Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a group of metabolic disorders that cause sustained high blood sugar levels. In the past, only two types of diabetes were known, type 1 and type 2. Gestational diabetes is a third type which occurs only during pregnancy. Now, DM has been reclassified into five subtypes.

Image Credit: Africa Studio
What is diabetes mellitus?
DM is a disease that prevents the body from producing energy from the food consumed. It is due to the reduced or absent production of insulin from the organ called the pancreas. Insulin is a hormone produced by the beta cells of the pancreas which helps the body cells to take up glucose from the bloodstream to use for energy for its various metabolic processes. DM can also be due to the production of non-functional insulin.
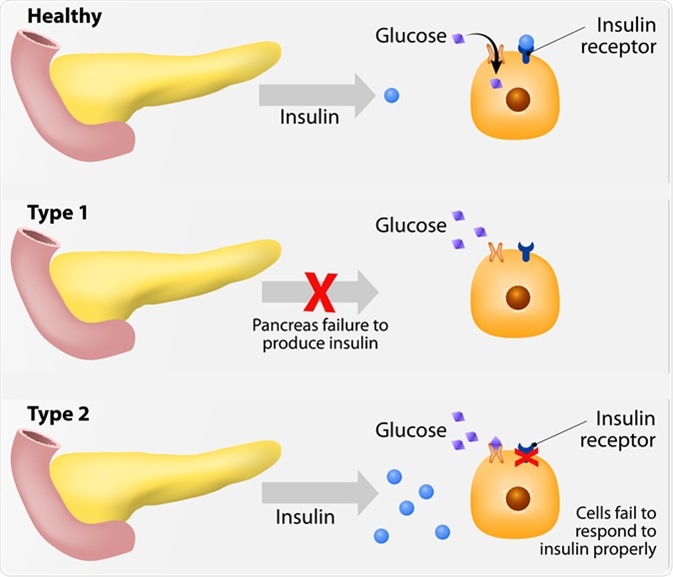
Main types of diabetes mellitus. Either the pancreas not producing enough insulin or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced. Image Credit: Designua / Shutterstock
Types of diabetes mellitus
DM was formerly classified as Type 1 or the insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) and non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). Gestational diabetes, on the other hand, occurs only in pregnant women.
IDDM occurs as a result of damage to the pancreatic beta cells, resulting in the inadequate production of insulin. With little or no insulin, blood glucose levels remain high, leading to a number of complications. Patients with IDDM require treatment with insulin injections to control their blood glucose levels.
NIDDM is a type of diabetes wherein the pancreas produces insulin, but in insufficient quantities, or when the insulin produced does not act upon the cells to promote the intake of glucose. The cells of the body may not react to the action of insulin, and this is called insulin resistance.
Newer research has shown that there are five subtypes of DM.

Diabetes patient shot by syringe with dose of insulin. Image Credit: goffkein.pro / Shutterstock
Cluster 1: Severe autoimmune diabetes (SAID)
A form of type 1 DM that affects people who are relatively young, this type was classified traditionally as type 1 diabetes, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the beta cells, affecting insulin production.
People with SAID are typically diagnosed early, at a young age. They usually have a low body mass index (BMI), insulin deficiency, poor control of blood sugar, and presence of glutamate decarboxylase antibodies (GADA). These antibodies are associated with late-onset autoimmune diabetes (LADA), often mistaken for type 2 diabetes, but requiring insulin treatment just like Type 1 DM.
Cluster 2: Severe insulin-deficient diabetes (SIDD)
Severe insulin-deficient diabetes (SIDD) is a subtype resembling cluster 1. These patients are also young at diagnosis, and have low BMI. However, they do not have GADA. These patients have defective beta cell function, but the reason is unknown.
Cluster 3: Severe insulin-resistant diabetes (SIRD)
People with SIRD are overweight and have high insulin resistance, which means their bodies produce insulin, but the cells fail to respond to it. Patients with SIRD are at a higher risk of developing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Cluster 4: Mild obesity-related diabetes (MOD)
Mild obesity-related diabetes (MOD) refers to patients who are obese or overweight but do not show insulin resistance. This subtype occurs in people with a milder form of diabetes, without as many metabolic problems as in the other subtypes.
Cluster 5: Mild age-related diabetes (MARD)
Mild age-related diabetes (MARD) is a subtype which affects people who are typically older than with the other subtypes. They have only mild difficulty with blood sugar control. This is the most common type of diabetes accounting for about 40% of cases.
Prediabetes
This is a common condition, often unrecognized, where blood glucose levels are persistently higher than normal but not within the diabetic range. These individuals have a higher risk of developing DM, but this can be reversed with a program focusing on lifestyle change.
What diabetes mellitus subtype is the most serious?
Patients who have cluster 3 or SIRD are at the highest risk of developing kidney disease. Kidney disease is a complication of diabetes, which can become severe over time. Cluster 2 has the greatest risk of diabetic retinopathy. This can lead to blindness or vision loss.
Early detection and proper treatment are important for appropriate treatment. The purpose of this classification is to enable appropriate treatment and to provide a better prognosis for the condition.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Dec 9, 2022