Today, the life sciences industry is facing more and more globalization, regulatory enforcement, and product supply chain complexity. Life sciences companies must show to auditors that they are in complete control of their training management programs and GxP document.
A study by UL Compliance to Performance showed that in 2015, 50% of 483 CDER observations were procedure-related, with “Procedures not in writing, fully followed” (21 CFR 211.22(d)) as the most cited observation by FDA investigators for pharmaceutical firms.
Regulatory agencies are increasingly focusing on GxP procedural issues, necessitating organizations to enhance training record management and document management.
There are many companies that have invested in “best-of-breed” Learning Management Systems (LMS) and Document Management Systems (DMS). For consistent operation and greater visibility, a LMS and DMS governance model is usually implemented to define important business processes including:
- How to manage impact from new releases
- How to use system security roles
- How to apply nomenclature
Integration of these applications enables organizations to easily achieve good governance, and simplifies the document creation, review, and approval to training distribution and receipt process.
This article discusses how advanced, cloud-based DMS to LMS integrations streamline the governance model for life sciences organizations. By adopting an integrated solution that supports well-defined administrative rights and targeted training groups, and speeds up key document creation to training processes companies can gain the following benefits:


Eliminating SOP management risks
With life sciences companies witnessing international growth, adding new suppliers or opening new facilities, they encounter three major document and training management risks:
1. Compliance
Compliance is the first, and possibly the most costly risk. The US FDA and other global regulatory agencies have made procedural control one of the top enforcement issues.
In 2015, “Procedures not in writing, fully followed” (21 CFR 211.22(d)) was the most cited US FDA observation of pharmaceutical companies.

2. Lost knowledge
“Lost knowledge” is the second risk. When a small set of people possess most of the operational knowledge, organizations face the risk of losing best practices.
A new team may take several months to define and map the governance process if key personnel move to new job roles, resulting in draining of organizational resources and affecting operational efficiency.
3. Change management

Change management is the third risk. There has been rapid expansion of companies, through acquisition or organic business growth. As business areas grow, new procedures on SOP management, and employee qualifications and training are being established.
For instance, a remote team could define its own nomenclature for managing SOPs and associated training items, or frame its own policies for departmental visibility into training management.
The ability of the quality assurance team and senior management executives may be challenged by siloed processes in order to gain an insight into the state of quality compliance across several product lines and facilities.
When new people are added to a process, success depends on a governance strategy capturing and enforcing key policies and operational rules. Such a policy is needed by a DMS to LMS workflow. In life sciences companies, key document owners must have the ability to access, review, approve, distribute, and assess competency on controlled documents including the SOPs.
Defined rules are also required to establish learner groups and manage training. The DMS to LMS process needs feedback from stakeholders such as subject matter experts, documentation personnel, and department and training managers.
Governance model spanning DMS and LMS applications
Several leading life sciences companies have developed governance models on the basis of these key areas in document and training management policies:
- SOP management policy: lays emphasis on document creation and SOP reviewer responsibilities, nomenclature, and definition of stages such as ‘Pending’, ‘Approval’, and ‘Effective’.
- Training policy: covers scope, training responsibilities, processes for GxP-trained and non-GxP personnel, training documentation, training curricula, yearly GxP training, and external training.
- Use and operation procedures: instructions for managers, administrators, and other personnel for general use and operations.
DMS avoid many of the “paper shuffling” tasks, reduce regulatory risk, and allow document owners to focus more on developing SOPs. The approval and filing process is streamlined by automation of routing of documents and version control, and by easily providing a full document history.
Cloud-based DMS applications allow document owners to engage in secured, real-time collaboration with authorized employees and partners located anywhere in the world, thus accelerating the document review and approval process.
Integrating DMS and LMS applications enables SOP management and training in a timely manner. The process is improved and made more effective and efficient by the use of modern, well-integrated solutions.
In order to develop a governance strategy that spans both DMS and LMS, organizations should take into account its impact on existing processes, and make sure that the DMS to LMS integration facilitates the alignment approach. Four types of “system governance” questions are usually asked during the design phase:
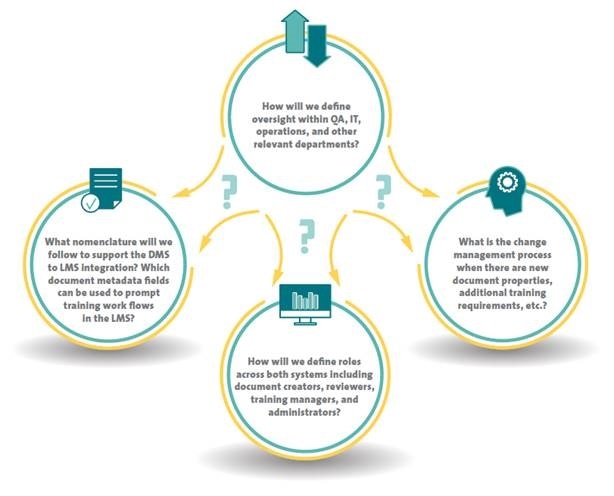
A governance strategy accommodating non-GxP and GxP departments enables better operational alignment, thus enhancing operational efficiencies. The strategy synchronizes document and training processes in various areas such as clinical, laboratories, quality assurance, and R&D in order to help continuous improvement and knowledge management in the entire organization.
An effective DMS to LMS integration shapes the company’s vision on managing critical content — improving business efficiencies and driving regulatory compliance.
Improving SOP management. top ten capabilities of seamlessly integrated DMS and LMS solutions
Today’s technology advances enable companies to leverage best-of-breed LMS and DMS applications to ensure seamless SOP management and training. In order to enhance productivity of all job roles of the process, the top 10 capabilities of well-integrated, modern solutions include:
1.Real-time integration
The LMS quickly detects metadata and document changes in the DMS such as new document title change, document version, etc. On the basis of the type of change, LMS automatically starts workflows for new training jobs or for trainers to review the training item.
Real-time integration is advantageous over a daily file-based batch import since the former shortens the time from when training impacted content is created or modified to in-use, reducing compliance risk and improving operational efficiency.
2.Training item status flow
Taxonomy mapping is facilitated by DMS to LMS integration, allowing critical document metadata fields to automatically initiate LMS workflows. For instance, if a DMS document shows a “pending” status, the training manager can add an assessment, through the LMS, prior to making it an “approved” document.
Version updates are automatically carried out, and new training assignments for targeted learners are enforced, when there are new SOPs or the SOPs are modified.
3.Flexible system security roles
Administrative, approver, learner systems enable proper definition of security roles in the LMS and DMS. For instance, an LMS administrator having a proper security profile may define training rules such as adding of an item in a curriculum and including a retraining period, or a quiz, etc.
4.Alternative training items
The LMS allows storing of a “link” to the source-controlled document in the DMS and allows a classroom event or assessment to be added, thus enabling a link back to the original SOP training item.
5.Audit trails
All document-related events, including learning and compliance actions or tasks, are logged in detailed audit trails from content creation, review, and approval to training completion and assessment.
6.Short implementation time
Cloud integrations have shorter implementation times than those of legacy solutions. Companies merely have to configure the integration to align the DMS and LMS in order to enable employees and partners to speed up content creation, sharing, and training.
7.Ease of “change control:”
With less IT involvement, the solution is conveniently modified to support downstream workflows when there is a change in the metadata of the DMS or LMS. Minimizing the change control costs is a major advantage of cloud-based applications over legacy solutions. For instance, an HTTPS Post Interface needs the IT team to manage and maintain business logic.
8.Accelerated validation
Companies are always on the lookout for the latest release with multi-tenant cloud. Applications designed for regulated industries ease validation and facilitate compliance such as performing IQ/OQ, and offering test scripts and other validation documentation related to integration with each release.
9.Ease-of-use
Modern, integrated cloud solutions feature a consumer web design to facilitate higher user adoption, and offer a seamless user experience across content creation, review, and approval to training and assessment process. It is also convenient to train partners and employees, thus accelerating the onboarding process.
10.Visibility into compliance risk
Operationally alignment of the LMS and DMS solutions allows more visibility into compliance and risk. Organizations become aware of which SOPs have been created but not yet trained on, or find out which SOPs have poor track performance and poor assessments with the recent versions of the critical document.
Case study: integrating Veeva Vault QualityDocs with ComplianceWire
With Veeva’s support, the UL team developed an integration tool called CWConnector that embeds governance best practices into the DMS to LMS integration. The tool exploits Vault’s Public APIs to facilitate the integration between UL’s ComplianceWire learning management system and the Veeva QualityDocs document management system.
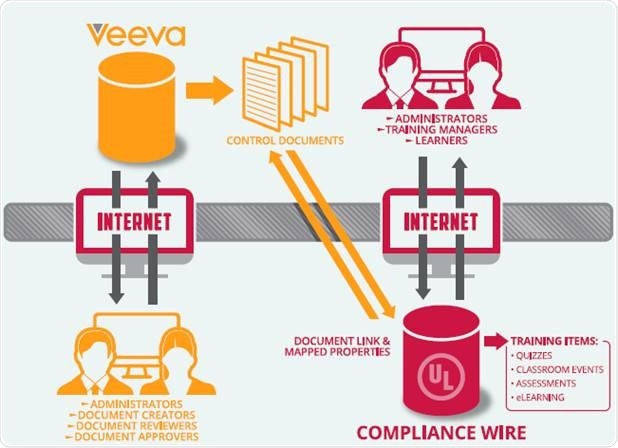
Once the CWConnector has been enabled for a client, metadata and document changes made in Vault QualityDocs, such as a document title change, new document version, etc. are detected by the tool. Next, CWConnector updates the equivalent “training item” for that specific document in ComplianceWire. For the latest controlled document in Veeva, the corresponding training item is defined in ComplianceWire.
The LMS administrator is capable of defining training rules, such as adding a quiz, adding a retraining period, including training items in a curriculum, and so on. Once the learners receive the training item assignment, they can click a link that shows the exact electronic file residing in Vault QualityDocs.
The integration of Vault QualityDocs and ComplianceWire guarantees that all document activities together with learning and compliance learning activities are logged in comprehensive audit trails that extend from content generation, review, and approval to assessment and training.
Conclusion
Operational alignment is improved when companies invest in a governance model to cover both DMS and LMS applications. This is important for achieving continuous process improvement and knowledge management in the entire organization.
By leveraging modern technology having several key capabilities, companies are able to easily support best practices for DMS and LMS integrations.
This entails gaining many benefits such as accelerated change management processes, efficient administration, and improved productivity of all employees involved in the content creation to training workflow. Therefore, organizations can focus more on developing important SOPs and promoting effective training processes.
Life sciences companies can ensure stronger adherence to international regulatory requirements by having more control over governance processes for DMS and LMS integrations and enhancing SOP management.
About UL Compliance to Performance
UL Compliance to Performance provides knowledge and expertise that empowers Life Sciences organizations globally to accelerate growth and move from compliance to performance.
Our solutions help companies enter new markets, manage compliance, optimize quality and elevate performance by supporting processes at every stage of a company’s evolution.
UL provides a powerful combination of advisory solutions with a strong modular SaaS backbone that features ComplianceWire®, our award-winning learning and performance platform.
UL is a premier global independent safety science company that has championed progress for 120 years. It’s more than 12,000 professionals are guided by the UL mission to promote safe working and living environments for all people.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.