Xenics, Europe's leading developer and manufacturer of advanced infrared imagers, cameras and customized imaging solutions from the LWIR to the visible realm, is collaborating in path breaking clinical research programs with the VU University Medical Center of Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
Central to the setup at VUmc is the Xenics thermal camera Gobi-640 for non-invasive diagnostics and treatment evaluation. One specific project is focused on burn wounds in collaboration with the Dutch Burn Center in Beverwijk. Researchers from VUmc will present a review paper on thermal imaging in medicine at SPIE BIOS in San Francisco on February 9, 2015. Xenics will exhibit at BiOS and Photonics West 2015 in Booth (8)834.
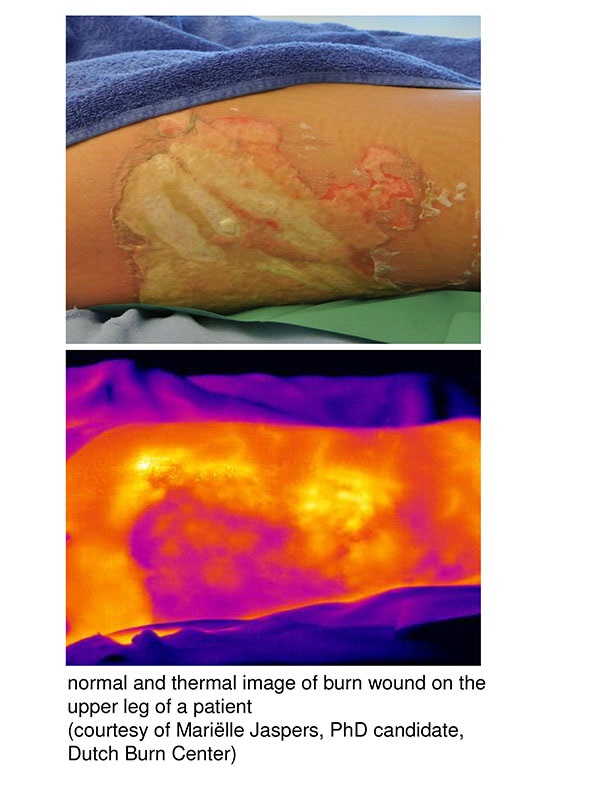
Assessing burn wounds of various degrees in terms of the incurred tissue damage and their healing prospects requires effective diagnostic tools to determine upfront whether the probability of scar development would necessitate a skin transplantation. Such diagnostic and treatment procedures should be based on a very simple, compact and cost-effective apparatus suited for the clinical environment for an easy, reliable and straightforward interpretation and statistical analysis. They also should allow real-time monitoring of the healing progress over the duration of the treatment.
Above all, as medical practitioners request, burn wound diagnostics should be non-contact alleviating the burden on patients by replacing traditional biopsy and histological examination as well as high-resolution microscopy, which is limited to the observation of relatively small skin areas.
This is where thermal imaging comes in, now that IR cameras have become easy to use without complicated calibration and cooling measures. Here, Xenics is breaking new ground with its thermal camera Gobi-640. Originally designed for demanding industrial research and manufacturing environments, the Gobi is proving its suitability for medical research and clinical practice due to its compact and affordable plug-and-play layout, on-board processing capabilities and extensive software platform Xeneth 2.5 for analysis.
"We feel honored to be a project partner of a distinguished academic institution such as VUmc, in a far reaching clinical research program", said Bob Grietens, Xenics founder and CEO. "This proves that Xenics is at the forefront of IR camera and systems design in terms of usability and versatility, as well as image quality and high reliability."
Rudolf M. Verdaasdonk, PhD, a professor at VU and Head of the Department of Physics and Medical Technology at the VU Medical Center, stated: "Thermal cameras have become small and practical with ever higher image and temperature resolutions. The Gobi-640 camera in particular has shown to be a versatile instrument for observing physiological processes such as in burns wounds. These observations are mainly based on perfusion, meaning the blood streaming from the core body through the peripheral vessels towards damaged skin tissue and showing the presence of an intact or damaged microvasculature, depending on the temperature measured."
Image resolution, Dr. Verdaasdonk explained, is the foremost consideration when using thermal cameras in this clinical context. Spatial resolution should reach 1 mm on the skin area examined, which the Gobi-640 readily achieves with its 640x480 pixel layout. Second is temperature resolution to discriminate between the minuscule differences in blood temperature specific to superficial or deep dermal burn wounds. In this regard Gobi-640 features a measurement threshold of 0.05 °C.
A specific advantage of thermography in the clinical study carried out at the Dutch Burn Center, under supervision of plastic surgeon professor Paul van Zuijlen, is that it enables the continued observation and real-time evaluations of burn wounds to notice improvements in the healing process. For this purpose, the infrared-sensitized Gobi-640 can be combined with a camera for the visible realm having the same field of view to compare both image representations.
Another benefit of the Gobi-640 is the included, extremely versatile Xeneth 2.5 software platform. It enables the continuous control of all camera settings to optimize the performance and processability of the captured IR imagery. It allows data export to standard scientific analysis programs such as LabVIEW for detailed investigations.
In sum, Dr. Verdaasdonk said, thermography could provide much better diagnostic options in the early stages of burn wounds, and it could enable a much better evaluation of the healing progress."I foresee that in the future every medical practitioner will have some smartphone device with a thermal camera in their pocket. This could even extend to popular health apps used at home."
About Xenics
Xenics is a pioneer of infrared technology with a proven track record of more than ten years. Xenics designs and markets infrared imagers, cores and cameras of best-in-class image quality to support innovative R&D, industrial automation, machine vision, process control and high-end security applications. Xenics offers a complete portfolio of line-scan and 2-D area-scan products for the VisNIR, SWIR, MWIR and LWIR ranges. A vertically integrated manufacturer with advanced production facilities and in-house know-how, Xenics delivers state-of-the-art solutions and optimized custom designs. As a European vendor with a worldwide sales and service network, Xenics supports its customers with simplified export procedures. More at: www.Xenics.com.
About VUmc
The VU Medical Center is closely linked with VU University (Vrije Universiteit) Amsterdam. Core objectives are delivering patient care in close association with scientific research, academic teaching and postgraduate training. About 700 full-time research staff maintain an internationally competitive position in its fields of specialization: cancer and immunology, neurosciences, cardiovascular diseases, movement sciences, public health, primary care, and long-term care issues. The research focus is tailored to human health and life science programs. VUmc currently participates in 40 EU-funded research projects. More at: www.vumc.com/research