Holotomography is used to image a microscopic label-free three-dimensional object in real time, such as tissues or cells using a laser.
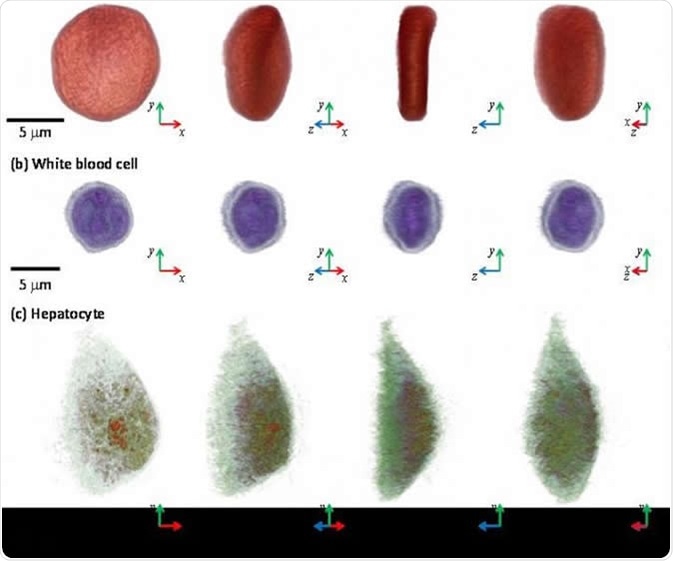
3-D images of a red blood cell, white blood cell, and hepatocyte via microscopic tool, the holotomography (HT)-1, TomoCube. IMAGE CREDIT: KAIST
How Does Holotomography Work?
Numerous 2D holographic images of a sample are measured across multiple angles of illumination by rotating either the laser source or the sample itself. Interferometry determines the refractive index of sample material along this plane. Laser light is divided into two, one beam passes through the sample and recombines at a detector. The optical phase of laser is affected by transmission through an object, such that the resulting difference in the phase of light upon recombination can be used to determine the density of a sample. The optical phase of light changes as it passes through an object as light is travels at a slower speed in different materials compared with vacuum.
[Webinar] Introduction to Holotomography SD
Holotomography in Cell Biology
Three-dimensional imaging of live cells without exogenous labeling agents is possible using holotomography. This method also provides cell information, such as cell volume, surface area, mass, membrane curvature, and protein concentration. The cell membrane and organelles can be imaged at a resolution of 100 nm, with no photobleaching or phototoxicity-induced damage to cells or interference with normal molecular activities. Although the refractive index values of materials can be precisely determined by holotomography, molecular determination can be difficult as most proteins have relatively similar refractive index values,. Holotomography can be applied to cytopathology, single-cell analysis, drug or toxicity reactions, cytology, and hematology.
Infectious Disease Diagnosis
RBC analysis
The analysis of red blood cells facilitates easier diagnosis of diseases, such as malaria or sickle cell anemia. Current methods are limited to counting red blood cells and measuring their properties in poor detail. Holotomography can determine the morphological, chemical, and mechanical properties of cells, including the presence of viral infection which is associated with unusually high refractive index values.
Scattering parameters
Scattering parameters of a tissue can be determined as laser light passes through significant volumes of tissue. There is uneven distribution of refractive indexes within the tissue, resulting in light refraction and reflection events. The morphological alterations of prostate, breast, and skin tissues that have become cancerous can be examined by holotomography to observe specific scattering effects. This provides potential diagnostic applications for holotomography in cancer treatment.
Future of Holotomography
The in vivo application of holotomography will significantly influence the early diagnosis of a variety of diseases. However, multiple light scattering through large volumes of biological tissue prevents acquisition of clear images. Recently progress has been to visualize red blood cells passing through micro capillaries near the surface of the skin, and also to image retinal cells in the eye using transcleral illumination. Future work will hopefully provide methods to extend the range of in vivo applications of holotomography.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Oct 24, 2018