Leica Microsystems CMS GmbH has entered into an exclusive, worldwide licensing agreement with Columbia University in New York to commercialize SCAPE microscopy for Life Science applications.
SCAPE (swept confocally aligned planar excitation) microscopy forms 3D images of living samples by scanning them with a sheet of laser light.
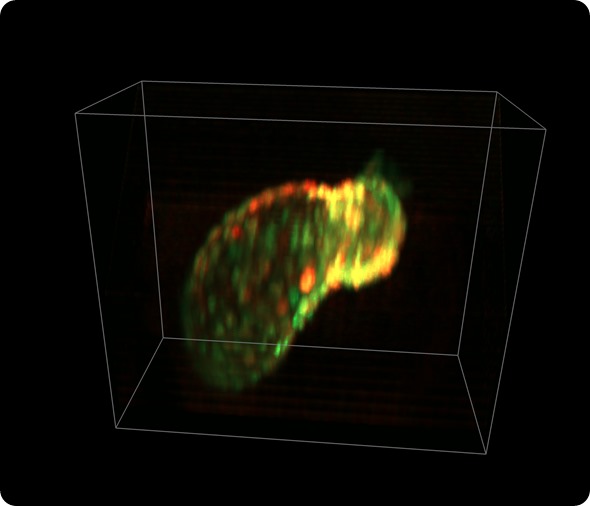
Zebrafish heart: Beating heart of zebrafish larva (56 hours after fertilization). Myocytes are expressing GCaMP (calcium indicator) and dsRed (cell marker). Imaged in-vivo using SCAPE at 25 volumes per second. 335 x 288 x 156 micron field of view. Credit: Hillman/Li/Targoff, Columbia University.
SCAPE’s unique capabilities allow scientists to perform fundamentally new kinds of experiments, from imaging individual neurons firing throughout the brain of adult fruit flies, to tracking calcium waves through cells in the beating heart of a zebrafish.
SCAPE also stands to create new inroads for understanding diseases such as cancer, and for the development of new drugs and therapies.
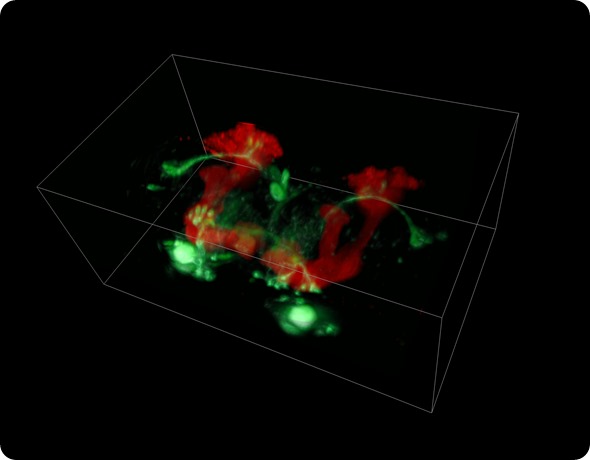
Fruit fly brain: Whole brain of adult Drosophila acquired in-vivo at 10 volumes per second using SCAPE. Neuronal subset expressing GFP (green), mushroom body neurons expressing dsRed. 450 x 264 x 227 micron field of view. Credit: Hillman/Li/Schaffer, Columbia University.
SCAPE microscopy was developed in the laboratory of Elizabeth Hillman, PhD, associate professor of biomedical engineering and radiology at Columbia University and a principal investigator at Columbia’s Mortimer B. Zuckerman Mind Brain Behavior Institute.
SCAPE’s ingenuity lies in being able to both scan and image a moving light sheet through a single, stationary objective lens. SCAPE delivers 3D-imaging speeds that are 10 to 100 times faster than conventional point-scanning microscopes, while maintaining the benefits of light-sheet imaging including low photodamage.
Compared to conventional light-sheet microscopes that require multiple objective lenses and complex sample positioning, SCAPE’s patented single-objective approach greatly diversifies the range of intact and freely moving samples that can be imaged in 3D at near video-rates. SCAPE technology was recognized late last year with a prestigious grant award from the National Institutes of Health BRAIN Initiative.
SCAPE’s ability to perform real-time 3D imaging at cellular resolution in living, freely moving organisms is a new frontier for neuroscience research,” said Dr. Hillman. “Beyond neuroscience, SCAPE is enabling fundamentally new scientific experiments by transforming our ability to capture 3D structure and function, movement, behavior and cellular activity in real-time across a wide range of organisms and biological samples.”
In addition to their own intellectual property, Leica Microsystems has also exclusively licensed OPM (Oblique Plane Microscopy) technology from Imperial Innovations. The technology was invented by Christopher Dunsby, PhD, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Department of Physics at Imperial College London.
“Leica Microsystems is committed to investing in the most promising technologies in order to drive our innovation, and these are excellent examples of that strategy” said Markus Lusser, President of Leica Microsystems.
“We recognize that the accelerating use of GCaMPs, fluorescent reporters and optogenetics presents an urgent need for high-speed volumetric imaging of living samples – and that this is a current major gap in the microscopy market. We are thrilled to have the opportunity to develop next-generation imaging systems that will drive discoveries in neuroscience, biology and medicine by capturing life in action” – said Prof. Julian F Burke, Chief Scientific Officer of Leica Microsystems.