscles to heal.
Role of isoleucine in the body
Isoleucine has a large range of different roles in the body. It shares some functions with leucine in regulating blood glucose and in the healing of wounds, but there also several unique functions. Isoleucine has a role in the detoxification of nitrogenous waste like ammonia, which is then excreted from the body by the kidneys.
Isoleucine is also essential for the production and formation of hemoglobin and the production of red blood cells. It is, therefore, an important amino acid in the process of recovery from blood loss or anemia.
Deficiency in leucine and isoleucine
Both of these amino acids are sourced from cheese, eggs, most meats, seeds, and nuts. These foods are normally common in the diet, so deficiencies are quite rare.
Isoleucine deficiency is most common in older people and can lead to the weakening and wasting of muscle, and tremors.
Leucine deficiency is much less common but can lead to similar symptoms, such as muscle weakness and blood sugar fluctuations
Branched-chain amino acids
Leucine, isoleucine, and valine (another amino acid) are grouped together as branched chain amino acids or BCAAs. All BCAAs are essential to human life. They are needed for the physiological response to stress, in energy production, and particularly for the normal metabolism and health of muscle.
These branched-chain amino acids also tend to be popular in bodybuilders and other people who focus on building physical strength, because the intake of BCAAs can reduce muscle loss and provide faster muscle recovery.
Application of BCAAs
BCAAs are administered to patients recovering from trauma or after surgery, to aid the healing of muscles and wounds. They can also help treat certain types of liver damage common in alcoholics, and reduce the symptoms of liver disease.
Another condition in which BCAAs can be beneficial is phenylketonuria, where the body is unable to synthesize the amino acid phenylalanine. Administration of BCAAs can help the body cope with the lack of this amino acid.
These amino acids are also beneficial while treating anorexia, as such persons often have weak or thin muscles which need to be built up. Leucine and isoleucine are especially useful in the build-up of muscle in these conditions.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jan 17, 2023