Introduction
Microbial Assays: An Overview
Microbial Assay Methods
Different Microbes Used in Microbial Assays
Culture Media Used
Summing Up
References
In pharmacological development and testing, many processes and techniques are employed to produce safe drugs for the worldwide market. This article will look at biological assays, a legal requirement in some countries.
Microbial Assays: An Overview
Microbial assays are a technique to assess a compound’s potency or concentration. This is carried out by exposing microorganisms to the compound and determining its effect on them. Microbial assays are required for antibiotic assay in the US Pharmacopoeia and the British Pharmacopoeia. This official publication lists medicinal drugs, their effects, and directions for their use.
Microbial assays provide information on how antibiotics inhibit microbial growth. The microbial assay is a comparative method. Other compounds whose activity can be studied with a microbial assay include amino acids and vitamins. Measured concentrations of the target compound are compared with the standard concentration of a particular compound with known activity, providing information on the compound under investigation.
Microbial assays are used for many purposes. These include antibiotic sterility testing, testing the mutagenicity or carcinogenicity of chemicals, disease diagnosis, and monitoring using immobilized enzymes. They are also used to evaluate the pharmacokinetic properties of drugs for human and animal use.
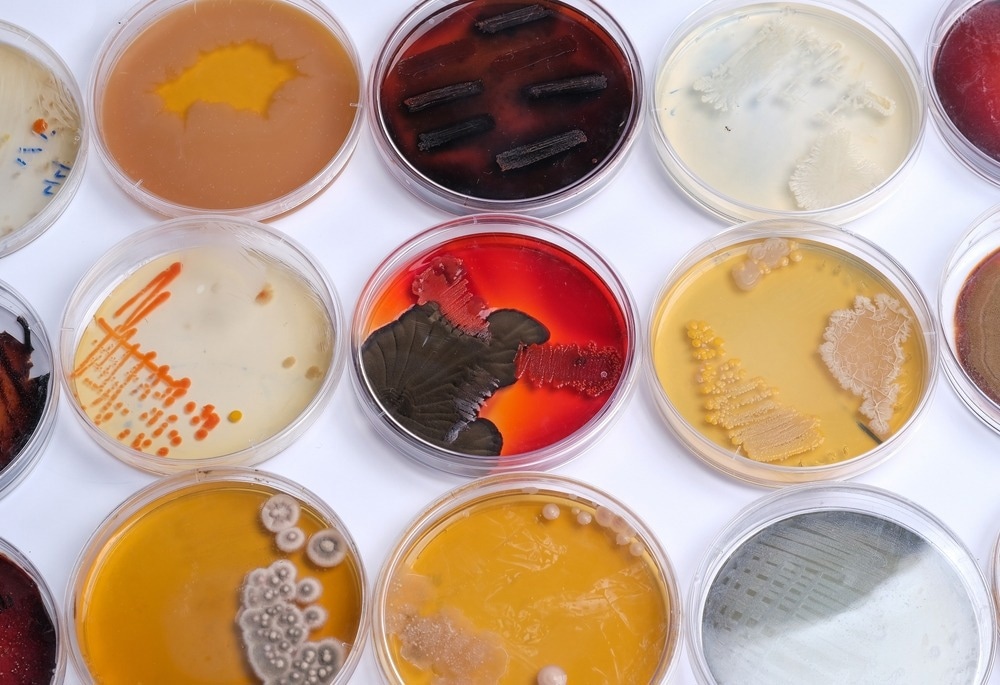
Image Credit: Mohammed_Al_Ali/Shutterstock.com
Microbial Assay Methods
There are several methods of performing a microbial assay. These include the disc diffusion method (otherwise known as the cylindrical cup plate method), the tube assay (or turbidimetric) method, the urease assay, and the luciferase assay. These methods have different uses.
The cylindrical cup plate method involves using circular plates of nutrient agar inoculated with a susceptible test organism. Some characteristics of the cup plate method include the selection of inoculant concentration to obtain suitable dose-response and sharp inhibition zones at different concentrations of the standard., keeping plates on a flat surface to ensure equal distribution of inoculant, and incubating plates at a suitable temperature over a set time.
Turbidimetric methods differ from the commonly used cylindrical cup plate assay by using tubes. Controls that are not inoculated with the target compound (usually antibiotics) are used to set the optical apparatus used to measure growth. When the tubes have been incubated, growth is arrested by adding formaldehyde R, or the opacity of tubes can be measured at a set incubation time. Appropriate statistical methods are used to calculate potency.
A urease assay is used to assay antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis, as these antibiotics also inhibit urea production. The urease production is indicated by an increase in the media’s pH. These antibiotics include streptomycin, netilmicin, azithromycin, and erythromycin. Certain microbes such as Proteus mirabilis can be used as these produce the enzyme urease. Urease assays have limited application.
Like urease assays, luciferase assays also have limited application. This assay uses the enzyme luciferase to detect the presence of ATP in a microbial sample. This is detected by bioluminescence. The assay can detect ATP at low concentrations in a bacterial culture. Antibiotics such as aminoglycosides inhibit ATP production, and this assay can be used to analyze the potency of these drugs.
Another type of assay is the radioenzymatic assay, which uses a radiolabelling element to analyze the potency of compounds.
Different Microbes Used in Microbial Assays
There is no single microbe used in a microbial assay. The selection of a microbial strain depends on the antibiotic being selected for testing. These include Staphylococcus aureus (for amikacin, tylosin, and tobramycin), Bacillus pumilus (for chlortetracycline, spiramycin, and kanamycin sulfate), Staphylococcus epidermis (for antibiotics such as gentamicin, neomycin, and novobiocin) and Klebsiella pnumoniae (for streptomycin.)
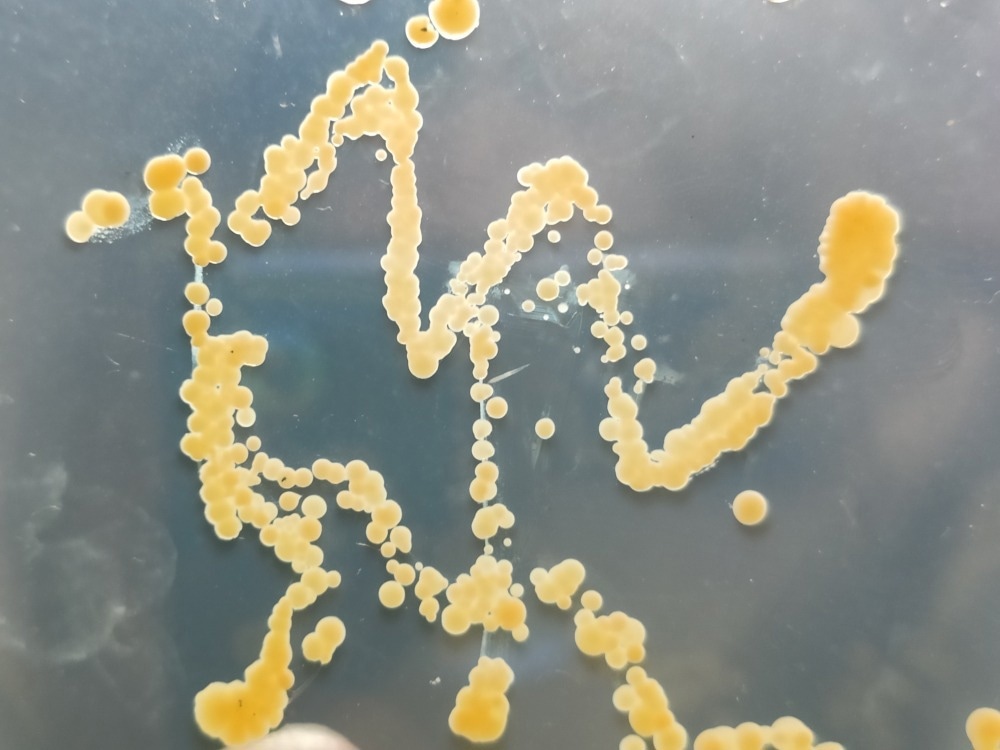
Image Credit: Kore/Shutterstock.com
Culture Media Used
Different culture media can be used in a microbial assay. The type of media selected depends on the microbe being used in the assay, for example, anaerobic bacteria, aerobic bacteria, or fungi. A fluid thioglycollate medium is used for anaerobic bacteria but can also be used for aerobic bacteria. Soyabean-casein digest is a culture medium for aerobic bacteria and fungi. Additionally, alternative thioglycolate medium can be used for viscous and turbid products as well as in devices that possess tubes with small lumina.
Culture media must be produced under strict conditions to ensure sterility so that the results obtained by the microbial assay on the potency of target compounds are error-free.
Summing Up
Microbial assays are crucial during research into the potency of drugs, chemicals, and other compounds. They are a requirement in numerous biomedical fields, and scientists can use several types of assays.
Different microbial strains are used in each assay to test the potency of drugs, and different culture media can be selected depending on the type of microbe used in the assay. Microbial assays are an important safety step in the process of drug and chemical research.
References:
Last Updated: Jan 31, 2023