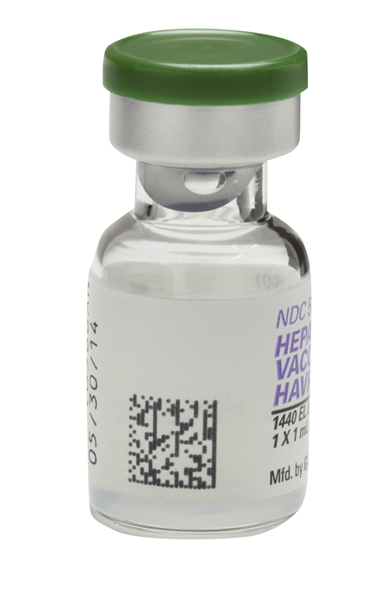
2D barcodes contain product identification, lot number, and expiration date. Linear barcodes only contain product identification information.
Additionally, 2D barcodes have much more capacity and take up less space. A 2D barcode with Data Matrix technology can hold approximately 2,300 characters while a traditional linear barcode can hold approximately 48 characters.

Why have GlaxoSmithKline recently announced that they will be placing two-dimensional (2D) barcodes on both the inner containers and outer boxes of the majority of their U.S. vaccines?
GSK believes 2D barcoding is important because it is an initiative in response to customer needs and a move to support electronic medical records. With the necessary hardware and software for this technology, healthcare providers can update their inventory management system, patient records and vaccination reports automatically, reducing the need for manual entry of information, which can be susceptible to administrative errors and incomplete record keeping.
With the separate 2D barcode on the box, it may help facilitate tracking and inventory management of unopened boxes as soon as they arrive in a healthcare provider or institutional pharmacy’s practice and/or as the vials or pre-filled syringes are administered to patients.
In addition, through the regular electronic scanning of the additional information contained in 2D barcoding, we believe that a more accurate and complete picture of US vaccine usage could emerge.
GSK’s decision to implement 2D barcoding represents a commitment beyond the pilot initiative, which the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) began in 2011 with support from key organizations, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and other manufacturers.

What are the benefits of 2D barcoding and are there any drawbacks over traditional linear methods?
2D barcodes contain product identification, lot number, and expiration date. Linear bar codes only contain product identification information. Additionally, 2D bar codes have much more capacity and take up less space. Having 2D barcodes on vaccines, while an important piece, is only the first step of many that practices will need to fully utilize 2D barcoding in the office.

What will the records of immunization taken from the vaccines with 2D barcodes be used for?
The data scanned from the 2D barcode will be entered into the patient’s electronic medical health record, which is then sent to the state’s Immunization Information System (IIS).
In addition, the data scanned from the 2D barcode can be entered into the immunizer’s electronic vaccine inventory management system.
Last but not least, immunizers also have the option to scan 2D barcodes on the Vaccine Information Statements (VIS), which the CDC began adding in 2012. Immunizers are required to give the statement to each patient who receives a vaccine so they are aware of each vaccine’s risk/benefit profile.
Do GSK plan to place 2D barcodes on all of their products?
There are no plans at this time to add 2D barcodes to our prescription medicines.
 How important do you think 2D barcoding will be in the future?
How important do you think 2D barcoding will be in the future?
Through the regular electronic scanning of the additional information contained in 2D barcoding, we believe that a more accurate and complete picture of US vaccine usage could emerge.
What are GSK’s plans for the future?
GSK vaccines that are approved in the US and packaged and shipped out of a US facility (Marietta, PA) will contain the 2D barcodes. In time, GSK plans to add 2D barcodes to vaccines approved in the US but are packaged and shipped from abroad.
Where can readers find more information?
For more information about the CDC’s 2D barcoding pilot project, including the CDC’s initiative to add 2D barcoding to Vaccine Information Statements, please visit http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/programs/iis/2d-vaccine-barcodes/.
In addition, healthcare providers can visit http://www2.aap.org/immunization/pediatricians/barcoding.html for the AAP’s clinical guidance to help implement the necessary technology to use 2D barcoding. Having 2D barcodes on vaccines, while an important piece, is only the first step of many that practices will need to fully utilize 2D barcoding in the office.
About Dr. Leonard Friedland
 Leonard Friedland, MD, is a pediatrician and pediatric emergency medicine trained physician, and vaccine research scientist.
Leonard Friedland, MD, is a pediatrician and pediatric emergency medicine trained physician, and vaccine research scientist.
Leonard is a graduate of Vassar College and Mount Sinai School of Medicine. His residency and fellowship training was in Philadelphia at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and St. Christopher’s Hospital for Children.
He was on staff at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center (Assistant Professor) and Temple University Children’s Hospital (Associate Professor) before joining GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals in 2003.
Leonard currently is Vice President and Director of Scientific Affairs and Public Health, Vaccines in North America at GSK. He has been involved with the development of many vaccines currently recommended for use in infants, children, adolescents, adults and the elderly.