Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells possess a nucleus enclosed within a cell membrane, making up one of the three domains of life, Eukaryota. They include multicellular organisms such as plants, animals, and fungi.
Bacteria and Archaea, the other two domains of life, are prokaryotic cells. They do not possess membrane-bound cellular compartments, such as nuclei.
 Lukiyanova Natalia Frenta | Shutterstock
Lukiyanova Natalia Frenta | Shutterstock
Similarities between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
Cell Membrane
Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells bear a lipid bilayer, which is an arrangement of phospholipids and proteins that acts as a selective barrier between the internal and external environment of the cell.
Genetic Material
Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells both use deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) as the basis for their genetic information. This genetic material is needed to regulate and inform cell function through the creation of RNA by transcription, followed by the generation of proteins through translation.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes facilitate RNA translation and the creation of protein, which is essential to the functioning of both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the medium in which the biochemical reactions of the cell take place, of which the primary component is cytosol.
In eukaryotic cells, the cytoplasm comprises everything between the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope, including the organelles; the material within the nucleus is termed the nucleoplasm. In prokaryotes the cytoplasm encompasses everything within the plasma membrane, including the cytoskeleton and genetic material.
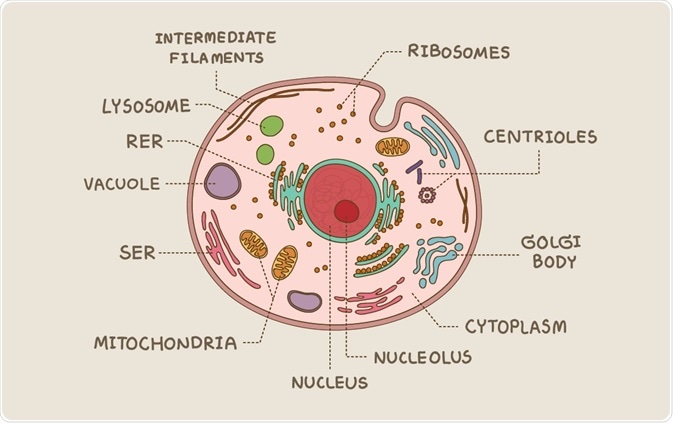 Structure of a eukaryotic cell. (Arisa_J / Shutterstock)
Structure of a eukaryotic cell. (Arisa_J / Shutterstock)
Differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
Cell size
Eukaryotic cells are ordinarily larger (10 – 100um) than prokaryotic cells (1 – 10um).
Cell arrangement
Eukaryotes are often multicellular whereas prokaryotes are unicellular. There are however some exceptions –unicellular eukaryotes include amoebas, paramecium, yeast.
True membrane-bound nucleus
Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus bound by a double membrane. It contains the DNA-related functions of the large cell in a smaller enclosure to ensure close proximity of materials and increased efficiency for cellular communication and functions.
In contrast, the smaller prokaryotic cells have no nucleus. The materials are already fairly close to each other and there is only a "nucleoid" which is the central open region of the cell where the DNA is located.
DNA structure
Eukaryotic DNA is linear and complexed with packaging proteins called "histones," before organization into a number of chromosomes
Prokaryotic DNA is circular and is neither associated with histones nor organized into chromosomes. A prokaryotic cell is simpler and requires far fewer genes to function than the eukaryotic cell. Therefore, it contains only one circular DNA molecule and various smaller DNA circlets (plasmids).
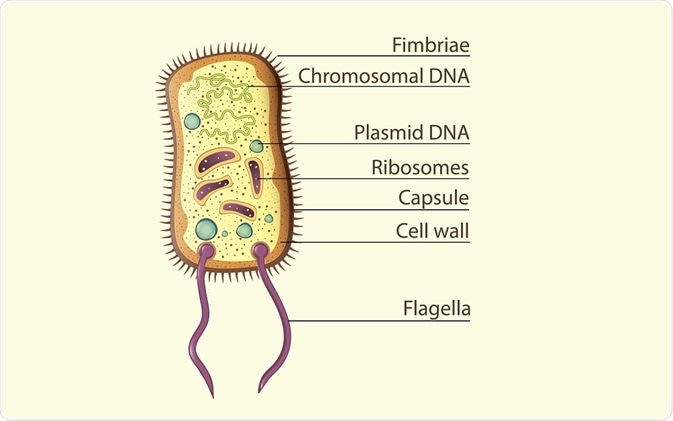 Structure of a prokaryotic cell. (In Art / Shutterstock)
Structure of a prokaryotic cell. (In Art / Shutterstock)
Membrane-bound organelles
Eukaryotic cells contain many membrane-enclosed, large, complex organelles in the cytoplasm whereas prokaryotic cells do not contain these membrane-bound organelles.
This is a key difference because it allows a high level of intracellular division of labor and contributes to the greater complexity characteristic of eukaryotic cells.
Due to the larger size of the eukaryotic cells, confining certain cellular process to a smaller area also increases the efficiency of functions by improving communication and movement within the cell.
Only eukaryotes possess a membrane-bound nucleus and membrane-bound organelles such as the mitochondria, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, peroxisomes and ER.
Ribosome size
Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells contain many ribosomes; however the ribosomes of the eukaryotic cells are larger than prokaryotic ribosomes i.e. 80S compared to 70S.
Eukaryotic ribosomes also show more complexity than prokaryotic – they are constructed of five kinds of ribosomal RNA and about eighty kinds of proteins. In contrast, prokaryotic ribosomes are composed of only three kinds of rRNA and about fifty kinds of protein.
Cytoskeleton
This is a multicomponent system in eukaryotes composed of microtubules, actin filaments and intermediate filaments. It is required for maintaining cell shape, providing internal organization and mechanical support. It is also paramount in movement and cell division.
Sexual reproduction
Most eukaryotes undergo sexual reproduction whilst prokaryotes reproduce asexually. Sexual reproduction in eukaryotes results in offspring with genetic material which is a mixture of the parents’ genome and during this process, genetic variation is generated via sexual recombination.
On the other hand, a prokaryote will reproduce clones of itself via binary fission and relies more on horizontal genetic transfer for variation.
Cell division
This occurs by mitosis for eukaryotic cells and binary fission for prokaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic cells undergo mitosis then cytokinesis. This involves numerous stages - the nuclear membrane disintegrates then the chromosomes are sorted and separated to ensure that each daughter cell receives two sets (a diploid number) of chromosomes. Following this, the cytoplasm divides to form two genetically identical daughter cells i.e. cytokinesis.
In contrast, prokaryotes undergo a simpler process of binary fission. This is faster than mitosis and involves DNA (nucleoid) replication, chromosomal segregation, and ultimately cell separation into two daughter cells genetically identical to the parent cell. Unlike mitosis, this process does not involve the nuclear envelope and centromere and spindle formation.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jul 19, 2023