Cytokines, a class of protein signaling molecules synthesized by immune cells, are crucial in regulating immune responses and inflammation.
Under normal conditions, cytokines aid in pathogen recognition and elimination while contributing to immune system homeostasis. When the immune system malfunctions, irregularities in cytokine production and control can arise, potentially triggering autoimmune diseases.
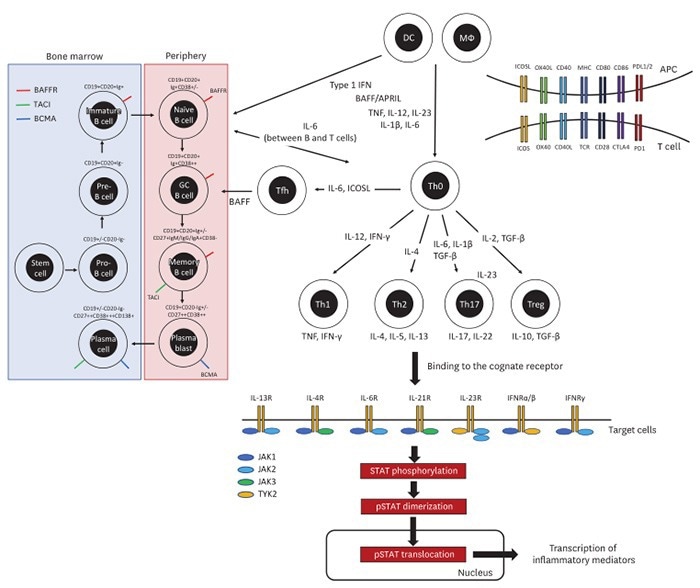
Key therapeutic targets in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and multiple sclerosis
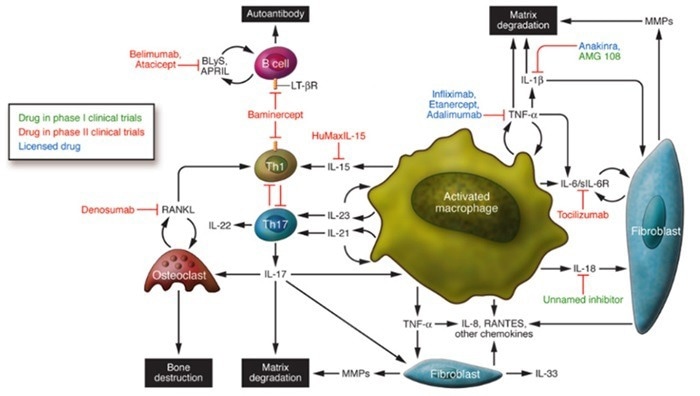
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
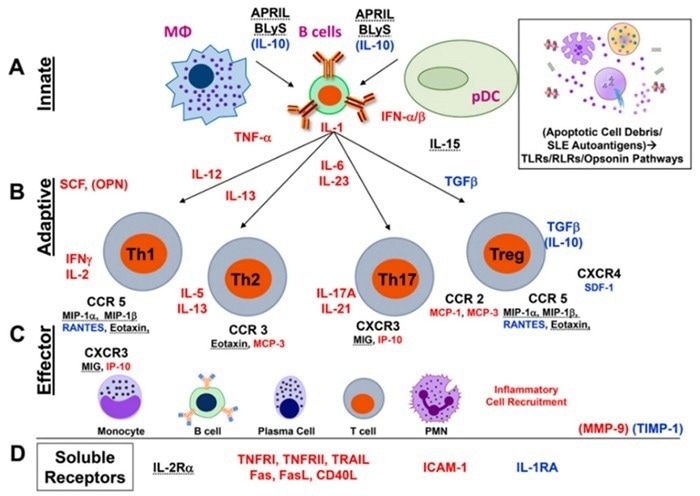
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
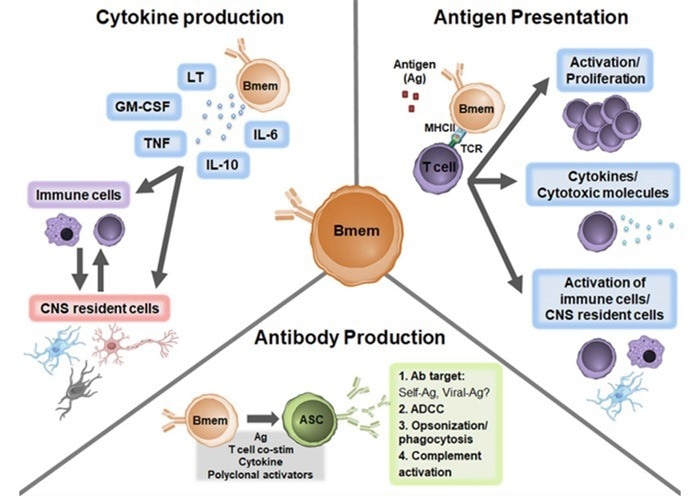
Multiple Sclerosis. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common autoimmune disease in which the immune system recognizes autoantigens on otherwise healthy joint tissues as foreign invaders, inducing a localized inflammatory response.
Excessive tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) production stimulates inflammatory cell activation and joint destruction. To effectively combat this molecular imbalance, anti-TNF-α drugs such as infliximab, adalimumab, and certolizumab pegol are widely used in the treatment of RA.
In addition to TNF-α, interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) also play a role in inflammation and joint degradation, prompting the use of their inhibitors, such as tocilizumab and canakinumab, respectively, for RA treatment. Notably, interleukin-17 (IL-17) and interleukin-23 (IL-23) also play important roles in this disease.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a complex autoimmune disease caused by the deposition of autoantibodies and immune complexes that affect almost all bodily organs.
Elevated type I interferon (IFN) levels activate immune cells, instigating inflammation and promoting SLE development. Emapalumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits IFN signaling, is prescribed for adult SLE treatment.
Heightened concentrations of IL-6 correlate with SLE activity and severity, prompting the use of tocilizumab, an anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody, for refractory cases. IL-1 involvement in SLE pathogenesis has led to trials of anakinra, an IL-1 inhibitor, for SLE treatment management.
Increased TNF-α contributes to inflammation and immune cell activation. Infliximab, etanercept, and adalimumab are used for SLE treatment. Although IL-10 and TGF-β help to regulate immunity in SLE, there are no specific drugs for SLE treatment targeting them.
Multiple sclerosis (MS), a chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system, sees various cytokines stimulating immune cell activation and neurodegeneration. Upregulated granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor 2 (GM-CSF) in patients with MS induces immune cell activation and proliferation, exacerbating inflammation and potentially contributing to neurodegeneration.
Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that is upregulated in patients with MS, leading to immune cell activation, which can encourage inflammation. Another important cytokine involved in the pathogenesis of MS is TNF-α.
IL-17, synthesized by Th17 cells, can trigger inflammation and damage the myelin sheath, while interleukin-2 (IL-2) can enhance the function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and promote the excessive activation of the immune system.
IL-2 is under investigation as an MS treatment to bolster the number and function of Tregs and balance the immune response. Targeted therapies against these cytokines hold promise in alleviating inflammation and neurodegeneration, slowing MS progression, and enhancing patient quality of life.
Exploring the support ACROBiosystems offers in tackling autoimmune diseases
Understanding and intervening in the roles of various cytokines in autoimmune diseases is key to understanding disease mechanisms and providing effective treatment strategies. Therapies targeting different cytokines have become an important strategy in treatment, offering hope and opportunities for improving patients' quality of life.
ACROBiosystems is a provider of recombinant cytokines and their receptors - including interleukins, growth factors, TNFs, chemokines, CSFs, IFNs, and complement components with high purity, high bioactivity, and high batch-to-batch consistency - aimed at accelerating autoimmune diseases drug development programs.
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.