The scanR high-content screening (HCS) station provides fully automated image acquisition and data analysis. Version 3.3 improves the deep-learning technology’s capabilities to reliably separate objects in biological samples using instance segmentation, the ability to detect and delineate distinct objects of interest in an image.
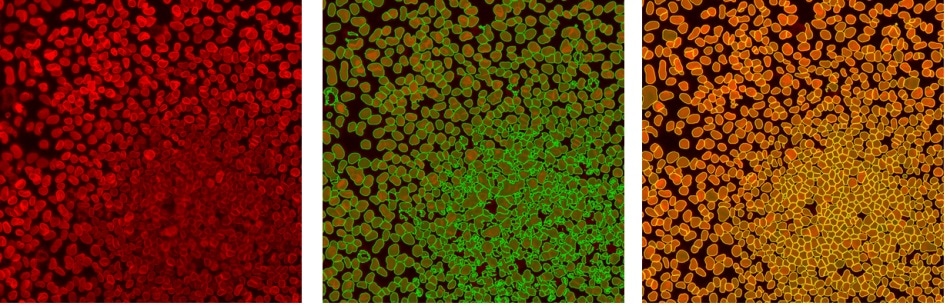 Accurate object segmentation: raw data (left), standard threshold (middle), TrueAI instance segmentation (right). Instance segmentation reliably separates difficult-to-distinguish objects that are very close together, such as cells or nuclei in colonies or tissue. Image Credit: Olympus Life Science Solutions
Accurate object segmentation: raw data (left), standard threshold (middle), TrueAI instance segmentation (right). Instance segmentation reliably separates difficult-to-distinguish objects that are very close together, such as cells or nuclei in colonies or tissue. Image Credit: Olympus Life Science Solutions
Reliable image segmentation
Using a self-learning microscopy approach, the scanR system’s AI automatically analyzes data in an assay-based workflow. The deep-learning technology can detect cells, nuclei and subcellular objects, and extract features from a list of over 100 object parameters. Version 3.3 significantly improves the deep learning object segmentation capabilities to more accurately segment difficult-to-distinguish objects, such as cells or nuclei that are very close together, like in cell colonies or tissue.
Pretrained models
In addition to tools to develop neural network models for specific applications, scanR version 3.3 comes with pretrained neural network models for nuclei and cells. These can be used in a broad range of standard applications, including the ability to distinguish between confluent cells and dense nuclei, eliminating the time to train the neural network.
Easier calibration and collaboration
Version 3.3 of the scanR software also includes a well plate calibration assistant that makes it fast and simple to calibrate a new well plate for the system. In addition, a new level of license enables collaborators to open, review and re-gate scanR analysis files for easier results sharing.