Jun 3 2005
Abnormal prion proteins are little understood disease agents involved in causing horrific brain-wasting diseases such as Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease in people, mad cow disease in cattle and chronic wasting disease in deer and elk.
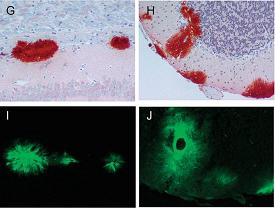 |
|
Abnormal prion proteins (red stain) also appear as plaques (green stain) in the brains of scrapie-infected mice expressing anchorless prion proteins. |
Now, new research suggests that a variant form of abnormal prion protein--one lacking an "anchor" into the cell membrane--may be unable to signal cells to start the lethal disease process, according to scientists at the Rocky Mountain Laboratories (RML), part of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
"This work provides novel insights into how prion and other neurodegenerative diseases develop and it provides tantalizing clues as to how we might delay or even prevent such diseases by preventing certain cellular interactions," notes NIAID Director Anthony S. Fauci, M.D. A paper describing the research was released online by the journal Science. RML virologist Bruce Chesebro, M.D., directed the project. Other key co-authors from the Hamilton, MT, RML laboratory include Richard Race, D.V.M., and Gerald Baron, Ph.D. Their collaborators included Michael Oldstone, M.D., and Matthew Trifilo, Ph.D., of The Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, CA, and Eliezer Masliah, M.D., of the University of California, San Diego (UCSD).
Drawing on experimental concepts first developed at RML a decade ago, the research team exposed two groups of 6-week-old mice to different strains of the agent that causes scrapie, a brain-wasting disease of sheep. Within 150 days of being inoculated with the natural form of scrapie prion protein, all 70 mice in the control group showed visible signs of infection: twitching, emaciation and poor coordination. In contrast, the scientists observed 128 transgenic mice--those engineered to produce prion protein without a glycophosphoinositol (GPI) cell membrane anchor--for 500 to 600 days and saw no signs of scrapie disease. Subsequent electron microscopic examinations at UCSD, however, confirmed that they produced amyloid fibrils, an abnormal form of prion protein, and that they even had brain lesions. More remarkably, according to Dr. Chesebro, the diseased brain tissue resembled that found in Alzheimer's disease rather than in scrapie.
Chesebro mentions two theories as to why the transgenic mice did not show symptoms of illness despite being infected:
- The host cell might require the GPI anchor to receive the "toxic signal" from the abnormal prion protein
- The plaques might be less toxic than the non-plaque form of prion protein clumps
In either case, more time might be required to produce disease due to the reduced toxicity, Dr. Chesebro says.
"There was so much about this research that surprised us and gave us ideas to pursue," says Dr. Chesebro. "First, the mice didn't get sick. That's very significant. Second, the dense accumulations of scrapie plaque in the brain resembled the plaque seen in Alzheimer's, but it wasn't toxic," which might support more recent concepts about plaque in Alzheimer's patients. "Previously, most researchers thought plaques were the toxic component of Alzheimer's that kills neurons, and many treatments focus on removing the plaques. But what if the plaques are inert, as they were in this research? What if only small clumps are toxic?"
If this hypothesis proves correct, Dr. Chesebro says, the ongoing research could eventually alter scientists' views on preventing prion diseases, shifting emphasis away from stopping the production of prion protein clumps and toward preventing interactions with prion protein anchored to cells, or learning to direct abnormal prion protein accumulations to specific parts of the brain where they will not produce symptoms.
"Abnormal prion protein by itself may not be rapidly lethal--in these mice it wasn't," Dr. Chesebro says.