Sponsored Content by StäubliOct 5 2018
The importance of sterilizing medical connectors and equipment is impossible to overstate. According to the National Center for Health Statistics, 48 million surgical procedures were performed in the United States in 2009.1 Each one of these procedures involved contact between surgical instruments and patients; the combined influence of which represents hundreds of millions of potential opportunities for infection to be introduced to patients by medical equipment.
Credit sfam_photo | Shutterstock
The effects of failure to properly sterilize equipment are well documented, and it’s clear that these processes are crucial both for broad infection control and the wellbeing of individual patients.2,3
The electrical equipment used in medical environments is no different to scalpels and forceps in this regard: a multitude of leads, connectors, and devices with integrated electronics are used in modern medicine; and being able to effectively sterilize these sensitive pieces of equipment is vital.
As electrical connectors often cannot be housed inside the protective casing of the machine, considerations need to be made as they will be effectively cleaned and sterilized without damage. Stäubli Electrical Connectors works with OEM manufacturers and their Medicalline range of connectors to find the best solution based on how the product will be sterilized.
The removal of infectious agents from equipment in hospitals and other clinical settings can be broken down into three distinct stages: cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization.4
Cleaning refers to the manual removal of visible residues such as dust, dirt or blood; and is always the first step in the preparation of any equipment for use or reuse. Cleaning is often followed by either disinfection or sterilization depending on the application.
Disinfection is the reduction or complete removal of pathogenic microorganisms, which is carried out to varying degrees depending on the patient or application: Stethoscopes (which contact intact skin) should undergo “low-level” disinfection, while equipment such as endoscopes (which contact mucous membranes) should undergo “high-level” disinfection.
For some equipment, disinfection is not sufficient: Instead, it must be completely sterilized. This is the highest level of decontamination and refers to the complete removal of all microorganisms including bacterial spores.5
According to WHO and CDC guidelines, sterilization is required of anything coming into contact with the vascular system or sterile tissues inside the body: this includes all surgical instruments and implants, such as electrosurgical/ablation devices, electrophysiological equipment and pacemakers.6
The most common and reliable methods of sterilization involve the application of heat to kill microorganisms via protein denaturation.7 Generally these processes use either “dry heat”, where hot air is passed over materials; or “moist heat”, where the addition of steam improves heat penetration.
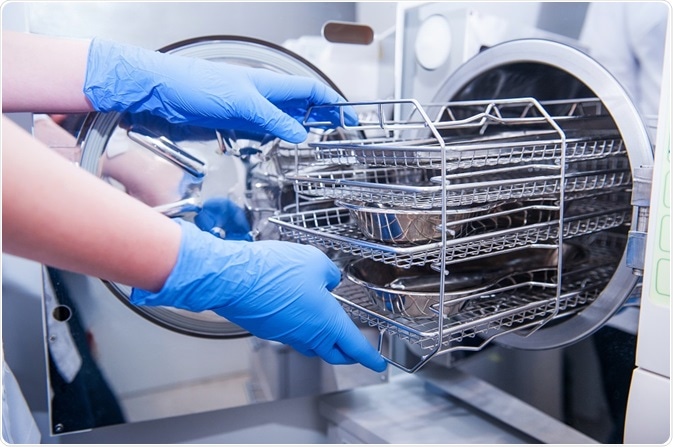
The use of high-pressure steam for sterilization is very common. Generally achieved using a specialized machine known as an autoclave, moist heat sterilization is routinely carried out within hospitals, research facilities, and other clinical environments in order to prepare instruments for reuse.

Credit Okrasyuk | Shutterstock
CDC guidelines advise minimum times and temperatures for various steam sterilization processes, which take between 4 and 30 minutes at temperatures between 121°C (250°F) and 132°C (270°F).8
However, applications of high-temperature sterilization techniques can be limited: moist heat processes are unsuitable for hydrophilic or moisture-sensitive items such as electrosurgery and ablation equipment, as well as other electronic devices; while many materials such as plastics can be damaged by moist or dry heat processes.
Africa Studio | Shutterstock
Other methods of sterilization are therefore used for particularly sensitive equipment: among the most common of these low-temperature sterilization techniques in healthcare is treatment with ethylene oxide (EtO).
Ethylene oxide is a colorless and highly reactive organic compound which exists as a gas at room temperature. EtO reacts vigorously with many of the molecules found within cells; causing rapid denaturation and lysis of DNA, cellular membranes, and other important molecules.9
This disrupts vital cellular processes, making EtO highly toxic to all microorganisms and therefore highly effective as a sterilizing agent. EtO sterilization can generally be performed at temperatures below 60°C (140°F), making it suitable for sterilization of catheters, electrodes, stents and devices with integrated electronics.10
In fact, EtO sterilization is often the only sterilization method compatible with a number of sensitive devices, and has in itself enabled the development of a number of delicate and sophisticated medical devices which would otherwise not be sterilizable.11 EtO is frequently used to sterilize electrical or single-use medical devices before shipment to medical facilities.
Sterilizable Connectors and Components for Medical Devices
As medical technology improves, our use of electrical medical devices is increasing. These include biomedical sensors such as glucose monitors; implants such as pacemakers and spinal cord stimulators; and electrosurgical implements.
It is of course crucial that all these devices are compatible with existing sterilization techniques: all devices must be sterilized before shipment, and any parts of equipment that could come into contact with a patient must be sterilized after each use.
Stäubli’s Medicalline range of electrical connectors were developed with this need in mind. As well as being constructed to high standards of safety and durability; the carefully selected materials ensure that most Medicalline connectors and cables used in North America can be steam sterilized. Responding to customer requests, certain connectors have also been validated for EtO sterilization.12
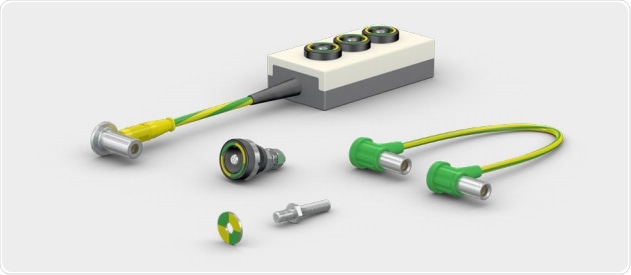
Stäubli Medicalline connectors and wires are perfectly suited to the construction of medical devices with switchable connections, and also enable connectors and plugs for conventional equipment in operating rooms and other clinical environments to be fully sterilized between uses.

In addition to the Medicalline range, Stäubli offer customized connector solutions for the medical industry and are able to carry out testing of other products and devices for a range of sterilization methods.
References and Further Reading
- Surgery Statistics - Surgery Clinic | Stanford Health Care. Available at: https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-clinics/general-surgery.html.
- An Outbreak of Mycobacterium chelonae Infection Following Liposuction. Meyers, H. et al. Clin. Infect. Dis. 34, 1500–1507 (2002).
- Lessons From Outbreaks Associated With Bronchoscopy. Weber, D. J. & Rutala, W. A. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 22, 403–408 (2001).
- Preventing the Spread of Infection in Hospitals | Sterilization & Infection Control Blog. Available at: https://tuttnauer.com/autoclave-sterilization/preventing-the-spread-of-infection-in-hospitals.
- Disinfection and Sterilization in Health Care Facilities: What Clinicians Need to Know. Rutala, W. A. & Weber, D. J. Healthc. Epidemiol. 39, 702–709 (2004).
- Guideline for Disinfection and Sterilization in Healthcare Facilities, 2008. Rutala, W. A. & Weber, D. J.
- GUIDANCE DOCUMENT Compatibility of materials used for Sterile Barrier Systems with sterilisation processes. Available at: www.sterilebarrier.org.
- Steam Sterilization | Disinfection & Sterilization Guidelines | Guidelines Library | Infection Control | CDC. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/infection-control/hcp/disinfection-and-sterilization/index.html.
- How does Ethylene Oxide sterilize? Available at: https://www.iit.edu/.
- Sterilization Methods and their Impact on Medical Devices Containing Electronics. Available at: https://pdfserv.maximintegrated.com/en/an/AN5068.pdf.
- Ethylene oxide sterilization of medical devices: A review. Mendes, G. C. C., Brandão, T. R. S. & Silva, C. L. M. Am. J. Infect. Control 35, 574–581 (2007).
- Medical technology Main catalog Medicalline | Medical industry connectors. (2018).
About Stäubli Electrical Connectors Inc.
Welcome to Stäubli Electrical Connectors in North America.
As a leading provider of electrical and electronic connectors, Stäubli Electrical Connectors offers innovative and safe quality products for power and data connection.
The Stäubli Electrical Connectors product range includes interconnection systems for the most demanding applications in Aerospace, Medical, Robotics, Solar Energy, General Industry and Test & Measurement. Our plufs and sockets are designed for high performance, high mating cycles, low insertion and extraction forces, and ideally suited for low and high current applications.
We develop customized solutions to fit your particular needs.
Stäubli Electrical Connectors is part of the Stäubli group and a wholly owned subsidiary of the Swiss-based Stäubli AG, a leading manufacturer of precision electrical and electronic sensors.

Our philosophy: We win together
We dedicate ourselves to our customers' success by providing the most advanced contact technology solutions. We strive to achieve the best - in our employee development, in our products, and in our customers' satisfaction.
Global presence
In addition to our global headquarters in Basel, Switzerland, Multi-Contact has production sites in the U.S., Germany, France and China. Business units operate across Europe as well as in Asia and the Americas.
Stäubli Electrical Connectors is part of the Stäubli Group, an international mechatronics solutions provider with three dedicated divisions: Textile machinery, Connectors and Robotics. With a workforce of 4000, the Group maintains a presence in 25 countries through its sales and customer service subsidiaries. This network is completed by agents in 50 countries around the word.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.