The client wanted to confirm the dose-dependent capacity of AAV constructs to transduce retinal tissue, specifically the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE).
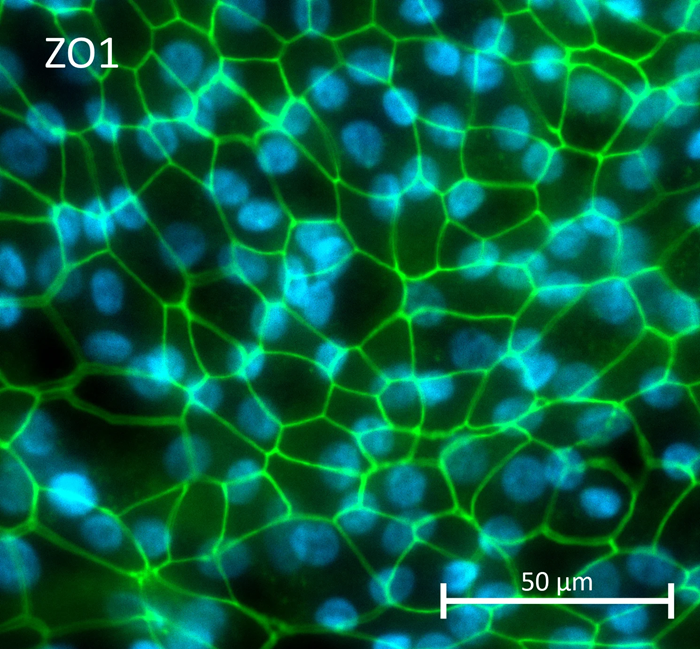
Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
Newcells’ approach to developing a solution
To create a customized solution, Newcells followed its established process.
Step 1:
Understanding the problem
Newcells’ technical experts precisely outlined the problem and the questions to be answered during an in-depth discussion with the client.
The client wanted to quickly determine whether their AAV vector could transduce RPE cells and whether transduction effectiveness was dose-dependent.
Taking all project-specific aspects into account, Newcells recommended a two-step method as the best fit for the situation:
- Step 1: Optimize RPE transduction with AAV vector.
- Step 2: Measure transduction efficiency through image quantification and flow cytometry.
Step 2:
Developing a customized experimental plan
Newcells created the specific tests and detailed the plan in its Statement of Work. The experimental strategy included utilizing completely verified human iPSC-derived RPE.
For Step 1: RPE transduction
- Human RPE cells were transduced with an AAV vector containing a GPF reporter gene and an AAV5 capsid. Live imaging evaluated transgene expression up to 27 days after transduction.
- Experiments evaluated AAV constructs’ transduction efficiency at two doses.
For Step 2: Imaging analysis
- Quantification of the percentage of GFP-positive cells.
- Quantification of the AVV vector’s transduction efficiency in RPE using flow cytometry.
Step 3:
Project execution
Newcells’ scientists completed the agreed-upon research within three months, delivering regular updates to the client.
The study included an experimental phase, data processing, analysis, and summary presentation.
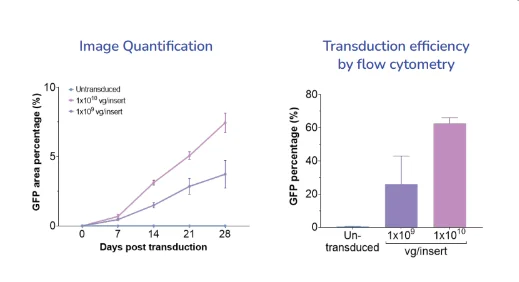
Image Credit: Newcells Biotech
Step 4:
Result delivery
Newcells provided a complete report with a credible dataset, which was shared digitally and reviewed via phone call upon request.
The findings clearly demonstrated:
- Percentage of the area with GFP-positive cells over 28 days post-transduction increased over time and in a dose-dependent manner
- Flow cytometry analysis allowed for accurate quantification and confirmed the transduction efficiency of RPE with AAV was dose- and time-dependent.
The transduction of iPSC-derived RPE cells confirmed the efficacy of the AAV5 gene therapy vector, allowing for further preclinical and in vivo experiments.
Outcomes for the Client
Newcells supplied a robust dataset demonstrating that human IPSC-derived RPE cells are a reliable in vitro model for evaluating AAV constructs. The study allows the client to confidently progress to preclinical studies using their AAV construct.
About Newcells Biotech
Newcells Biotech develops in vitro cell-based assays for drug and chemical discovery and development.
Using our expertise in induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), cellular physiology, and organoid technology, we build models that incorporate the “best biology” for predicting in vivo behavior of new drugs.
Our experts have developed and launched assays to measure transporter function, safety, and efficacy in a range of cell and tissue types, including kidney, retina and lungs.
We have the capability to develop and implement protocols to measure cilia beat frequency and toxicity on small airway epithelial cells model, retinal toxicity and disease modelling on retinal organoids and retina epithelium, as well as drug transport in the kidney, DDI and nephrotoxicity across human and a range of preclinical species.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.